In a world increasingly driven by automation, smart technology, and robotics, the role of the electromechanical engineer has never been more critical. These professionals are the architects of modern machinery, blending electrical and mechanical principles to create the complex systems that power our lives. If you're drawn to this dynamic field, you're likely wondering about its financial rewards.
The great news is that a career in electromechanical engineering is not only intellectually stimulating but also financially lucrative. With a strong demand for these specialized skills, professionals in this field can expect competitive compensation, often commanding six-figure salaries as they advance in their careers. This guide will break down what you can expect to earn and the key factors that will shape your salary potential.
What Does an Electromechanical Engineer Do?
At its core, an electromechanical engineer is a multidisciplinary problem-solver. They are the crucial link between the worlds of circuits and gears, software and hardware. Their primary role is to design, develop, test, and manufacture systems that involve both electrical and mechanical components.
Their daily responsibilities can include:
- Designing and developing robotic systems, automated manufacturing lines, and consumer electronics.
- Creating prototypes and running simulations to test new products.
- Integrating sensors, controllers, and actuators into complex mechanical systems.
- Overseeing the manufacturing process to ensure products meet design specifications and quality standards.
- Troubleshooting and improving existing electromechanical systems.
From the anti-lock brakes in your car to the sophisticated robots on an assembly line, the work of an electromechanical engineer is all around us.
Average Electromechanical Engineering Salary
When analyzing compensation for this role, it's clear that the combination of electrical and mechanical expertise is highly valued. While exact figures vary based on several factors, we can establish a strong baseline using data from leading sources.
According to Salary.com (2024), the median annual salary for an Electromechanical Engineer in the United States is approximately $104,748. The typical salary range is quite broad, reflecting the influence of experience, location, and specialization. Most professionals in this role earn between $85,082 and $126,818.
- Entry-Level (Bottom 10%): Newly graduated engineers can expect to start around $75,000.
- Senior-Level (Top 10%): Experienced engineers with specialized skills and a proven track record can command salaries upwards of $140,000.
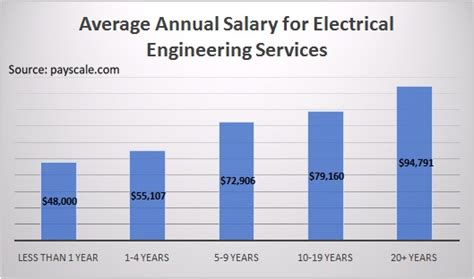
Data from Payscale (2024) corroborates this, reporting an average salary of $86,750, with a common range from $64,000 to $124,000, which often includes base salary and standard bonuses. These figures confirm that electromechanical engineering is a high-paying field with significant growth potential.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary will be determined by a combination of personal qualifications and external market forces. Understanding these factors is key to maximizing your earning potential.
### Level of Education
A solid educational foundation is the non-negotiable entry ticket to this profession.
- Bachelor's Degree: A Bachelor of Science (B.S.) in Electromechanical Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, or Electrical Engineering is the standard requirement. This degree provides the fundamental knowledge needed for entry-level positions.
- Master's Degree: Pursuing a Master of Science (M.S.) can provide a significant salary boost, often between 10% and 20%. A master's degree allows for deep specialization in high-demand areas like robotics, control systems, or mechatronics. It qualifies you for advanced research and development (R&D) roles and can fast-track you into management positions.
- Ph.D.: While less common for industry roles, a Ph.D. is essential for careers in academia or highly specialized corporate research, where you would be leading cutting-edge innovation.
### Years of Experience
Experience is one of the most significant drivers of salary growth. As you build your skills and portfolio of successful projects, your value to employers increases exponentially.
