Financial Advisor Salary: A Comprehensive Guide for 2024

In a world of complex financial markets and ever-changing economic landscapes, the demand for skilled Financial Advisors has never been greater. This is a career path that offers not only significant earning potential but also the deep satisfaction of helping individuals and families achieve their most important life goals. With a projected growth rate that far outpaces the national average and a median salary nearing six figures, becoming a Financial Advisor is a compelling option for analytical and relationship-driven professionals.
This guide will break down what it takes to succeed in this field and the key factors that determine your earning potential.
What Does a Financial Advisor Do?

A Financial Advisor acts as a financial guide, helping clients navigate their financial lives. They work directly with individuals, families, and sometimes businesses to develop strategies for saving, investing, and growing their money. Their goal is to help clients meet long-term financial objectives, such as a comfortable retirement, funding a child's education, or building generational wealth.
Key responsibilities often include:
- Meeting with clients to understand their financial situation and life goals.
- Analyzing clients' income, expenses, assets, and liabilities.
- Recommending and managing investment portfolios (stocks, bonds, mutual funds).
- Advising on retirement plans (401(k)s, IRAs) and estate planning.
- Providing guidance on insurance needs and risk management.
- Monitoring clients' financial progress and adjusting strategies as needed.
It's a role that blends sharp analytical skills with strong interpersonal communication, as building trust with clients is paramount.
Average Financial Advisor Salary
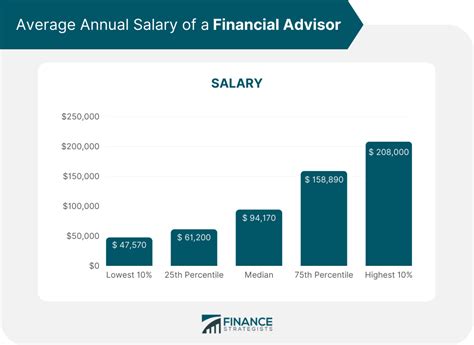
The earning potential for a Financial Advisor is substantial and often tied to performance, experience, and client base.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for personal financial advisors was $99,580 as of May 2023.
However, this figure is just a midpoint. The salary range is incredibly wide, reflecting the diverse compensation models in the industry (salary, commission, bonuses, or a combination).
- Entry-Level (0-2 Years): Typically earn between $61,000 and $78,000, often starting in support roles while building their client book and earning certifications.
- Experienced (5-10+ Years): Can expect to earn well into the six figures, with Salary.com reporting a typical range of $95,000 to $125,000 for base salary alone.
- Top Earners: Senior advisors, especially those managing portfolios for high-net-worth clients, can earn $200,000 or more annually, with total compensation including bonuses and commissions pushing this figure even higher.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your salary as a Financial Advisor is not a fixed number. It is influenced by a combination of your qualifications, choices, and environment. Understanding these factors is key to maximizing your income.
###
Level of Education and Certification
While a bachelor's degree in finance, economics, accounting, or business is the standard entry point, advanced credentials are what truly unlock higher earning potential. Professional certifications demonstrate a mastery of the field and a commitment to ethical standards, which clients and employers value highly.
- CFP® (Certified Financial Planner™): This is the gold standard in personal finance. CFP® professionals have completed rigorous coursework and passed a comprehensive exam covering everything from investment strategy to estate planning. Payscale reports that holding a CFP® can significantly boost an advisor's salary.
- CFA® (Chartered Financial Analyst): This highly respected credential focuses on investment analysis and portfolio management, often leading to roles in wealth management and asset management with very high earning potential.
- ChFC® (Chartered Financial Consultant): Similar to the CFP®, this designation also signals deep expertise in personal financial planning.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the most critical factor in a Financial Advisor's career. Trust is built over time, as is a book of business (your client list). As advisors gain experience, they become more adept at navigating market volatility, understanding complex financial products, and managing larger, more profitable client accounts.
- Associate Advisor: Early-career professionals often work under a senior advisor, learning the ropes and supporting existing clients. Compensation is more likely to be a fixed salary.
- Lead Advisor: With 5-10 years of experience, advisors manage their own client relationships and take a more strategic role, leading to higher compensation and performance-based bonuses.
- Senior/Principal Advisor: Advisors with 10+ years of experience often manage the firm's most valuable clients, mentor junior staff, and may hold an ownership stake in the practice, leading to the highest levels of income.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries for Financial Advisors are significantly higher in major metropolitan areas and financial hubs where there is a greater concentration of wealth.
For example, data from Salary.com shows that an advisor in New York, NY, or San Francisco, CA, can expect to earn 20-30% more than the national average. In contrast, salaries in smaller, lower-cost-of-living cities may be closer to or slightly below the national median. This premium is driven by both a higher cost of living and, more importantly, access to a larger pool of potential high-net-worth clients.
###
Company Type
The type of firm you work for directly impacts your compensation structure and culture.
- Large Wirehouses (e.g., Morgan Stanley, Merrill Lynch): These firms often offer a structured training program and a strong brand name. Compensation is typically a combination of a base salary plus production bonuses or commissions. The income potential is very high but can be a high-pressure environment.
- Independent Broker-Dealers: These firms offer more autonomy. Advisors are technically self-employed but affiliate with the firm for compliance and platform support. Compensation is almost entirely commission-based.
- Registered Investment Advisor (RIA) Firms: These firms have a fiduciary duty to act in their clients' best interests and are often "fee-only" or "fee-based." This model, favored by clients seeking transparency, provides more stable, predictable revenue based on the assets under management (AUM).
###
Area of Specialization
Generalist advisors are common, but specializing can lead to a more lucrative practice. By developing deep expertise in a specific niche, you can attract a dedicated client base willing to pay a premium for your knowledge.
- High-Net-Worth (HNW) Clients: Managing the complex financial lives of wealthy individuals is one of the most profitable specializations.
- Retirement Planning: With the large Baby Boomer generation entering or nearing retirement, specialists in income distribution, Social Security optimization, and long-term care are in high demand.
- Business Owners: Advising on succession planning, employee benefits, and tax strategies for entrepreneurs is another valuable niche.
Job Outlook

The future for Financial Advisors is exceptionally bright. The BLS projects that employment for personal financial advisors will grow 13% from 2022 to 2032, which is more than four times the average growth rate for all occupations.
This robust growth is fueled by two key trends: the aging of the U.S. population, which increases the need for retirement planning services, and the growing complexity of investment products, which drives more people to seek professional advice.
Conclusion

A career as a Financial Advisor offers a rare combination of high earning potential, strong job security, and meaningful work. While the path to a top salary requires dedication, the formula for success is clear: build a solid educational foundation, pursue advanced certifications like the CFP®, gain valuable experience, and strategically choose your location and area of focus. For those with a passion for finance and a genuine desire to help others, this career provides an unparalleled opportunity to build a prosperous and rewarding professional life.
