From the complex algorithms that power global financial markets to the stunning graphics engines in blockbuster video games and the critical control systems in autonomous vehicles, C++ is the invisible workhorse of the modern technological world. It’s the language of performance, efficiency, and control. For those who can master its intricacies, a career as a C++ developer isn't just a job; it's a gateway to solving some of the most challenging and rewarding problems in computing, with a c++ developer salary to match that high level of expertise.
If you're drawn to building foundational systems, optimizing code until it runs with breathtaking speed, and working "close to the metal," then this path may be your calling. The demand for skilled C++ programmers remains exceptionally strong, particularly in specialized, high-stakes industries where every nanosecond and every byte of memory counts. This translates directly into significant earning potential, with average salaries comfortably reaching into the six-figure range and top-tier specialists commanding compensation packages that rival those in any other area of technology.
I once spoke with a lead engineer at a high-frequency trading firm who put it perfectly: "We hire C++ developers not just to write code, but to control time. In our world, the difference between a profitable trade and a loss is measured in microseconds, and that's a domain where C++ is still king." That conversation crystallizes the immense value and responsibility placed on developers in this field—a value that is clearly reflected in their compensation.
This comprehensive guide will serve as your roadmap. We will dissect every component of a C++ developer's career, from their daily responsibilities to the factors that can dramatically increase their salary. We’ll explore the job outlook, uncover the most lucrative specializations, and provide a step-by-step plan to help you launch or advance your own career.
### Table of Contents
- [What Does a C++ Developer Do?](#what-they-do)
- [Average C++ Developer Salary: A Deep Dive](#salary-deep-dive)
- [Key Factors That Influence C++ Developer Salary](#key-factors)
- [Job Outlook and Career Growth for C++ Developers](#job-outlook)
- [How to Become a C++ Developer: A Step-by-Step Guide](#how-to-start)
- [Conclusion: Is a C++ Career Right for You?](#conclusion)
What Does a C++ Developer Do?
While many software developers build applications that users interact with daily—like mobile apps or websites—C++ developers often work a layer deeper. They are the architects and engineers of the digital infrastructure that makes everything else possible. Their primary focus is on performance, memory management, and concurrency. They write code that needs to run exceptionally fast, manage system resources efficiently, and handle multiple operations simultaneously without error.
C++ is a compiled language, which means the code is translated directly into machine-level instructions that the computer's processor can execute. This "close to the metal" proximity gives developers fine-grained control over hardware resources, a critical requirement in many high-performance domains.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks:
A C++ developer's role is multifaceted and extends far beyond simply writing code. Their responsibilities typically include:
- System Design and Architecture: Before a single line of code is written, senior C++ developers are involved in designing the high-level structure of a system. This involves deciding on data structures, algorithms, and how different software components will interact to meet stringent performance requirements.
- Writing High-Performance, Reusable Code: The core of the job is implementing system designs by writing clean, efficient, and robust C++ code. A key emphasis is on creating code that is not only fast but also maintainable and reusable in other parts of the application or in future projects.
- Memory Management: Unlike more modern, garbage-collected languages (like Java or Python), C++ requires developers to manually manage memory allocation and deallocation. This is a double-edged sword: it provides immense control and performance benefits but also introduces the risk of memory leaks and segmentation faults if not handled meticulously. A significant portion of a developer's time is spent ensuring memory safety.
- Performance Tuning and Optimization: C++ developers are often obsessed with performance. They use profiling tools to identify bottlenecks in the code—sections that are slow or consume too much memory—and then refactor them to be more efficient. This can involve rewriting algorithms, using advanced language features, or even leveraging specific hardware instructions.
- Debugging and Testing: Finding and fixing bugs in complex, multi-threaded C++ applications can be incredibly challenging. Developers use debuggers (like GDB), write extensive unit tests, and perform integration testing to ensure the software is reliable and correct.
- Code Reviews and Collaboration: Developers work in teams, and a critical part of the process is reviewing each other's code. This practice helps catch bugs early, ensures adherence to coding standards, and spreads knowledge throughout the team.
### A "Day in the Life" of a C++ Game Engine Developer
To make this more concrete, let's imagine a day for "Maria," a mid-level C++ developer working on a new game engine for a AAA studio.
- 9:00 AM - Daily Stand-up: Maria joins her team for a quick 15-minute meeting. She reports that yesterday she finished implementing a new particle effect system and today she will start tackling a bug that's causing frame rate drops when too many objects are on screen.
- 9:15 AM - Bug Investigation: Maria pulls the latest code from the repository and reproduces the bug on her local machine. She attaches a performance profiler to the game. The profiler shows that a specific physics collision-detection function is taking far too much time.
