Pursuing a Doctor of Audiology (Au.D.) degree is a significant commitment of time, effort, and resources. For those passionate about the science of hearing and balance, it's a deeply rewarding career path. But what does the financial landscape look like for these highly specialized healthcare professionals? The answer is encouraging: an audiology career offers not only personal fulfillment but also a strong, competitive salary with significant growth potential.
On average, audiologists in the United States can expect to earn a median salary of around $87,000 per year, with top earners exceeding $130,000 annually. In this in-depth guide, we will break down the salary you can expect as a Doctor of Audiology and explore the key factors that can maximize your earning potential.
What Does a Doctor of Audiology Do?
Before diving into the numbers, it's essential to understand the vital role audiologists play. They are doctoral-level experts in the healthcare field who diagnose, treat, and manage hearing loss, tinnitus, and balance disorders across all age groups. Their responsibilities are diverse and highly technical, including:
- Conducting comprehensive hearing and balance assessments.
- Fitting and programming hearing aids, cochlear implants, and other assistive listening devices.
- Developing and implementing rehabilitation plans for patients.
- Providing patient and family counseling on the effects of hearing loss.
- Working in noise-induced hearing loss prevention programs in industrial or military settings.
- Collaborating with other medical professionals, such as otolaryngologists (ENTs), pediatricians, and speech-language pathologists.
This high level of expertise and direct impact on patients' quality of life is a primary reason for the profession's strong financial standing.
Average Doctor of Audiology Salary
When analyzing compensation, it's best to look at multiple authoritative sources to get a complete picture. The data consistently shows a healthy and stable salary for audiologists.
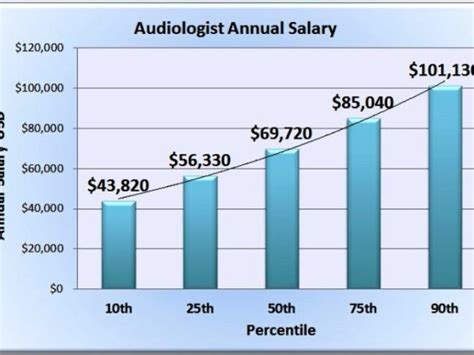
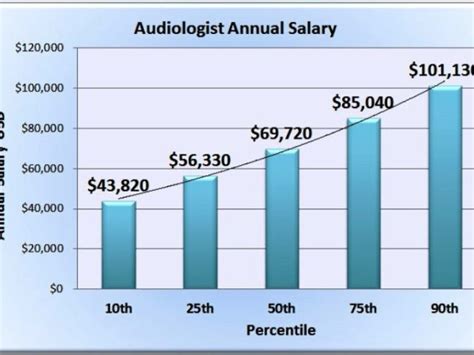
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Occupational Outlook Handbook, the median annual wage for audiologists was $87,740 as of May 2023. This is the midpoint, meaning half of all audiologists earned more than this amount and half earned less.
The BLS also provides a more detailed salary range:
- Lowest 10%: Earned less than $65,510
- Median (50%): $87,740
- Highest 10%: Earned more than $130,570
Reputable salary aggregators offer similar insights, reflecting data from thousands of user-submitted profiles:
- Salary.com reports a median salary for an Audiologist in the U.S. of around $93,392 as of early 2024, with a typical range falling between $85,417 and $102,570.
- Payscale notes an average base salary of approximately $82,300 per year, emphasizing how factors like experience heavily influence this figure.
This data illustrates that while a new graduate may start in the $70,000 range, a clear path exists to a six-figure salary with experience and strategic career choices.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary as a Doctor of Audiology is not a single, fixed number. It is influenced by a combination of professional and environmental factors. Understanding these can help you navigate your career and maximize your earnings.
### Level of Education
Today, the Doctor of Audiology (Au.D.) is the standard entry-level degree for clinical practice and is required for licensure in all states. Therefore, having an Au.D. is the primary key to unlocking the professional salary range. While a Ph.D. in audiology is also an option, it is typically pursued for a career in research or academia. A Ph.D. can lead to higher salaries, particularly in university settings for tenured professors or lead researchers, but for most clinical practitioners, the Au.D. is the terminal degree that establishes their earning potential.
