In a world increasingly driven by data, location intelligence has become a critical asset for businesses, governments, and organizations of all sizes. At the heart of this revolution is the Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Specialist, a professional who transforms raw geographic data into powerful insights. If you're considering a career in this dynamic field, you're likely wondering about your earning potential.
The short answer? A career as a GIS Specialist offers a stable and rewarding financial path. While salaries can start around $55,000, experienced and specialized professionals can command salaries well over $100,000 per year. This guide provides a deep dive into the factors that determine a GIS Specialist's salary, backed by the latest data from authoritative sources.
What Does a GIS Specialist Do?

Before we talk numbers, let's briefly define the role. A GIS Specialist is more than just a map-maker; they are data detectives, analysts, and storytellers. Their core responsibilities include:
- Data Management: Collecting, storing, and managing spatial data (like satellite imagery, aerial photography, and GPS coordinates) in complex geodatabases.
- Spatial Analysis: Using GIS software (like Esri's ArcGIS or open-source QGIS) to analyze spatial relationships, identify patterns, and model outcomes. For example, they might identify the best location for a new retail store, map environmental contamination, or optimize delivery routes.
- Cartography and Visualization: Creating clear, informative, and visually compelling maps and dashboards to communicate their findings to stakeholders.
- Problem-Solving: Applying geographic principles and technology to solve real-world problems in urban planning, environmental science, logistics, public health, and more.
Average GIS Specialist Salary
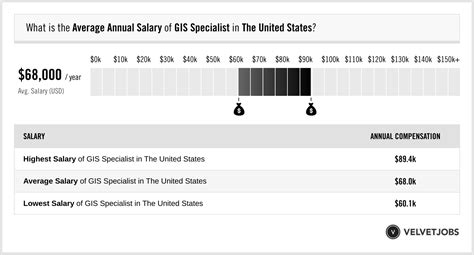
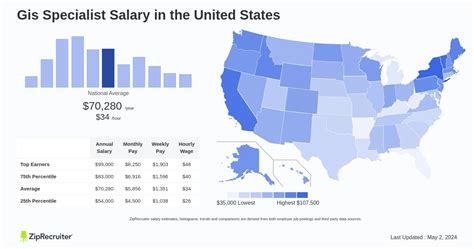
The salary for a GIS Specialist varies based on a number of factors, but we can establish a solid baseline by looking at data from leading sources.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for Cartographers and Photogrammetrists—the category that most closely represents GIS Specialists—was $74,850 in May 2023. The BLS also notes that Geographers, a related profession often involving more advanced research and analysis, earned a median salary of $91,950.
Reputable salary aggregators provide a more real-time, user-reported snapshot:
- Salary.com places the median salary for a GIS Specialist at around $68,500, with a typical range falling between $60,000 and $77,000.
- Glassdoor reports a total pay average of approximately $73,000 per year (base salary plus additional compensation like bonuses).
- Payscale shows an average salary closer to $61,000, which often reflects a higher proportion of entry-level and technician roles in its dataset.
Based on this data, a general salary progression looks like this:
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): $55,000 - $65,000
- Mid-Career (3-8 years): $65,000 - $85,000
- Senior-Level (8+ years): $85,000 - $110,000+
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary will be determined by a combination of factors. Understanding these levers is key to maximizing your earning potential throughout your career.
### Level of Education
Your educational background provides the foundational knowledge for your career. A Bachelor's degree in Geography, Geoinformatics, Environmental Science, Urban Planning, or Computer Science is typically the minimum requirement. However, advanced education can significantly boost your earning potential and open doors to more senior roles. A Master's degree in GIS or a related field often qualifies you for higher-level Analyst, Scientist, or Manager positions, which command higher salaries from the start. Furthermore, a GIS Certificate can be a powerful supplement for those who have a degree in another field, demonstrating specialized, job-ready skills.
### Years of Experience
Experience is one of the most significant drivers of salary growth. As you move from an entry-level GIS Technician or Specialist to a senior role, your value to an employer increases dramatically.
- Entry-Level (GIS Technician/Specialist I): Focuses on data entry, basic map creation, and supporting senior staff.
- Mid-Career (GIS Analyst/Specialist II): Takes on independent projects, performs complex spatial analysis, and may manage smaller projects or mentor junior staff.
- Senior-Level (Senior GIS Analyst, GIS Manager, GIS Architect): Leads major projects, develops strategic solutions, manages entire GIS departments, and designs complex enterprise-level systems. Professionals at this level, especially those with management responsibilities, often earn salaries exceeding $100,000.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries for GIS professionals are often higher in major metropolitan areas and states with high costs of living and a concentration of tech or engineering industries. According to BLS data and job market analysis, states like California, Colorado, Virginia, Washington, and Maryland often offer higher-than-average salaries, partly due to the presence of large tech companies, federal government agencies (like the NGA and USGS in the D.C. area), and major engineering firms.
### Company Type
The industry and sector you work in have a direct impact on compensation.
- Private Sector: This sector, including environmental consulting, engineering firms, real estate, logistics, and tech companies, often offers the highest salaries. These companies leverage GIS to gain a competitive edge and are willing to pay for top talent.
- Public Sector (Government): Federal, state, and local government jobs offer competitive salaries, excellent benefits, and strong job security. While the base salary might sometimes be slightly lower than in the private sector, the comprehensive benefits package can make the total compensation very attractive.
- Non-Profit and Academia: These roles typically offer lower salaries. However, they attract professionals who are passionate about a specific cause or dedicated to research and education, offering a different kind of reward.
### Area of Specialization
Moving beyond a generalist role and developing a specialization is the single most effective way to accelerate your salary growth. The "Specialist" who can simply use out-of-the-box software tools is becoming less valuable than the professional who can build, customize, and innovate. High-demand specializations include:
- GIS Development & Programming: Proficiency in languages like Python (especially ArcPy), JavaScript (for web mapping libraries like Leaflet or ArcGIS API for JavaScript), and SQL is a game-changer. A "GIS Developer" who can automate workflows and build custom web applications will earn significantly more than a non-programming specialist.
- Geospatial Data Science: Combining GIS with data science skills—like machine learning, statistical modeling, and big data analysis—is at the cutting edge of the field and commands a premium salary.
- GIS Database Administration: Expertise in managing complex enterprise geodatabases (like Esri's SDE or PostgreSQL/PostGIS) is a critical and well-compensated skill.
- Remote Sensing: Specializing in the analysis of satellite and drone imagery is highly valuable in agriculture, defense, and environmental monitoring.
Job Outlook

