Decoding Your Earning Potential: A Guide to the Average Yearly Salary in China
China's dynamic and rapidly evolving economy presents a landscape of immense opportunity for local and international professionals alike. If you're considering a career move to or within this global powerhouse, one of your first questions is likely: "What can I expect to earn?" While a single number can be misleading, understanding the national average salary is the first step in benchmarking your potential.
As of the latest reports, the average yearly salary in urban areas of China hovers around 120,698 Chinese Yuan (CNY), which is approximately $16,700 USD. However, this figure is just a starting point. Your actual earnings can vary dramatically, with top professionals in high-demand sectors and major cities earning many multiples of this average. This guide will break down the numbers, explore the key factors that drive salary, and provide a clear picture of what you can truly earn in China.
Understanding the "Average Salary" in China
Unlike a specific job title with defined responsibilities, the "average yearly salary in China" is a broad economic indicator. It represents the statistical mean of wages across an enormous and diverse workforce of over 700 million people. This average blends the earnings of a factory worker in a rural province with a finance director in Shanghai, and a public servant in Beijing with a software engineer in Shenzhen.
Therefore, it's crucial to view this national average not as a target salary, but as a baseline from which to understand a more nuanced reality. The most authoritative source for this data is China's National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), which releases annual figures, typically differentiating between "non-private" (often state-owned or state-affiliated) and "private" enterprises.
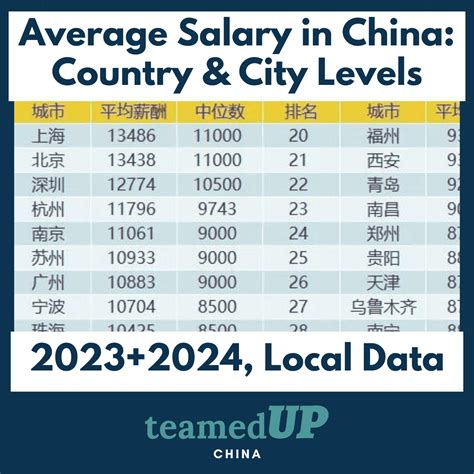
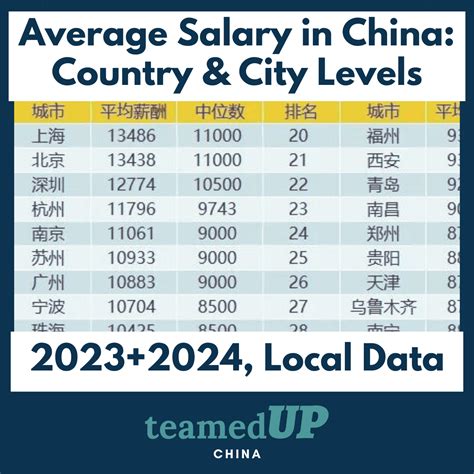
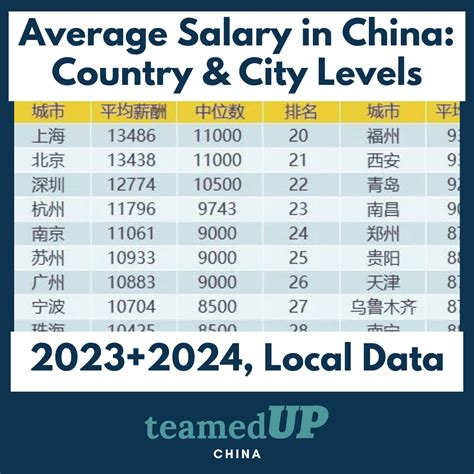
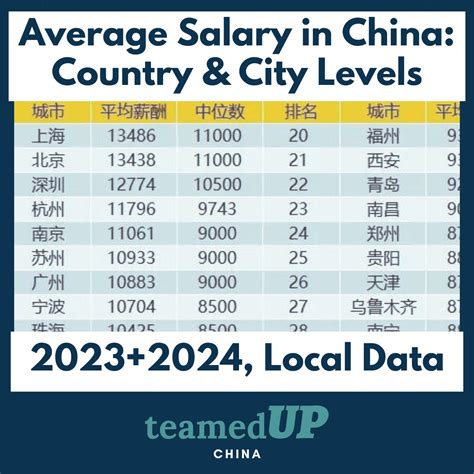
Average Yearly Salary in China: The Numbers

