A career as a City Manager is one of the most impactful and dynamic roles in public service. Tasked with overseeing the day-to-day operations of a municipality, these professionals are at the forefront of local governance, policy implementation, and community development. But beyond the significant responsibilities, what is the earning potential for this critical position?
For those considering a path in public administration, the financial prospects are strong. A city manager can expect to earn a competitive six-figure salary, with top professionals in major metropolitan areas commanding compensation packages well over $200,000. This article will break down the salary you can expect and the key factors that influence it.
What Does a City Manager Do?

A city manager serves as the Chief Administrative Officer of a municipality, appointed by the elected city council to carry out its policies and manage the government's operations. Think of them as the CEO of a city. Their core responsibilities are vast and varied, but typically include:
- Budgeting and Financial Management: Developing, presenting, and managing the annual city budget.
- Personnel Management: Hiring, supervising, and managing city department heads and staff.
- Policy Implementation: Translating the city council's goals and policies into actionable programs and services.
- Operational Oversight: Ensuring all city departments—from public works and parks to police and fire—are running efficiently and effectively.
- Community and Council Liaison: Serving as the primary point of contact between the city council, city staff, and the public.
Given their immense impact on a community's quality of life and financial health, city managers are compensated as high-level executives.
Average City Manager Salary
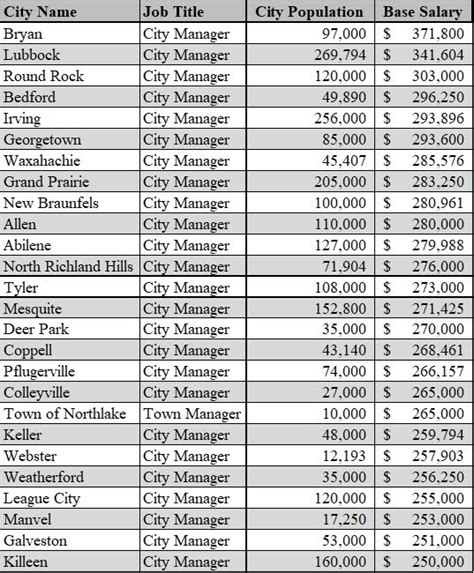
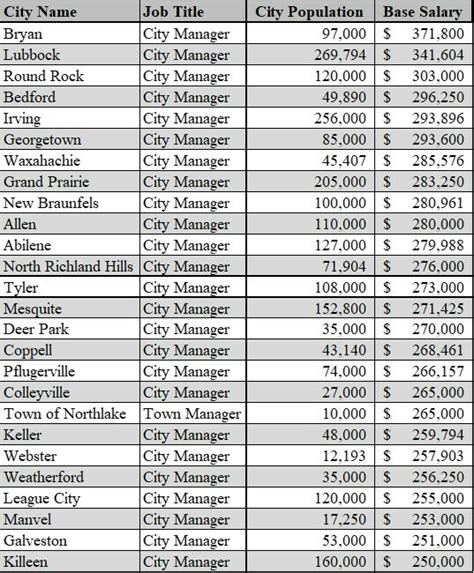
The salary for a city manager can vary significantly, but data from leading sources provides a clear picture of the typical earning potential.
According to a 2024 analysis by Salary.com, the median salary for a City Manager in the United States is approximately $187,935. The salary range is quite broad, reflecting the diversity of municipalities across the country. A typical range falls between $142,504 and $237,337.
Other salary aggregators provide a similar perspective:
- Payscale reports a wide range from $61,000 to $203,000, with an average base salary around $112,000, underscoring the impact of factors like city size and experience.
- Glassdoor lists an average base pay of around $124,000, with total pay (including additional compensation) potentially reaching over $160,000.
The key takeaway is that while a six-figure salary is the norm, the full spectrum is vast—stretching from around $65,000 for managers in very small towns to over $300,000 for those leading major cities with complex operational needs.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

