Does the NBA Have a Salary Cap? A Deep Dive into Player Earnings and League Economics

The world of professional basketball is synonymous with staggering financial figures. Aspiring athletes and sports business professionals alike are often captivated by the multi-million dollar contracts signed by NBA superstars. While the earning potential is immense, with average player salaries reaching heights unimaginable in most professions, these earnings are not limitless. They are governed by a complex and fascinating system known as the salary cap.
This article will break down the intricacies of the NBA's salary cap, explore how player salaries are determined, and analyze the key factors that influence an athlete's earning power in one of the world's most lucrative sports leagues.
What Is the NBA Salary Cap and What Does It Do?

In simple terms, yes, the NBA absolutely has a salary cap. However, it's far more nuanced than a simple hard limit. The NBA employs a "soft cap" system, which is a mechanism designed to promote competitive balance and control team spending.
The core purpose of the salary cap is to prevent large-market, wealthier teams from simply outspending smaller-market teams on player talent, which could lead to a league dominated by only a handful of franchises.
Key components of the system include:
- The Salary Cap: This is the primary threshold. For the 2023-2024 season, the salary cap is set at $136.021 million per team. In theory, this is the total amount a team can spend on its player salaries for the year.
- The "Soft" Nature: The "soft" part comes from the numerous exceptions that allow teams to exceed this cap to re-sign their own players or make specific types of signings (e.g., the Mid-Level Exception, the Bi-Annual Exception, and the famous "Larry Bird" Exception). This is why many top teams have payrolls well above the official cap number.
- The Luxury Tax: To penalize excessive spending, the league sets a secondary, higher threshold known as the luxury tax line ($165.294 million for 2023-2024). Teams with payrolls exceeding this line must pay a punitive tax to the league, which is then redistributed to non-tax-paying teams.
In essence, the salary cap system creates a complex puzzle for a team's General Manager and front office, who must strategically build a competitive roster while navigating a web of financial rules.
Average NBA Player Salary
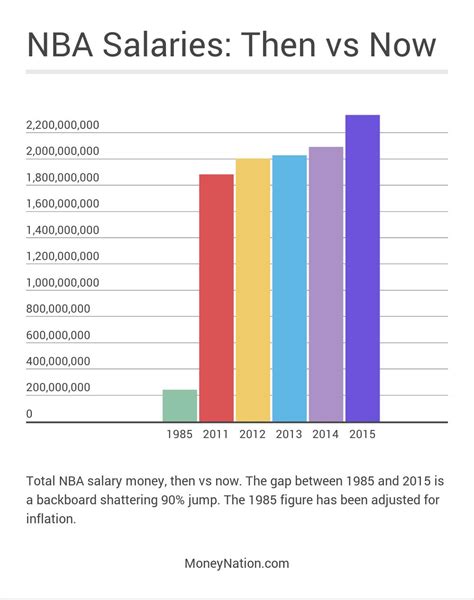
The salaries for athletes in the NBA are among the highest in the world. According to the National Basketball Players Association (NBPA), the average salary for an NBA player in the 2023-2024 season is projected to be approximately $10.5 million.
However, this average is skewed by the massive "max" and "supermax" contracts of superstars. The salary landscape is better understood as a wide range:
- Entry-Level (Minimum Salary): For a rookie in the 2023-2024 season, the minimum salary is approximately $1.1 million.
- Mid-Career (Average Salary): As noted, the league average hovers around $10.5 million.
- Senior/Superstar (Maximum Salary): Top players can earn over $50 million per year. For example, Stephen Curry's salary for the 2023-2024 season is over $51.9 million.
To put this in perspective, the median annual wage for all occupations in the United States was $46,310 in May 2022, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS).
Key Factors That Influence Salary