- 11:00 AM - Deep Dive and Refactoring: Maria spends the next couple of hours analyzing the algorithm in the collision-detection function. She realizes it's using a brute-force approach. She redesigns it to use a more efficient spatial partitioning data structure (like a quadtree) to dramatically reduce the number of checks needed.
- 1:00 PM - Lunch: A well-deserved break.
- 2:00 PM - Implementation and Testing: Maria implements the new quadtree-based solution. She writes several new unit tests to verify its correctness, ensuring it handles various edge cases.
- 4:00 PM - Code Review and Submission: Maria's initial tests show a 30% improvement in the frame rate under heavy load. Confident in her fix, she submits her code for a peer review. Her team lead provides some feedback, suggesting a minor change to improve memory handling.
- 4:45 PM - Final Touches: Maria incorporates the feedback, reruns her tests, and pushes the final code to the main branch. Her work for the day has made the entire game experience smoother for players.
This example highlights the problem-solving, analytical, and performance-oriented nature of the C++ developer role.
Average C++ Developer Salary: A Deep Dive
Now for the central question: how much does this expertise command in the marketplace? The C++ developer salary is consistently one of the highest in the software development field, reflecting the language's steep learning curve and its critical role in high-value industries.
It's important to understand that a "salary" is more than just a base number; it's part of a total compensation package that can include bonuses, stock options, and other benefits.
National Averages and Typical Ranges
Salary data varies slightly between aggregators due to different data sets and methodologies, but they all paint a similar picture of high earning potential.
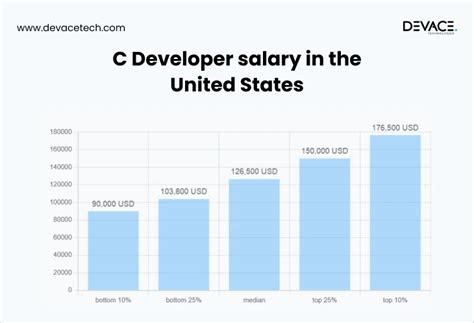
- Salary.com reports that the median C++ developer salary in the United States is $126,603 as of late 2023. The typical range falls between $111,822 and $139,401.
- Glassdoor lists the average base pay for a C++ developer at $120,495 per year, with a likely range between $92,000 and $158,000, based on user-submitted data.
- Payscale provides a slightly broader range, showing an average base salary of $95,357, but with a total pay range stretching from $66,000 to $147,000 before considering top-tier roles.
The key takeaway is that a six-figure salary is not just achievable but is the standard for an experienced C++ developer in the United States. Entry-level positions will start lower, while senior specialists in high-paying sectors can earn significantly more.
### Salary by Experience Level
Experience is arguably the single most significant factor in determining salary. As a developer gains a track record of solving complex problems, their value to an employer skyrockets. Here is a typical progression:
| Experience Level | Years of Experience | Typical Base Salary Range (USA) | Key Characteristics & Responsibilities |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Entry-Level Developer | 0 - 2 years | $75,000 - $105,000 | Focuses on learning the codebase, fixing bugs, implementing well-defined features. Requires significant mentorship. |
| Mid-Level Developer | 2 - 5 years | $105,000 - $140,000 | Works independently on complex features, contributes to design discussions, mentors junior developers. |
| Senior Developer | 5 - 10 years | $140,000 - $185,000+ | Leads design and architecture of major systems, solves the most difficult technical challenges, sets technical direction for the team. |
| Lead / Principal Engineer | 10+ years | $185,000 - $250,000++ | Acts as a top technical authority, influences strategy across multiple teams or the entire company, innovates and solves business-critical problems. |
*(Note: These ranges are national averages. They can be significantly higher in high-cost-of-living areas and specific industries, which we will explore next.)*
### Beyond the Base Salary: Understanding Total Compensation (TC)
In technology, especially at large corporations and in the finance sector, focusing solely on base salary can be misleading. The Total Compensation (TC) package provides a much more accurate picture of a developer's earnings.
Key components of a C++ developer's TC include:
- Base Salary: The fixed, predictable amount you are paid bi-weekly or monthly. This forms the foundation of your compensation.
- Annual Bonus: This is a variable cash payment, often based on a combination of individual performance, team performance, and company performance. It can range from a modest 5-10% of the base salary to over 100% in high-stakes industries like quantitative finance.
- Stock Options / Restricted Stock Units (RSUs): This is a major component of compensation at publicly traded tech companies (like Google, Microsoft, NVIDIA) and promising startups. RSUs are grants of company stock that vest (become yours) over a period, typically four years. This can add tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars to your annual income, tying your financial success directly to the company's growth.
- Signing Bonus: A one-time cash payment offered to a new employee as an incentive to join the company. These are common in competitive hiring markets and can range from a few thousand dollars to $50,000 or more for highly sought-after senior talent.
