Unlocking Your Earnings Potential: A Guide to the Series 7 License Salary

The world of finance offers some of the most dynamic and rewarding career paths available, and for many aspiring professionals, the journey begins with the Series 7 license. This critical qualification serves as a gateway to advising clients and executing trades, opening doors to significant earning potential. While a six-figure income is well within reach for dedicated professionals, your actual salary will depend on a combination of experience, location, and specialization. A typical salary range can span from $65,000 for entry-level roles to well over $200,000 for seasoned veterans, making it a highly attractive field for those with a passion for the markets.
This guide will break down what you can expect to earn with a Series 7 license and the key factors that will shape your financial success.
What Does a Series 7 License Holder Do?

Before diving into the numbers, it's essential to understand that the "Series 7 license" is not a job title itself. It is a credential—the General Securities Representative Qualification Examination (GS)—that authorizes a professional to sell a broad range of securities, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and variable annuities.
The license is sponsored by a FINRA member firm (your employer) and demonstrates you have the competence to perform your job as a registered representative. Professionals who hold a Series 7 license often work in roles such as:
- Financial Advisor: Works with individuals and families to create long-term financial plans, manage investments, and provide guidance on retirement, education, and estate planning.
- Stockbroker / Registered Representative: Buys and sells securities on behalf of clients. This role is often heavily commission-based.
- Wealth Management Advisor: A specialized type of financial advisor who caters to high-net-worth and ultra-high-net-worth individuals and families, offering more complex investment strategies and services.
- Investment Banker (Analyst/Associate): While more licenses are often required, the Series 7 is a core component for many client-facing roles in investment banking.
Essentially, a Series 7 license is your ticket to participate directly in the buying and selling of most types of securities, making you a vital player in the financial services industry.
Average Series 7 Holder Salary
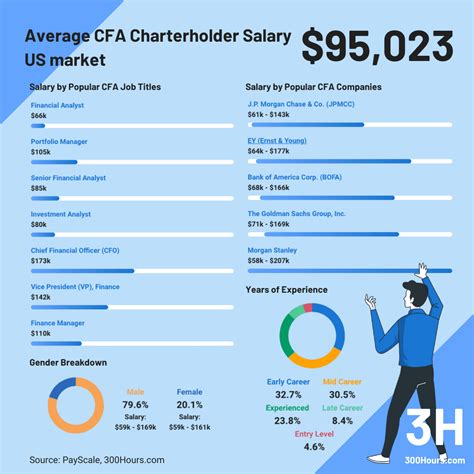
Compensation in finance is notoriously variable, often composed of a base salary plus commissions, bonuses, and sometimes a percentage of assets under management (AUM). Therefore, looking at a single "average" can be misleading, but we can establish a reliable baseline using data from authoritative sources.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) provides a strong benchmark. For Personal Financial Advisors, a primary role for Series 7 holders, the median annual wage was $99,580 as of May 2023. The lowest 10 percent earned less than $48,470, while the top 10 percent earned more than $239,200.
Reputable salary aggregators provide a similar picture, often showing a wide range based on user-reported data:
- Salary.com reports that the typical salary range for a Financial Advisor in the United States falls between $65,049 and $97,801, but this often represents base salary before the significant impact of commissions and bonuses.
- Payscale notes that the average base salary for a holder of a Series 7 license is approximately $71,000 per year, with total pay (including bonuses and profit sharing) ranging from $46,000 to $178,000.
Key Takeaway: A starting professional might see a base salary in the $50k-$70k range, but with experience and a growing client base, a total compensation package well into the six figures is standard.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your individual earnings will be determined by several critical factors. Understanding these levers is key to maximizing your career's financial potential.
###
Level of Education
While a bachelor's degree is the standard entry requirement (typically in finance, economics, or business), advanced education can significantly boost your earning potential. A Master of Business Administration (MBA) or a Master of Science in Finance can lead to higher starting salaries and open doors to more senior or specialized roles.
Furthermore, additional professional certifications are highly influential. The Certified Financial Planner (CFP®) designation is considered the gold standard and can substantially increase client trust and compensation. Other valuable certifications include the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) for investment analysis and the Chartered Financial Consultant (ChFC).
###
Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the single most important factor in determining a Series 7 holder's salary. Earnings are directly tied to your ability to attract and retain clients and grow their assets.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): Professionals are often in training programs, earning a modest base salary while building their book of business. Total compensation might range from $50,000 to $80,000.
- Mid-Career (3-10 years): With an established client base and a proven track record, advisors see a significant jump in income as commissions and AUM-based fees become a larger portion of their pay. Earnings typically move into the $90,000 to $150,000+ range.
- Senior-Level (10+ years): Top performers with a large and loyal client portfolio can earn substantial incomes, often exceeding $200,000 or $300,000 per year. Their compensation is heavily weighted toward performance.
###
Geographic Location
As with most professions, where you work matters. Major financial centers offer higher salary potential due to a greater concentration of wealth and corporate headquarters. Cities like New York, San Francisco, Chicago, and Boston typically offer the highest compensation but also come with a higher cost of living. For example, according to Salary.com, a Financial Advisor in New York City can expect to earn roughly 20% more than the national average.
###
Company Type
The type of firm you work for dramatically impacts your compensation structure and overall earnings.
- Wirehouses (e.g., Morgan Stanley, Merrill Lynch): These large, full-service firms offer strong brand recognition, training programs, and support. Compensation is often a mix of salary and a structured payout grid based on production.
- Independent Broker-Dealers (e.g., LPL Financial, Ameriprise): Advisors here operate more like independent business owners. They receive less direct support but keep a much higher percentage of the revenue they generate (a higher payout). This model offers immense potential for high-performing, entrepreneurial advisors.
- Banks and Credit Unions: Financial advisors at banks often work with existing bank customers. The compensation model may include a more stable salary with bonuses tied to referrals and sales goals.
- Discount Brokerages (e.g., Charles Schwab, Fidelity): Advisors in these firms are often salaried employees who assist clients calling in for guidance, with bonuses tied to company-wide performance and customer satisfaction metrics.
###
Area of Specialization
Specializing in a high-demand niche can lead to greater earnings. An advisor focusing on high-net-worth (HNW) or ultra-high-net-worth (UHNW) clients, for example, will manage larger portfolios and generate higher fees than an advisor serving the mass market. Other lucrative specializations include retirement income planning for baby boomers, executive compensation (stock options, deferred comp), and working with small business owners on succession planning.
Job Outlook

The future for Series 7 professionals is bright. The BLS projects that employment for Personal Financial Advisors will grow 13% from 2022 to 2032, which is much faster than the average for all occupations.
This strong growth is driven by two key trends:
1. An Aging Population: The large baby-boomer generation is entering or nearing retirement, creating a massive demand for professional advice on managing their savings and investments.
2. Increasing Complexity: As financial products and regulations become more complex, individuals are increasingly seeking professional guidance to navigate their financial lives.
This sustained demand ensures that skilled and licensed professionals will remain highly sought-after for the foreseeable future.
Conclusion

Obtaining a Series 7 license is a powerful first step toward a prosperous and impactful career in the financial services industry. While a high salary is not guaranteed, the potential is undeniable. Your earnings will not be defined by the license itself, but by how you leverage it.
By focusing on continuous education, gaining valuable experience, choosing the right company and location, and building a strong client base, you can chart a path toward a highly rewarding career. For those who are ambitious, client-focused, and driven, the Series 7 license is more than just a qualification—it's a launchpad for success.
