For those who combine a passion for aviation with a dedication to helping others, a career as a medical helicopter pilot is one of the most demanding and rewarding paths available. These elite pilots, also known as HEMS (Helicopter Emergency Medical Services) pilots, are critical first responders, navigating challenging conditions to deliver life-saving care.
But beyond the immense personal fulfillment, what is the financial potential of this high-stakes career? The earning potential is significant, with the average medical helicopter pilot salary in the United States often exceeding $100,000 per year, and top earners commanding even higher figures. This article provides a data-driven analysis of what you can expect to earn and the key factors that will shape your salary.
What Does a Medical Helicopter Pilot Do?

A medical helicopter pilot is a highly skilled aviator responsible for the safe and rapid transportation of medical crews, patients, and vital equipment. Their missions are time-sensitive and often occur under high-pressure circumstances.
Key responsibilities include:
- Transporting Critical Patients: Flying patients from accident scenes to trauma centers or between medical facilities for specialized care.
- Navigating Complex Environments: Safely operating a helicopter in diverse conditions, including night flights, inclement weather, and landings in unprepared, remote, or urban areas.
- Crew Collaboration: Working seamlessly with a medical team of flight nurses and paramedics to ensure missions are conducted efficiently and safely.
- Safety and Compliance: Conducting rigorous pre-flight checks, adhering to all Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulations, and making ultimate command decisions regarding flight safety.
This role requires not just exceptional piloting skills but also composure, sound judgment, and a profound commitment to safety.
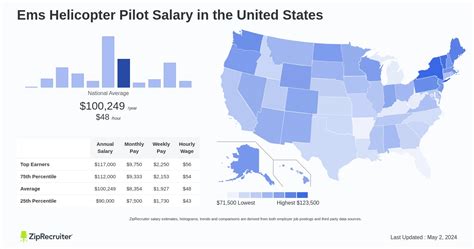
Average Medical Helicopter Pilot Salary
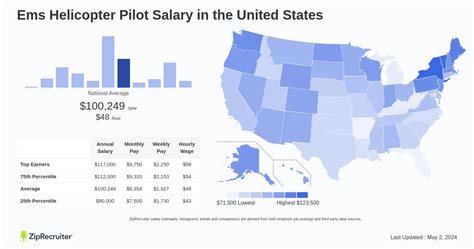
While salaries can vary significantly, the data shows a strong earning potential for qualified HEMS pilots.
According to data from Salary.com (May 2024), the average helicopter pilot salary in the United States is $107,364. The typical salary range is quite broad, generally falling between $91,073 on the lower end and $135,148 for highly experienced pilots.
Other authoritative sources corroborate this data:
- Glassdoor (June 2024) reports a similar average base pay of $104,286 per year.
- The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), in its May 2023 data for the broader category of "Airline and Commercial Pilots," lists a median annual wage of $148,900. While this category includes fixed-wing airline pilots who often have higher pay scales, it indicates that senior helicopter pilots in specialized roles are well-positioned to earn in the top tiers of the profession.
This data paints a clear picture: a six-figure salary is not an exception but the standard for a competent, experienced medical helicopter pilot.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary as a medical helicopter pilot will be influenced by a combination of factors. Understanding these variables is key to maximizing your earning potential throughout your career.
### Level of Education & Certification
Unlike many professions, a four-year college degree is not a strict requirement. Instead, the focus is on highly specialized FAA certifications. The essential certifications include a Commercial Pilot Certificate and an Instrument Rating (IR). The IR is particularly crucial in the HEMS industry, as it allows a pilot to fly in low-visibility weather conditions, significantly increasing their operational value and, consequently, their salary.
While a degree isn't mandatory, some operators may view a bachelor's degree in aviation, engineering, or a related field favorably. The pinnacle certification, the Airline Transport Pilot (ATP) certificate, represents the highest level of pilot qualification and can lead to lead pilot roles and higher pay.
### Years of Experience
Experience, measured primarily in flight hours, is arguably the single most important factor determining a pilot's salary. HEMS operators have stringent flight-hour minimums for insurance and safety reasons, typically requiring at least 2,000 to 2,500 total flight hours, with a significant portion as Pilot in Command (PIC).
Payscale.com provides a clear look at how compensation grows with experience:
- Early Career (1-4 years): Pilots who have met the minimums but are relatively new to the HEMS field can expect to earn at the lower end of the salary range, starting around $75,000 to $90,000.
- Mid-Career (5-9 years): With a solid track record and several thousand hours of HEMS-specific experience, pilots can expect to earn comfortably within the average range of $90,000 to $115,000.
- Senior/Experienced (10+ years): Pilots with over a decade of experience, specialized qualifications (like Night Vision Goggle Instructor), and leadership responsibilities (like a Base Lead Pilot or Check Airman) can command salaries at the top end of the spectrum, often exceeding $135,000.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries for medical helicopter pilots are often adjusted based on the cost of living and regional demand.
- High-Cost-of-Living Areas: Pilots based in or near major metropolitan centers (e.g., California, New York, Boston) often receive higher base pay to offset living expenses.
- Remote or Challenging Locations: Companies may offer higher salaries, location stipends, or favorable rotational schedules (e.g., two weeks on, two weeks off) to attract pilots to bases in remote regions like Alaska, the Rocky Mountains, or other rural areas where air medical transport is essential.
- Competitive Markets: Regions with multiple competing air medical services may drive salaries up as companies vie for a limited pool of highly qualified pilots.
### Company Type
The structure of the hiring organization plays a significant role in compensation and benefits. The main employers in the HEMS industry are:
- Large, Independent Operators: Companies like Air Methods, Med-Trans (GMR), and PHI Air Medical are among the largest employers of HEMS pilots. They often have standardized pay scales, comprehensive benefits, and clear career progression paths. Their sheer size allows for competitive, market-driven salaries.
- Hospital-Based Programs: Some hospitals or university health systems operate their own flight programs. These positions may offer salaries and benefits (including pensions and tuition remission) in line with other hospital employees, which can be very attractive.
- Government/Public Service: A smaller number of pilots work for state police, fire departments, or federal agencies in a search-and-rescue or medical transport capacity. These roles often come with government-level job security and robust retirement benefits.
### Area of Specialization
Within the HEMS field, further specialization can enhance your value and pay. A key differentiator is flying under Instrument Flight Rules (IFR) versus Visual Flight Rules (VFR).
- IFR-Qualified Pilots: These pilots are trained to fly solely by reference to their instruments, a critical skill for completing missions in poor weather. Because IFR capabilities increase the reliability and availability of the service, IFR-qualified pilots are in higher demand and are compensated accordingly. Many HEMS programs operate IFR-specific aircraft and bases, which typically carry a higher pay grade.
- Additional Responsibilities: Taking on roles beyond flying, such as Base Lead Pilot, Safety Officer, or Training Captain, involves administrative and leadership duties that come with a significant pay increase.
Job Outlook