According to the most recent data released by China's National Bureau of Statistics for the year 2023, the average annual salaries in urban enterprises were as follows:
- Urban Non-Private Units: The average annual salary was 120,698 CNY (approx. $16,760 USD).
- Urban Private Units: The average annual salary was 73,147 CNY (approx. $10,160 USD).
*(Note: USD conversions are based on an approximate exchange rate of 1 USD = 7.2 CNY and are for illustrative purposes. Fluctuation will occur.)*
The significant difference between non-private and private units highlights the first layer of complexity. Non-private units often include sectors with higher capital and knowledge intensity, such as finance, energy, and telecommunications, which traditionally offer higher pay and more comprehensive benefits.
Key Factors That Influence Your Salary in China
Your personal salary will be determined by a combination of critical factors. Understanding these levers is the key to maximizing your earning potential.
### Geographic Location
This is arguably the most significant factor influencing salary in China. The country's economic activity is concentrated in Tier 1 and "New Tier 1" cities, where compensation can be double or even triple that of lower-tier cities.
- Tier 1 Cities (Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Guangzhou): These megacities are the economic, financial, and tech hubs. They host the headquarters of most multinational corporations and domestic tech giants, leading to intense competition for talent and substantially higher salaries. According to salary reports from recruitment agencies like Michael Page, salaries in these cities can easily be 50-100% higher than the national average.
- New Tier 1 & Tier 2 Cities (Hangzhou, Nanjing, Chengdu, Wuhan): These cities are experiencing rapid growth, especially in tech and advanced manufacturing. While salaries are typically lower than in Tier 1, the cost of living is also more manageable, offering an excellent quality of life.
- Tier 3 & 4 Cities: These smaller cities offer much lower average salaries, often aligning more closely with the national average for private units, as their economies are more focused on traditional manufacturing and agriculture.
### Industry / Area of Specialization
Your industry has a direct and powerful impact on your earnings. Data from the NBS consistently shows a wide gap between the highest and lowest-paying sectors.
- Top-Paying Industries:
1. Information Technology (IT): Driven by giants like Tencent and Alibaba, as well as a thriving startup scene, IT professionals (software engineers, data scientists, cybersecurity experts) command top salaries.
2. Finance and Investment: Professionals in banking, asset management, and securities consistently rank among the highest earners, particularly in financial centers like Shanghai and Shenzhen.
3. Scientific Research & Technical Services: With China's push for innovation, roles in R&D, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology are increasingly lucrative.
- Lower-Paying Industries: Sectors like hospitality, food service, agriculture, and general manufacturing typically report salaries at the lower end of the spectrum.
### Years of Experience
As with any job market, experience is highly valued and directly compensated. Salary aggregator data from sources like Glassdoor and Payscale for China-based roles reflects a clear upward trajectory.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): Graduates and early-career professionals can expect a salary closer to the local average for their city and industry.
- Mid-Career (3-8 years): Professionals with proven skills and experience see significant salary jumps as they take on more responsibility.
- Senior/Management (8+ years): Senior managers, directors, and executives command premium salaries, often supplemented by significant bonuses and stock options, especially in the tech and finance sectors.
### Company Type
The type of company you work for is a major determinant of your compensation package.
- Multinational Corporations (MNCs) / Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprises (WFOEs): These companies often pay the most competitive salaries to attract top-tier talent and typically benchmark their pay scales against global standards.
- Private Domestic Giants (e.g., Huawei, Alibaba, Tencent): These leading Chinese companies compete directly with MNCs for talent and offer highly competitive salaries, bonuses, and valuable stock options.
- State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs): While base salaries may be slightly more modest than at top private firms, SOEs often provide exceptional job security, generous housing allowances, and comprehensive social benefits, which constitute a significant part of the total compensation package.
- Start-ups and SMEs: Salaries can vary widely. Well-funded tech startups may offer high pay and equity to attract talent, while smaller, more traditional businesses will likely offer more modest compensation.
### Level of Education
Higher education, particularly from a prestigious university, can unlock doors to higher-paying, specialized roles. A Master's degree, MBA, or Ph.D. is often a prerequisite for senior positions in finance, R&D, and strategic consulting. An overseas degree from a globally recognized university can also give candidates a competitive edge, especially in roles at multinational corporations.
Job Outlook

While we cannot cite the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) for China, the country's economic plans provide a clear roadmap for job growth. China's 14th Five-Year Plan and long-range objectives emphasize a shift toward a high-tech, innovation-driven economy.
The job outlook is exceptionally strong in sectors aligned with these national priorities, including:
- Advanced Technology: Artificial Intelligence (AI), 5G, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
- Green Energy: Renewable energy, electric vehicles (EVs), and environmental technology.
- Biotechnology and Healthcare: Driven by an aging population and a focus on public health.
- Advanced Manufacturing & Robotics: The "Made in China 2025" initiative continues to fuel demand for skilled engineers and technicians.
Professionals with skills in these high-growth areas will find a robust and competitive job market with excellent long-term career prospects.
Conclusion

The "average yearly salary in China" is a complex figure that serves as a useful economic benchmark but tells only part of the story. Your real earning potential is a product of strategic career choices.
To summarize the key takeaways:
- The National Average is a Starting Point: Use the NBS figure of ~120,698 CNY as a baseline, but don't anchor your expectations to it.
- Location is King: Your salary will be influenced more by *where* you work (e.g., Shanghai vs. a Tier 3 city) than any other single factor.
- Industry Matters Immensely: Aim for high-growth sectors like IT, Finance, and Green Tech to maximize your earnings.
- Your Experience and Employer Define Your Value: Build your skills and target companies—whether multinational, domestic giants, or SOEs—that align with your compensation and career goals.
For prospective students and professionals, the message is clear: China's economy offers vast and varied opportunities. By targeting the right location, industry, and company, you can build a rewarding career and achieve a salary that far exceeds the national average.