What accounts for this wide salary range? Several key factors determine a city manager's earning potential. Understanding them is crucial for anyone aspiring to maximize their compensation in this field.
###
Level of Education
Education is the bedrock of a city manager's qualifications. While a bachelor's degree in public administration, political science, or business is often the minimum requirement, a master's degree is the industry standard for senior-level positions. The Master of Public Administration (MPA) is considered the gold standard credential. An MPA equips candidates with specialized knowledge in public finance, urban planning, ethics, and leadership, making them significantly more competitive. Holding an MPA or a related graduate degree (e.g., an MBA with a public sector focus) can lead to higher starting salaries and is often a prerequisite for top-tier positions in larger, higher-paying municipalities.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the most critical factor in determining salary. The career path is progressive, with compensation rising in step with responsibility and a proven track record of success.
- Entry-Level (0-5 Years): Professionals often start as administrative assistants, analysts, or assistant to the city manager. In these roles, they learn the fundamentals and can expect salaries in the $60,000 to $90,000 range.
- Mid-Career (5-15 Years): With solid experience, individuals can become assistant city managers or take on the top role in a smaller town or city. Salaries at this stage typically move well into the six figures, from $95,000 to $150,000.
- Senior/Experienced (15+ Years): Seasoned city managers with decades of experience, particularly those who have successfully managed multiple cities, are highly sought after. They command the highest salaries, often exceeding $200,000, especially when they are hired to lead large or complex metropolitan areas.
###
Geographic Location
Where a city is located has a direct and powerful impact on salary. This is driven by two main elements: the local cost of living and the population size of the municipality. A city manager in a major coastal city like San Jose, California, or Bellevue, Washington, will earn a significantly higher salary than a manager in a small, rural town in the Midwest, partly to offset the higher cost of living.
According to surveys by the International City/County Management Association (ICMA), salaries are strongly correlated with population. For example, a manager in a town with fewer than 2,500 residents might earn less than $80,000, while a manager in a city with a population over 250,000 can easily earn over $250,000.
###
Municipality Size and Budget
For a public sector role, "company type" is best understood as the size, complexity, and budget of the municipality. A larger city comes with a larger budget, more employees, a wider array of public services, and more complex political and social challenges. The responsibility of managing a $500 million budget is vastly different from managing a $5 million budget. Consequently, city councils are willing to pay a premium for executives capable of handling that scale and complexity. The larger the city's population and annual operating budget, the higher the city manager's salary will be.
###
Area of Specialization
While "city manager" is a generalist role, a specialized background can significantly boost a candidate's value and earning potential. Individuals with deep expertise in certain high-demand areas are often more attractive to city councils and can negotiate higher compensation. Key areas of specialization include:
- Public Finance and Budgeting: A proven ability to navigate fiscal crises or secure new revenue streams is highly prized.
- Economic Development: Experience in attracting new businesses, revitalizing downtowns, and growing the local tax base is a major asset.
- Urban Planning and Infrastructure: A background in managing large-scale capital projects, from transportation to water systems, is critical for growing cities.
- Labor Relations: Skill in negotiating with public employee unions can be a decisive factor in some municipalities.
Job Outlook

The career outlook for skilled public administrators is stable and promising. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that employment for Top Executives, the category that includes city managers, will grow by 3% from 2022 to 2032. This indicates a steady, consistent demand for these professionals.
As local governments continue to face complex modern challenges—such as sustainable development, housing shortages, public safety, and aging infrastructure—the need for professional, non-partisan management will remain strong. Communities will always require capable leaders to implement solutions and ensure efficient governance, securing the city manager role's relevance for the foreseeable future.
Conclusion

For those drawn to leadership, public service, and the challenge of shaping a community, the role of a city manager is an exceptionally rewarding career path. The position offers not only the chance to make a tangible difference but also the potential for significant financial compensation.
As we've seen, while the average salary is well into the six figures, your ultimate earning potential will be shaped by your commitment to education (especially an MPA), your years of dedicated experience, and your willingness to take on the challenges of larger, more complex municipalities. For aspiring public administrators, the message is clear: the path to a high-impact, high-reward career as a city manager is well-defined and full of opportunity.