The career outlook for medical helicopter pilots is stable and promising. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that employment for all commercial pilots will grow by 4% from 2022 to 2032, which is about as fast as the average for all occupations.
Several trends support a steady demand for HEMS pilots specifically:
- An aging U.S. population requires more emergency and specialized medical services.
- The consolidation of hospitals and the closure of smaller rural facilities increase the need for rapid transport to larger, more distant trauma centers.
- Advancements in aviation and medical technology continue to expand the capabilities of air ambulance services.
Conclusion

A career as a medical helicopter pilot offers a rare blend of challenge, purpose, and financial security. While the path to becoming a HEMS pilot is long and requires immense dedication to build the necessary flight hours and certifications, the rewards are substantial.
For aspiring aviators and current pilots considering this field, the key takeaways are:
- Expect a Strong Salary: A six-figure salary is the industry standard for experienced pilots.
- Experience is King: Your total flight hours, especially as Pilot in Command, are the primary driver of your career opportunities and salary.
- Specialize for Higher Pay: Pursuing an Instrument Rating (IR) and ultimately an ATP certificate will unlock the highest-paying roles.
- Location and Employer Matter: Be strategic about where you want to work and for which type of organization to maximize your compensation package.
For those with the right skills and unwavering resolve, the sky is not the limit—it's the office. And it's an office that offers one of the most fulfilling and well-compensated careers in aviation.