An NBA player's salary isn't arbitrary. It is meticulously determined by a set of rules laid out in the league's Collective Bargaining Agreement (CBA). The following are the most critical factors influencing a player's earnings.
### Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the most significant factor in determining both the floor and the ceiling of a player's potential salary. The CBA explicitly defines minimum and maximum salary tiers based on a player's years of service in the league.
- Minimum Salaries: The league minimum salary increases with each year of experience. A player with 0 years of experience earns a minimum of ~$1.1M, while a veteran with 10+ years of experience has a minimum salary of over $3.1 million.
- Maximum Salaries: The maximum amount a player can earn is also tied to their tenure.
- 0-6 years of experience: Can earn a max contract worth 25% of the total salary cap.
- 7-9 years of experience: Can earn a max contract worth 30% of the total salary cap.
- 10+ years of experience: Can earn a max contract worth 35% of the total salary cap.
### Area of Specialization (Player Performance and Accolades)
In the context of the NBA, "specialization" translates to on-court performance and official awards. Elite performance is the key to unlocking the highest salary tiers. A player who has achieved certain benchmarks in the seasons leading up to their contract negotiation can qualify for a "supermax" contract (formally the Designated Veteran Player Extension), which can be worth up to 35% of the cap, even if they don't yet have 10 years of experience. These accolades include:
- Being named to an All-NBA Team (First, Second, or Third).
- Being named the NBA Defensive Player of the Year.
- Being named the NBA Most Valuable Player (MVP).
Achieving one of these awards in the designated timeframe can be the difference between a standard max contract and a supermax deal worth tens of millions of dollars more.
### Geographic Location
While the base salary is negotiated with the team, the player's actual take-home pay is significantly impacted by geographic location due to state and local income taxes. A player on a team in a state with no state income tax, such as the Miami Heat (Florida), Dallas Mavericks (Texas), or San Antonio Spurs (Texas), will have a higher net income than a player earning the exact same gross salary with the Los Angeles Lakers (California) or New York Knicks (New York), which have high state income tax rates. This "tax-free" advantage can be a powerful negotiating tool for teams in those states.
### Company Type (Team Strategy and Market Size)
The "company" is the individual NBA franchise, and its financial strategy plays a huge role.
- Willingness to Pay Luxury Tax: Teams in a "win-now" mode with deep-pocketed ownership (e.g., Golden State Warriors, LA Clippers) are often willing to build rosters that soar past the luxury tax line, paying tens or even hundreds of millions in tax penalties to compete for a championship.
- Market Size: While the cap promotes parity, larger market teams (L.A., New York, Chicago) often generate more revenue, which can support higher payrolls and luxury tax payments.
- Rebuilding Teams: A rebuilding team may intentionally stay under the salary cap to maintain financial flexibility, preserve future draft assets, and develop young, inexpensive talent. A player's salary prospects are directly tied to the competitive and financial cycle of the team they play for.
### Level of Education
Unlike many traditional careers, a formal level of education does not directly correlate to salary in the NBA. While the vast majority of players attend college for at least one year (a requirement for most U.S.-based players), obtaining a degree has no bearing on the salary brackets defined by the CBA. A player's draft position, and subsequently their performance and experience, are the determining factors, not their academic credentials.
Job Outlook

The career outlook for a professional basketball player is unique. The number of available jobs is extremely limited and static. There are 30 NBA teams, each with 15 standard roster spots and three two-way spots, meaning there are only about 540 total jobs in the entire league at any given time.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) groups NBA players under the broader category of "Athletes and Sports Competitors." For this category, the BLS projects a job growth rate of 9% from 2022 to 2032, which is much faster than the average for all occupations. However, this growth largely reflects opportunities in other sports, fitness, and recreation sectors. The number of NBA jobs remains relatively fixed, making the competition for these highly lucrative positions unimaginably fierce.
Conclusion

So, does the NBA have a salary cap? Yes—a sophisticated "soft cap" that forms the foundation of the league's entire economic structure. It's a system designed to balance immense earning potential with competitive fairness. For any athlete looking to make it in the league, or any professional aspiring to work in a sports front office, understanding these rules is crucial.
An NBA player's salary is not just a number; it's the result of a complex calculation involving:
- Years of service in the league.
- Elite on-court performance recognized by official awards.
- The financial strategy and market of their team.
- The powerful, behind-the-scenes influence of state tax laws.
While the path to becoming a professional NBA player is one of the most challenging in the world, the financial rewards for those who reach the top are governed by a fascinating and complex system that makes the business of basketball as compelling as the game itself.