- Benefits: While not direct cash, a strong benefits package has significant financial value. This includes comprehensive health insurance, a 401(k) retirement plan with a generous company match, paid time off, and other perks like wellness stipends or professional development budgets.
For a senior C++ developer at a top tech firm in a major hub, a base salary of $175,000 might be supplemented by a 15% bonus ($26,250) and an annual RSU grant worth $80,000, bringing their first-year TC to over $280,000. This demonstrates why it's crucial to evaluate the entire offer, not just the base number.
Key Factors That Influence a C++ Developer Salary

A national average provides a useful benchmark, but your actual salary will be determined by a combination of powerful factors. Understanding these levers is the key to maximizing your earning potential throughout your career. This is the most critical section for anyone looking to strategically build a high-paying C++ career.
### Level of Education
While practical skill and experience ultimately outweigh formal education, your academic background provides the foundation and can influence your starting salary and career trajectory.
- Bachelor's Degree: A Bachelor of Science (B.S.) in Computer Science, Computer Engineering, or a related field is the standard entry requirement for most C++ developer positions. It provides essential theoretical knowledge in data structures, algorithms, operating systems, and computer architecture—all of which are paramount in C++ development.
- Master's Degree: A Master of Science (M.S.) can provide a significant advantage, particularly for specialized roles. A Master's degree focused on areas like computer graphics, artificial intelligence, robotics, or scientific computing can make you a more attractive candidate for R&D positions at companies like NVIDIA, or for roles in advanced research labs. This can lead to a 10-15% higher starting salary compared to a candidate with only a Bachelor's degree.
- Ph.D.: A doctorate is generally required only for highly specialized research and development roles, such as creating novel algorithms for quantitative trading, designing next-generation compiler technology, or fundamental research in academic or corporate labs. For these niche positions, the compensation can be exceptionally high, but they represent a very small fraction of C++ jobs.
- Certifications: Unlike other IT fields, formal C++ certifications are less common and carry less weight than a strong portfolio and interview performance. However, completing specialized training or certifications in related areas like cloud platforms (AWS, Azure) or specific technologies (e.g., Qt Certified Developer) can demonstrate initiative and specialized knowledge.
### Years of Experience
As detailed in the previous section, experience is the primary driver of salary growth. The journey from a junior developer to a principal engineer is marked by increasing autonomy, responsibility, and impact.
- 0-2 Years (Entry-Level): At this stage, your salary reflects your potential. You are being paid to learn and grow under supervision. Your primary goal is to absorb as much knowledge as possible and build a track record of reliability.
- 2-5 Years (Mid-Level): You've proven your ability to contribute independently. Your salary increases reflect your growing productivity and ability to tackle complex tasks without constant oversight. This is often the period of the most rapid percentage-based salary growth.
- 5-10 Years (Senior): You are now a technical leader. Your value lies not just in your own code, but in your ability to design robust systems and mentor others. Your salary reflects this force-multiplier effect. You are trusted to handle critical, high-impact projects.
- 10+ Years (Lead/Principal/Architect): At this level, you are setting technical strategy. Your decisions impact entire product lines or business units. Compensation can include significant leadership bonuses and larger equity grants, as your work is directly tied to the company's strategic success. The salary ceiling becomes very high, often determined more by impact than by a standard pay band.
### Geographic Location
Where you work has a dramatic impact on your salary, though the rise of remote work has started to complicate this picture. Salaries are typically adjusted for the local cost of living and the concentration of high-paying companies.
Top-Tier Paying Metropolitan Areas (USA):
- San Francisco Bay Area, CA (San Francisco, San Jose, Palo Alto): The epicenter of the tech world. Offers the highest salaries but also has an extremely high cost of living. A senior C++ developer here can easily command a base salary well over $200,000, with total compensation reaching $300,000 - $400,000+.
- Seattle, WA: Home to Microsoft and Amazon, this is another top-tier tech hub with salaries that are highly competitive with the Bay Area.
- New York, NY: A major hub for both "FinTech" (Financial Technology) and big tech companies. The demand for C++ developers in quantitative finance pushes salaries to some of the highest levels in the country.
- Boston, MA: A strong hub for robotics, biotech, and a growing tech scene.
- Austin, TX: A rapidly growing tech hub with a lower cost of living than the coastal cities, attracting major companies and offering strong salaries.
Salary Comparison by City (Illustrative - Senior C++ Developer Base Salary):
- San Jose, CA: $195,000
- New York, NY: $188,000
- Seattle, WA: $182,000
- Austin, TX: $165,000
- Chicago, IL: $155,000
- Kansas City, MO: $135,000
*(Data synthesized from various aggregators and is for illustrative purposes of relative differences.)*
The Impact of Remote Work: Some companies now offer location-agnostic salaries, paying the same regardless of where the employee lives. However, many large companies still use a geo-adjusted model, where your salary is tied to a cost-of-living tier based on your location. This is a critical point to clarify during negotiations for a remote role.
