For millions of American professionals, the line between earning a fixed salary and being eligible for overtime pay is determined by a critical number set by the U.S. government. This figure, the federal exempt salary threshold, has a profound impact on paychecks, work-life balance, and a company's budget. With significant updates taking effect in 2024 and 2025, understanding where this threshold stands is more important than ever. This guide will provide a clear, data-driven overview of what you need to know.
What Is the Federal Exempt Salary Threshold?
The federal exempt salary threshold is a key component of the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), the federal law that establishes minimum wage, overtime pay, and recordkeeping standards. Under the FLSA, employees are classified as either "non-exempt" or "exempt."
- Non-Exempt Employees are entitled to overtime pay (at a rate of at least 1.5 times their regular rate) for any hours worked over 40 in a workweek.
- Exempt Employees are not entitled to overtime pay. To be classified as exempt, an employee must meet three criteria:
1. Salary Basis Test: Be paid a predetermined, fixed salary that is not subject to reduction because of variations in the quality or quantity of work performed.
2. Salary Level Test: Earn a salary that meets or exceeds the federal exempt salary threshold.
3. Duties Test: Primarily perform job duties that are considered executive, administrative, or professional (EAP) in nature, as defined by the Department of Labor (DOL).
The "federal exempt salary threshold" refers specifically to the minimum salary required for the Salary Level Test. If an employee meets the duties test but their salary falls below this threshold, they must be classified as non-exempt and paid overtime.
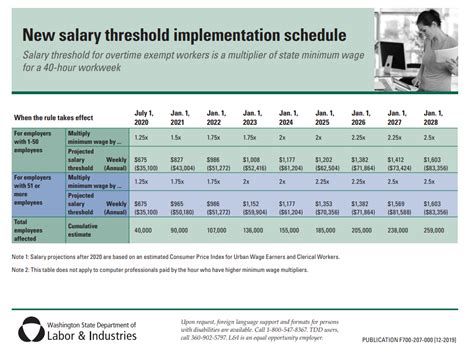
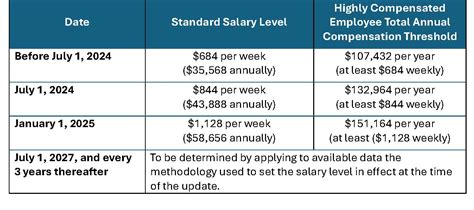
The 2024 and 2025 Federal Exempt Salary Threshold Levels
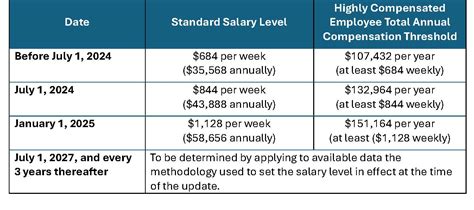
In April 2024, the U.S. Department of Labor announced a final rule significantly increasing the salary threshold for EAP-exempt employees. The update is phased in two steps, impacting both standard salaried workers and highly compensated employees (HCEs).
According to the U.S. Department of Labor, the new thresholds are as follows:
- Effective July 1, 2024: The standard salary threshold will increase from the current $35,568 per year to $43,888 per year (equivalent to $844 per week).
- Effective January 1, 2025: The threshold will increase again to $58,656 per year (equivalent to $1,128 per week).
For Highly Compensated Employees (HCEs), who are subject to a more minimal duties test, the total annual compensation threshold will also increase:
- Effective July 1, 2024: The HCE threshold will rise to $132,964 per year.
- Effective January 1, 2025: The HCE threshold will rise again to $151,164 per year.
Crucially, the new rule also establishes a mechanism for these thresholds to be automatically updated every three years to reflect changes in earnings data.
Key Factors That Influence Exemption Status (Besides Salary)
While the salary threshold is a bright-line test, it's not the only factor. An employee's actual job responsibilities are paramount. Here’s how various factors play into the crucial "duties test."
