For those who blend technical skill with creative vision, a career as a Computer-Aided Design (CAD) designer is a compelling path. You get to be at the forefront of innovation, turning concepts into detailed digital blueprints that shape our world. But beyond the professional satisfaction lies a critical question: what is the earning potential?
A career as a CAD designer is not only professionally rewarding but also financially stable, with typical salaries in the United States ranging from $50,000 for entry-level positions to over $95,000 for senior or specialized roles. This article will break down what a CAD designer does, the average salary you can expect, and the key factors that can significantly increase your paycheck.
What Does a CAD Designer Do?
At its core, a CAD designer is a digital architect and a virtual builder. Using specialized software like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Revit, or CATIA, they create highly detailed 2D drawings and 3D models of products and structures. These technical designs are the essential blueprints used in a vast array of industries, including:
- Manufacturing: Designing machine parts, tools, and consumer products.
- Architecture: Drafting plans for residential, commercial, and public buildings.
- Engineering: Creating models for infrastructure like bridges, roads, and water systems.
- Aerospace & Automotive: Designing everything from engine components to aircraft fuselages.
- Electronics: Laying out printed circuit boards (PCBs) and electronic schematics.
They work closely with engineers, architects, and project managers to ensure designs are accurate, functional, and meet all project specifications.
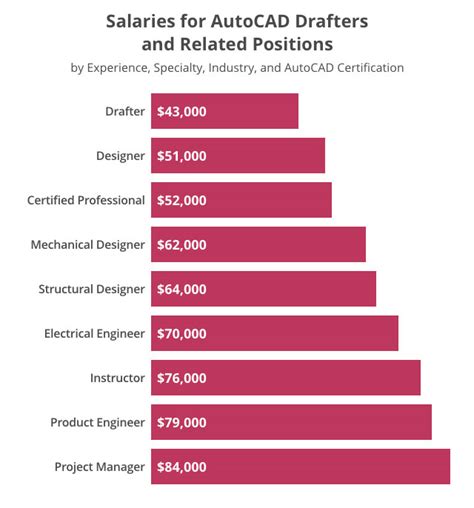
Average CAD Designer Salary

While salaries can vary widely, we can establish a strong baseline using data from authoritative sources.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for drafters (the category under which most CAD designers fall) was $62,110 in May 2023. This means half of all CAD designers earned more than this amount, and half earned less.
Reputable salary aggregators provide a more granular view:
- Salary.com reports that the median salary for a CAD Designer I (entry-level) is around $61,500, while a Senior CAD Designer (Level III) has a median salary closer to $86,000.
- Glassdoor lists a national average base pay of approximately $64,000 per year as of early 2024, with a likely range between $52,000 and $80,000.
- Payscale shows a similar average of around $63,500 per year, with the top 10% of earners exceeding $91,000.
Synthesizing this data, a general salary progression looks like this:
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): $50,000 - $62,000
- Mid-Career (3-8 years): $63,000 - $80,000
- Senior/Lead (8+ years): $81,000 - $95,000+
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your base salary is just the starting point. Several key factors can dramatically influence your earning potential. Understanding these levers is the key to maximizing your income in this field.
### Level of Education
While you can enter the field with a vocational certificate or an associate's degree in drafting or CAD technology, further education often translates to a higher salary. An associate's degree is the most common educational path and provides a solid foundation. However, a bachelor's degree in a related field like mechanical engineering, civil engineering, or architecture can open doors to higher-level design roles and a significantly higher starting salary. Employers often see candidates with a bachelor's degree as having a deeper understanding of design principles and project requirements.
### Years of Experience
Experience is one of the most significant drivers of salary growth. As you progress in your career, you move from executing basic drafting tasks to leading complex design projects.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): You are primarily focused on learning software, understanding industry standards, and making revisions to existing drawings.
- Mid-Career (3-8 years): You can work independently, create complex designs from scratch, and may begin to check the work of junior designers. Your value and salary increase accordingly.
- Senior/Lead (8+ years): You are a subject matter expert. You may manage a team of designers, interface directly with clients and engineers, solve high-level design challenges, and be responsible for the quality of all technical drawings for a project. This level of responsibility commands the highest salaries.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries for CAD designers are heavily influenced by local demand and cost of living. Major metropolitan areas with strong engineering, tech, or manufacturing hubs tend to offer higher pay.
According to BLS data and salary aggregators, states with the highest average salaries for CAD designers include:
- California
- Washington
- Alaska
- Massachusetts
- District of Columbia
A CAD designer in San Jose, California, might earn 25-30% above the national average to compensate for the high cost of living, while a designer in a rural area may earn 10-15% below the average.
### Company Type and Industry
The industry you work in has a massive impact on your paycheck. Industries dealing with high-stakes, complex, and high-revenue projects typically pay more.
- Top-Paying Industries: Aerospace, oil and gas exploration, semiconductor manufacturing, and scientific research and development services often offer the highest salaries due to the complexity and precision required.
- Mid-Tier Industries: General manufacturing, automotive, and engineering services firms offer competitive, solid salaries.
- Standard-Tier Industries: Architectural firms and local or state governments, while offering stable careers, may have salaries that are closer to or slightly below the national median.
### Area of Specialization
General CAD skills are valuable, but specialized expertise is where you can truly boost your income. Certain niches are in high demand and command a premium.
- Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&ID): Highly sought after in the oil & gas and chemical processing industries.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): Specialists using software like Revit for complex architectural and construction projects are in high demand.
- Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T): Deep expertise in GD&T is critical in precision manufacturing and is a highly valued skill.
- Electrical/PCB Design: Designing circuit boards and electronic systems is a specialized and lucrative field.
Mastering a specific software (like CATIA for aerospace or Revit for architecture) and a specific design discipline will make you a more valuable asset.
Job Outlook

The nature of the CAD designer role is evolving. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 2% decline in employment for drafters from 2022 to 2032.
However, this number requires context. While automation and the ability for engineers to perform their own basic CAD work may reduce the need for traditional, low-skill "drafters," the demand for highly skilled CAD designers and specialists remains strong. The future of the profession lies in specialization, proficiency in advanced 3D modeling and BIM software, and a deep understanding of the industry you serve. Professionals who adapt and grow their skills will find robust opportunities.
Conclusion

A career as a CAD designer offers a solid and rewarding financial path for detail-oriented individuals with a passion for technology and design. While the national median salary hovers around the low $60,000s, this is merely a starting point.
The key takeaways for maximizing your earning potential are clear:
- Build a Strong Foundation: An associate's or bachelor's degree will set you up for success.
- Gain Experience: Your value and salary will grow significantly as you move from junior to senior roles.
- Be Strategic About Location: Consider working in a geographic area with high demand for your skills.
- Specialize, Specialize, Specialize: Developing expertise in a high-demand industry or software is the single most effective way to increase your salary and job security.
For those willing to invest in continuous learning and strategic career planning, the role of a CAD designer is a gateway to a successful, engaging, and financially prosperous future.