A career in the United States Senate represents one of the highest levels of public service in the nation. While driven by a commitment to constituents and country, it is also a demanding profession with a unique compensation structure. For those curious about the earnings of a public servant like Senator Joni Ernst, the salary is standardized, currently set at $174,000 per year.
This article will break down the salary for a U.S. Senator, explore the factors that define this unique career, and provide a clear picture of the professional landscape for one of the country's most prominent roles.
What Does a U.S. Senator Do?


A United States Senator, such as Joni Ernst representing Iowa, serves as a legislator in the upper chamber of the U.S. Congress. Their role is multifaceted and carries immense responsibility. Key duties include:
- Representing Constituents: Acting as the voice for the people of their state at the federal level, addressing their concerns, and providing assistance with federal agencies.
- Legislating: Drafting, debating, and voting on bills that can become national law. This involves extensive research, negotiation, and collaboration.
- Committee Work: Serving on various committees that focus on specific policy areas like Armed Services, Agriculture, Finance, or the Judiciary. This is where much of the detailed legislative and oversight work happens.
- Oversight: Conducting oversight of the executive branch to ensure that federal agencies are implementing laws and spending funds as Congress intended.
- Approving Nominations: Voting to confirm or deny presidential appointments, including cabinet secretaries, ambassadors, and federal judges.
A senator's work is divided between Washington, D.C., where legislative sessions occur, and their home state, where they connect with the citizens they represent.
Average U.S. Senator Salary
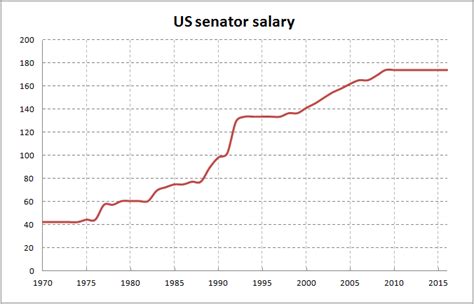

Unlike most professions, the salary for a U.S. Senator is not determined by market forces or individual negotiation. It is set by federal law.
As of 2023, the standard annual salary for a rank-and-file member of the U.S. Senate (and the House of Representatives) is $174,000. This figure has remained unchanged since 2009. Therefore, Senator Joni Ernst's official congressional salary is $174,000.
While this base salary is standard, certain leadership roles within the Senate receive higher compensation to reflect their additional responsibilities.
- Rank-and-File Senator/Representative: $174,000
- Senate & House Majority/Minority Leaders: $193,400
- President Pro Tempore of the Senate: $193,400
- Speaker of the House: $223,500
Source: Congressional Research Service, "Congressional Salaries and Allowances: In Brief" (November 9, 2023).
Key Factors That Influence a Senator's Career and Compensation


While the base salary is largely fixed, several factors shape a senator's career trajectory, influence, and overall compensation package.
###
Leadership Position
The most direct way a senator's salary can increase is by being elected to a leadership position by their party's caucus. Roles like Majority Leader, Minority Leader, or President pro tempore come with a statutorily defined pay raise, as noted in the figures above. These positions carry significant additional duties in managing the legislative agenda and acting as a principal spokesperson for their party.
###
Years of Experience (Seniority)
In Congress, years of experience translate into seniority. While seniority does not provide a direct pay raise, it is a critical factor for career advancement and influence. More senior senators often gain more powerful committee assignments, including chairmanships of key committees like Finance or Appropriations. This influence is a significant, though non-monetary, form of professional reward and power.
###
Geographic Location
The location a senator represents does not impact their salary; a senator from a high-cost-of-living state like California earns the same $174,000 as a senator from a lower-cost state like Iowa. However, location significantly impacts the *effective value* of that salary. Senators must often maintain residences in both Washington, D.C.—one of the most expensive metropolitan areas in the country—and their home state, which can place a considerable strain on their finances.
###
"Company Type" - The Public Sector
Working as a senator means being a public employee of the U.S. Government. This differs fundamentally from the private sector. Compensation is not tied to performance metrics or profit but is instead a matter of public law. The total compensation package also includes government benefits, such as access to the Federal Employees Health Benefits (FEHB) program and a retirement plan through the Federal Employees Retirement System (FERS).
###
Area of Specialization (Committee Assignments)
A senator's committee assignments function as their areas of specialization. While serving on the high-profile Judiciary Committee or the powerful Appropriations Committee does not come with a pay increase, it drastically elevates a senator's influence on national policy. Specializing in an area vital to their state's interests (e.g., the Agriculture Committee for an Iowa senator) allows them to deliver more effectively for their constituents, which is crucial for re-election and career longevity.
Job Outlook


The "job outlook" for a U.S. Senator is unlike any profession tracked by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). There are always exactly 100 U.S. Senate positions. Career stability is defined by a six-year term, but long-term prospects are entirely dependent on re-election.
The outlook for any individual senator is determined by political factors, including:
- Voter approval ratings.
- The political climate in their state and nationally.
- Fundraising ability and campaign effectiveness.
- Legislative accomplishments.
Success in this career is not measured by industry growth but by electoral success and the ability to maintain the trust of one's constituents.
Conclusion


For those considering a career in public service at the highest level, understanding the role of a U.S. Senator is key. While the query for "Joni Ernst salary" leads to a straightforward answer of $174,000 per year, the career itself is far more complex.
Here are the key takeaways:
- Standardized Pay: The salary is fixed by law and is the same for nearly all members of Congress.
- Influence as Currency: True advancement comes not from pay raises but from gaining seniority, securing powerful committee assignments, and earning leadership roles.
- A Career of Service: The role is defined by a commitment to public service rather than financial enrichment, and it comes with unique financial pressures, such as maintaining two residences.
- Success is Political: Job security is tied directly to the six-year election cycle and a senator's ability to effectively represent their constituents.
A career in the U.S. Senate is a challenging and demanding path, but for those dedicated to shaping the future of the country, it offers an unparalleled opportunity to make a lasting impact.