### Company Type & Size
The type of company you work for is a massive determinant of both your salary and your day-to-day experience.
- Big Tech (FAANG - Meta, Apple, Amazon, Netflix, Google & others like Microsoft, NVIDIA): These companies offer very high base salaries and, most importantly, enormous RSU grants that can double or even triple the base salary over the vesting period. The work involves large-scale systems and cutting-edge technology, but can also be highly specialized and bureaucratic.
- Quantitative Finance / High-Frequency Trading (HFT): This is often the most lucrative sector for C++ developers. Firms like Jane Street, Hudson River Trading, and Citadel Securities pay astronomical salaries and bonuses because a developer's performance-tuning skills can translate directly into millions of dollars of profit. The work is extremely demanding, high-pressure, and the interview process is notoriously difficult.
- Game Development (AAA Studios vs. Indie): AAA studios (like Blizzard, Epic Games, Naughty Dog) have a huge demand for C++ engineers for engine development, graphics, and gameplay systems. Salaries can be very competitive, but historically have sometimes lagged behind Big Tech due to the so-called "passion tax"—people are willing to earn less to work on games. Indie studios will have much lower salaries but offer more creative freedom and ownership.
- Startups: Compensation at a startup is a high-risk, high-reward proposition. The base salary will likely be lower than at an established corporation. The real incentive is a significant grant of stock options or equity. If the startup succeeds, this equity could be worth a fortune. If it fails, it's worthless.
- Defense, Aerospace, and Automotive: Companies like Lockheed Martin, Boeing, and Ford employ C++ developers for critical embedded systems (e.g., flight control, engine management, autonomous driving). These jobs offer stability, good benefits, and often require a U.S. security clearance, which can itself be a valuable and compensated credential. Salaries are strong but may not reach the peaks of finance or Big Tech.
### Area of Specialization
Within the world of C++, some skills are more valuable than others. Specializing in a high-demand, high-impact niche is the most effective way to become a top earner.
- High-Frequency Trading (HFT): As mentioned, this is the pinnacle of C++ earning potential. It requires deep expertise in low-latency programming, network protocols, and hardware architecture to shave microseconds off transaction times.
- Game Engine and Graphics Programming: Developers who work on the core engine (like Unreal Engine or Unity, which is written in C++) or write advanced graphics shaders and rendering pipelines are highly sought after. This requires strong 3D math skills and knowledge of APIs like DirectX, Vulkan, or Metal.
- Embedded Systems and IoT: This involves writing code for resource-constrained devices like microcontrollers in cars, medical devices, or smart home appliances. It demands a deep understanding of hardware interaction, real-time operating systems (RTOS), and memory optimization.
- Compilers and Operating Systems: This is a fundamental and highly complex area. Developers who can work on the internals of compilers (like Clang or GCC) or contribute to operating system kernels (like Windows or Linux) are among the most respected and well-compensated engineers in the field.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC) and Scientific Computing: This specialization is found in national labs, universities, and industries like oil and gas or weather forecasting. It involves writing code to run on massive supercomputer clusters, often using parallel programming frameworks like MPI and OpenMP.
### In-Demand Skills
Beyond your specialization, specific technical skills can make your resume stand out and give you leverage in salary negotiations.
- Modern C++ Standards (C++11/14/17/20/23): The language has evolved dramatically. Proficiency in modern features like smart pointers, move semantics, lambdas, and concepts is no longer optional; it's a requirement for any serious C++ role. It shows you are current and write safer, more expressive code.
- Concurrency and Multithreading: Expertise in writing safe and efficient multithreaded code using `std::thread`, `std::mutex`, and `std::atomic` is critical for leveraging modern multi-core processors.
- Performance Profiling and Optimization Tools: Knowing how to use tools like Valgrind, GDB, Perf, Intel VTune, or AMD uProf to diagnose performance and memory issues is a core competency.
- Build Systems and Toolchains: Deep knowledge of CMake is a de facto standard in the C++ world. Familiarity with compilers (GCC, Clang, MSVC) and linkers is also essential.
- Key Libraries and Frameworks: Experience with widely used libraries like Boost (a collection of high-quality C++ libraries), Qt (for cross-platform GUI development), or Asio (for networking) is highly valued.
- Data Structures and Algorithms: This is non-negotiable. A C++ developer interview will almost certainly involve rigorous testing of your knowledge of fundamental data structures and your ability to analyze algorithmic complexity.
Job Outlook and Career Growth

While newer languages often grab headlines, the job outlook for skilled C++ developers remains robust and stable. The reason is simple: for a specific class of problems, C++ is still the best—and sometimes the only—tool for the job.
Official Projections:
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects the employment of software developers, quality assurance analysts
