Stepping into the role of an elementary school principal is a powerful career move for dedicated educators looking to make a broader impact. It's a position of leadership, vision, and immense responsibility. But beyond the profound professional rewards, it also offers significant financial potential. For those considering this path, a key question is: What can you expect to earn?
This guide provides a data-driven look at elementary principal salaries across the United States. While the national average often exceeds six figures, your actual compensation will depend on a variety of critical factors. Let's break down the numbers and explore what influences your earning potential as a school leader.
What Does an Elementary Principal Do?

Before diving into the salary figures, it's essential to understand the scope of the role. An elementary principal is the chief executive and instructional leader of their school. They are not just administrators; they are community builders, budget managers, and the driving force behind a school's culture and academic success.
Key responsibilities include:
- Instructional Leadership: Observing classrooms, evaluating teacher performance, and implementing curriculum standards to improve student outcomes.
- Operations and Budget Management: Overseeing the school's daily operations, managing its budget, and ensuring resources are allocated effectively.
- Staff Management: Hiring, training, and mentoring teachers and support staff.
- Student Support: Handling student discipline, overseeing special education programs, and ensuring a safe and productive learning environment.
- Community Engagement: Acting as the primary liaison between the school and parents, the school district, and the wider community.
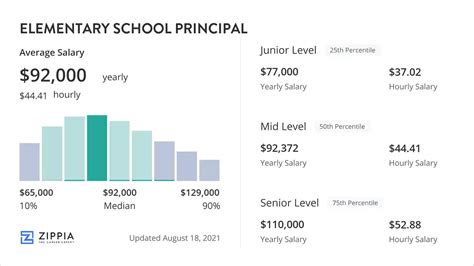
Average Elementary Principal Salary
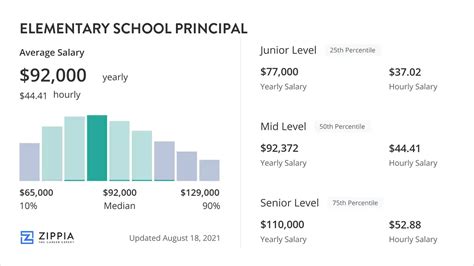
The compensation for an elementary principal is competitive, reflecting the high level of education and experience required.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for all elementary, middle, and high school principals was $103,460 in May 2023. The BLS also notes a wide salary spectrum, with the lowest 10 percent earning less than $69,070 and the highest 10 percent earning more than $166,150.
Reputable salary aggregators offer more specific data for the elementary level as of early 2024:
- Salary.com reports the median salary for an Elementary School Principal in the United States is $119,053, with a typical range falling between $105,330 and $134,138.
- Payscale places the average base salary at around $101,155 per year, with total pay packages (including bonuses) reaching up to $145,000.
- Glassdoor estimates a total pay average of $111,547 per year, based on user-submitted data.
These figures show that while a six-figure salary is common, your specific earnings are influenced by several key variables.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Where you work, your level of experience, and the type of school you lead all play a significant role in determining your final compensation.
### Level of Education
A master's degree is the standard educational requirement for becoming a principal. Most aspiring principals earn a Master of Education (M.Ed.) in Educational Leadership or Educational Administration. However, pursuing a doctorate can provide a significant salary advantage. Principals holding a Doctor of Education (Ed.D.) or a Ph.D. in a related field are often top candidates for positions in larger, higher-paying districts and may see a salary bump of 5-10% or more.
### Years of Experience
Experience is one of the most significant drivers of salary growth. School districts almost always follow a tiered pay scale that rewards longevity and expertise.
- Entry-Level (0-3 years): An early-career principal, often promoted from an assistant principal or lead teacher role, will typically start at the lower end of the salary range for their district.
- Mid-Career (4-9 years): With a proven track record of school management and student achievement, principals can expect steady salary increases.
- Experienced (10-20+ years): Senior principals with a decade or more of experience command the highest salaries. They are often sought after to lead larger schools or mentor other administrators, putting them at the top of the pay scale. Payscale data clearly shows this upward trend, with experienced principals earning significantly more than their entry-level counterparts.
### Geographic Location
Where you live and work is a major factor. Salaries are adjusted to reflect regional costs of living and state-level education funding.
- Top-Paying States: States with high costs of living and strong teachers' unions tend to offer the highest principal salaries. According to BLS data, the top-paying states for school administrators include Washington, California, New York, Connecticut, and New Jersey. Principals in major metropolitan areas within these states can earn well above the national average.
- Lower-Paying States: Conversely, states in the South and rural Midwest often have lower salary ranges, though this is typically offset by a lower cost of living. States like Mississippi, Oklahoma, and South Dakota tend to fall on the lower end of the national scale.
### School and District Type
The type of school or district you lead directly impacts your compensation package.
- Public vs. Private: Public school principals' salaries are funded by tax dollars and are often transparent and standardized based on district-wide pay scales. Larger, urban public school districts generally offer higher pay than smaller, rural districts. Private school salaries can vary dramatically. Elite, independent preparatory schools may offer salaries that far exceed those in the public sector, while smaller, parochial schools may pay less.
- District Size and Funding: A principal in a large, well-funded suburban district with thousands of students will almost certainly earn more than a principal in a small, rural district with limited funding and a smaller student body.
- Title I Schools: Principals in schools with a high percentage of low-income students (Title I schools) may receive additional stipends or higher base pay to compensate for the added challenges and responsibilities.
### School Focus and Specialization
While "specialization" is less formal than in other professions, leading a school with a unique focus can influence pay. Principals of magnet schools (e.g., STEM, Arts, Language Immersion) or those overseeing significant special education programs may have more complex roles that command higher compensation, either through a higher base salary or specific stipends offered by the district.
Job Outlook

The career outlook for elementary principals is stable and positive. The BLS projects that employment for elementary, middle, and high school principals will grow 1 percent from 2022 to 2032. While this is slower than the average for all occupations, it still translates to about 19,800 projected job openings each year over the decade.
This consistent demand is driven primarily by the need to replace principals who are retiring or transitioning to other roles, such as district superintendent. As long as there are schools, there will be a need for qualified, effective leaders to run them.
Conclusion

Becoming an elementary school principal is a challenging yet profoundly rewarding career path for educators who aspire to leadership. The financial compensation is strong, with the potential to earn a six-figure salary that grows steadily with experience and expertise.
For aspiring school leaders, the key takeaways are:
- Aim for an advanced degree: A master's is required, and a doctorate can unlock higher earning potential.
- Build your experience: A successful track record as a teacher and assistant principal is the foundation for a top-tier salary.
- Be strategic about location: Your earning potential is heavily influenced by the state and district where you choose to work.
- Understand the landscape: Public, private, urban, and rural schools all offer different compensation structures.
For dedicated educators ready to take the next step, a principalship offers not only a significant financial reward but also the profound opportunity to shape the future of an entire school community.