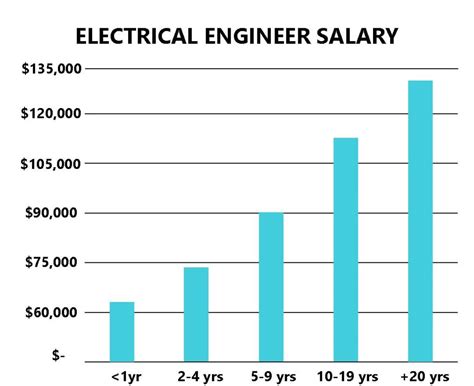
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): In this stage, you're applying theoretical knowledge to real-world problems. Salaries typically fall in the $70,000 to $85,000 range.
- Mid-Career (3-9 years): With several years of experience, you can manage projects independently and mentor junior engineers. Salaries often climb into the $90,000 to $115,000 range.
- Senior/Lead (10+ years): At this level, you are a subject matter expert, leading complex projects, setting technical strategy, and potentially managing entire engineering teams. Senior and Principal Electromechanical Engineers can expect salaries of $120,000 to $150,000+.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries for electromechanical engineers vary significantly across the United States due to differences in cost of living and the concentration of tech and manufacturing hubs.
- Top-Paying States: States with major technology, aerospace, and defense industries tend to offer the highest salaries. According to U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) data for related engineering fields, states like California, Massachusetts, Washington, Virginia, and Texas often pay well above the national average.
- Metropolitan Hotspots: Cities like San Jose, CA; Boston, MA; Seattle, WA; and Austin, TX, are hubs for innovation and offer top-tier salaries to attract top talent, though this is balanced by a higher cost of living.
### Company Type
The type of company you work for will also influence your compensation package.
- Large Tech & Aerospace Corporations (e.g., Google, Apple, Lockheed Martin, Boeing): These companies typically offer the highest base salaries, comprehensive benefits packages, and bonuses.
- Automotive and Manufacturing Companies (e.g., Ford, General Motors, Procter & Gamble): Offer competitive, stable salaries and are major employers of electromechanical talent.
- Startups: While the base salary might be slightly lower than at a large corporation, startups often offer significant stock options or equity, which can lead to a substantial financial windfall if the company succeeds.
- Government and Defense Contractors: Provide stable careers with excellent benefits and competitive, though sometimes less spectacular, salaries compared to the top commercial tech firms.
### Area of Specialization
Within electromechanical engineering, certain specializations are in higher demand and can command premium salaries.
- Robotics and Automation: As industries increasingly turn to automation, engineers who can design and implement robotic systems are highly sought after.
- Mechatronics: This is a closely related discipline that integrates mechanics, electronics, computer science, and control engineering to design "smart" products.
- Medical Devices: Designing sophisticated medical equipment, from surgical robots to diagnostic tools, is a highly regulated and high-value field.
- Aerospace and Defense: Developing systems for aircraft, spacecraft, and defense technology requires an extremely high level of precision and expertise, which is reflected in compensation.
Job Outlook

The future for electromechanical engineers is bright. While the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) often groups this specific role with broader categories, the demand for the underlying skills is set to grow. The BLS projects that employment for closely related fields like Mechanical Engineering and Electrical Engineering will grow by about 3% from 2022 to 2032, which is as fast as the average for all occupations.
However, this number doesn't tell the whole story. The "Fourth Industrial Revolution"—characterized by AI, the Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced automation—is entirely dependent on electromechanical expertise. As industries from agriculture to healthcare become "smarter" and more automated, the demand for engineers who can bridge the gap between the physical and digital worlds will only intensify.
Conclusion

Choosing a career as an electromechanical engineer is a strategic move for those passionate about innovation and technology. It is a field that promises not only challenging and impactful work but also a highly rewarding financial future. With a median salary well above the national average and pathways to earn over $140,000, it represents an excellent return on investment for your education.
To maximize your earning potential, focus on continuous learning, consider pursuing an advanced degree or specialization in a high-growth area like robotics, and be strategic about your location and choice of employer. By doing so, you can build a successful and prosperous career at the forefront of modern engineering.