### Years of Experience
Experience is one of the most significant drivers of salary growth. As you gain expertise, refine your clinical skills, and build a professional reputation, your value to employers increases substantially.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): New graduates can expect to earn a salary on the lower end of the spectrum, typically between $70,000 and $80,000. This period is focused on applying academic knowledge in a real-world clinical fellowship year (CFY) and the first years of practice.
- Mid-Career (5-10 years): With solid experience, audiologists see a significant salary increase, often moving well into the $85,000 to $100,000 range. They can take on more complex cases, supervise junior staff, or manage a clinic.
- Senior/Experienced (10+ years): Highly experienced audiologists, especially those in specialized roles or leadership positions, represent the top earners in the field. Salaries can regularly exceed $110,000, with those at the top 10% earning over $130,000, according to BLS data.
### Geographic Location
Where you practice matters. Salaries vary significantly between states and even between metropolitan and rural areas, largely due to differences in cost of living and demand for services.
According to the BLS, the states with the highest annual mean wages for audiologists include:
- California: $116,460
- District of Columbia: $110,050
- Oregon: $106,780
- Washington: $103,130
- Hawaii: $101,600
Conversely, states with a lower cost of living may offer salaries closer to or slightly below the national median. However, the purchasing power in these areas may still be very strong.
### Company Type / Work Setting
The setting in which an audiologist works is a major determinant of salary. The American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) and the BLS provide excellent data on median salaries by work setting.
- Hospitals (State, Local, and Private): This is one of the highest-paying settings, with a BLS-reported median salary of $93,690. Hospital-based audiologists often deal with complex cases, including cochlear implants and advanced diagnostics.
- Private Practice (ENT/Physician's Offices): Working in a practice owned by a physician or group of physicians is very common and lucrative, with a BLS median of $88,110.
- Private Practice (Self-Owned): While it comes with the risks of entrepreneurship, owning a private practice offers the highest earning potential. Successful practice owners can earn well into the six figures, as they profit from both their clinical services and the dispensing of hearing aids.
- Educational Services (Schools and Universities): Audiologists working in public schools or universities tend to have a lower median salary, around $80,390 according to the BLS. This is often due to 9- or 10-month contracts and different funding structures, though it can come with excellent benefits and work-life balance.
### Area of Specialization
Within the broad field of audiology, developing a niche expertise can lead to higher compensation.
- Cochlear Implants: This is a highly specialized and technical area requiring close work with surgeons and extensive patient programming. Specialists are in high demand and can command top-tier salaries.
- Vestibular/Balance Specialist: Diagnosing and treating dizziness and balance disorders requires advanced training and equipment, making these practitioners highly valuable.
- Pediatric Audiology: Working with infants and children requires a unique skill set and is critical for early intervention. Specialists in this area are sought after in children's hospitals and specialty clinics.
- Industrial Audiology: Consultants who help companies manage occupational hearing conservation programs can earn high fees for their services.
Job Outlook

The future for Doctors of Audiology is exceptionally bright. The BLS projects that employment for audiologists will grow by 11% from 2022 to 2032, which is considered "much faster than the average" for all occupations.
This robust demand is driven by several key factors:
- An Aging Population: The large baby-boomer generation is entering an age where hearing loss and balance issues become more prevalent, increasing the need for audiological services.
- Early Diagnosis: Improved newborn hearing screening programs mean that hearing loss is being identified and treated at a much younger age.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in hearing aid technology and cochlear implants are making treatment more effective and desirable.
Conclusion

A career as a Doctor of Audiology is a wise choice for those seeking a profession that is both intellectually stimulating and financially rewarding. With a strong median salary and a clear path to six-figure earnings, the financial outlook is positive. Your ultimate salary will be shaped by your years of experience, the location and setting you choose to practice in, and any specializations you pursue.
For prospective students and practicing professionals alike, the data is clear: the demand for skilled audiologists is growing rapidly, ensuring job security and a competitive salary for years to come. It is a field where you can build a successful, lifelong career while making a profound difference in the lives of others.