The future for GIS professionals is bright. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 2% growth for "Cartographers and Photogrammetrists" from 2022 to 2032. However, this number can be misleading.
While the specific *title* of "GIS Specialist" may show modest growth, the *application of GIS skills* is exploding across nearly every industry. Businesses in logistics, marketing, finance, and healthcare are rapidly adopting location intelligence, creating immense demand for professionals who can interpret spatial data. The real growth lies not in traditional mapping roles but in integrated positions like Data Analyst, Solutions Engineer, Business Analyst, and Data Scientist—all of whom increasingly require strong GIS skills.
Conclusion

A career as a GIS Specialist offers a compelling combination of intellectually stimulating work and strong financial potential. While a comfortable salary is attainable with a bachelor's degree and a few years of experience, the path to a six-figure income is paved with continuous learning and specialization.
To maximize your earnings, focus on:
1. Building a Strong Foundation: Earn a relevant degree and never stop learning.
2. Gaining Experience: Take on challenging projects that showcase your analytical abilities.
3. Developing Technical Skills: Master programming languages like Python and SQL and learn web mapping technologies.
4. Specializing: Become the go-to expert in a high-demand niche like development, data science, or enterprise systems.
By strategically developing your skills and experience, you can build a highly rewarding and lucrative career at the intersection of geography and technology.