### Level of Education
Education is a key consideration for the "Learned Professional" exemption. To qualify, an employee's primary duty must be work requiring knowledge of an advanced type in a field of science or learning, customarily acquired by a prolonged course of specialized intellectual instruction. This typically applies to traditional professions like doctors, lawyers, registered nurses, accountants, engineers, and scientists. Simply having an advanced degree is not enough; the job itself must require that level of knowledge.
### Years of Experience
Experience is central to the "Executive" exemption. To qualify, an employee’s primary duty must be managing the enterprise or a recognized department. They must customarily and regularly direct the work of at least two or more other full-time employees and have the authority to hire or fire other employees (or their recommendations on these matters must be given particular weight). Seniority and a long track record of supervisory experience are often indicators that an employee meets this test.
### Geographic Location
While the FLSA sets a federal floor, it does not preempt state law. Many states have their own, often higher, salary thresholds for exemption. If a state's threshold is higher than the federal level, employers in that state must abide by the state-level requirement.
- California: As of January 1, 2024, the minimum salary for exempt employees is $66,560 per year, regardless of employer size. This is already higher than the new federal threshold taking effect in January 2025.
- New York: As of January 1, 2024, the threshold varies by location, ranging from $62,400 per year in New York City and surrounding counties to $58,500 in the rest of the state.
- Washington: As of January 1, 2024, the threshold is 2 times the state minimum wage, resulting in a minimum salary of $67,724.80 per year.
Employers and employees must always check their state and local laws, as they often provide greater protection.
### Company Type
The industry and type of company can influence how roles are classified. A "manager" in a retail setting might have different primary duties than a "project manager" in a tech company. For example, a retail manager who spends most of their time on non-managerial tasks like stocking shelves or running a cash register may not qualify for the executive exemption, even if their title is "manager." Conversely, a software company is more likely to employ individuals who qualify for the "Computer Employee" exemption, which has its own specific duties test and a separate salary requirement ($27.63 per hour under federal law).
### Area of Specialization
Specific career fields have unique exemption criteria. The "Creative Professional" exemption applies to roles requiring invention, imagination, originality, or talent in a recognized field of artistic or creative endeavor (e.g., musicians, writers, graphic artists). The "Administrative" exemption is for employees whose primary duty is the performance of office or non-manual work directly related to the management or general business operations of the employer or its customers. This often includes roles in finance, human resources, accounting, and marketing.
Job Outlook: The Impact of the New Threshold

The Department of Labor projects that the new rule will have a significant impact. In the first year of the update (beginning July 1, 2024), an estimated 4 million salaried workers whose earnings are below the new threshold will become newly entitled to overtime pay if they work more than 40 hours a week.
This change creates two primary outlooks:
1. For Employees: Workers earning between the old and new thresholds may see an increase in take-home pay through overtime, or employers may reclassify them and limit their hours to 40 per week to control costs. This could lead to better work-life balance for some.
2. For Employers: Businesses must conduct audits of their payroll to identify employees affected by the change. They will need to decide whether to increase salaries to meet the new threshold or reclassify employees to non-exempt and begin paying overtime. This will have a direct impact on labor budgets and workforce management strategies.
Conclusion

The 2024 and 2025 updates to the federal exempt salary threshold represent one of the most significant changes to U.S. wage and hour law in years. For professionals, it's a critical time to understand your rights and classification.
Key Takeaways:
- Know the New Numbers: The standard threshold rises to $43,888 on July 1, 2024, and $58,656 on January 1, 2025.
- Duties Matter: Salary is only one part of the equation. Your primary job responsibilities are just as important for determining your exemption status.
- State Laws Are Crucial: Your state may have a higher salary threshold, which your employer must follow.
- Expect Changes: The new rule will prompt employers to re-evaluate salaries and job classifications, potentially affecting millions of workers' pay structures and work hours.
Whether you are charting your career path or managing a team, a firm grasp of the federal exempt salary threshold is essential for navigating the modern professional landscape and ensuring fair and legal compensation.