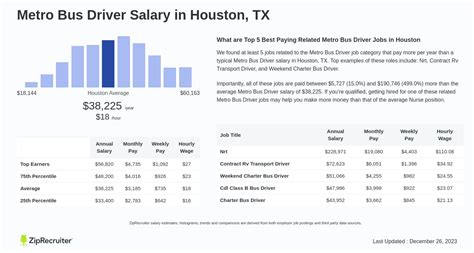
A career as a metro bus driver is more than just a job; it's a vital public service that keeps our cities moving. For individuals who enjoy driving, interacting with people, and desire a stable career with solid earning potential, becoming a bus driver can be an excellent path. But what does that earning potential look like?
On average, metro bus drivers in the United States can expect to earn a median salary of around $55,000 per year, with a typical salary range falling between $46,000 and $70,000. However, top earners in high-demand locations can make significantly more, often exceeding $80,000 annually, especially when factoring in overtime and benefits.
This guide will break down everything you need to know about a metro bus driver's salary, the factors that influence it, and the future outlook for this essential profession.
What Does a Metro Bus Driver Do?

At its core, a metro bus driver's primary responsibility is the safe transportation of passengers along a predetermined route. However, the role is far more dynamic than simply sitting behind the wheel. Daily responsibilities include:
- Ensuring Passenger Safety: This is the number one priority, involving defensive driving, managing passenger conduct, and responding to emergencies.
- Customer Service: Answering questions about routes, schedules, and fares, and providing a welcoming environment for all passengers.
- Vehicle Operation and Inspection: Performing pre-trip and post-trip inspections of the bus to check tires, brakes, lights, and safety equipment.
- Time Management: Adhering to a strict schedule to ensure routes run on time.
- Accessibility: Operating lifts and ramps to assist passengers with disabilities, ensuring compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
It's a role that requires a unique blend of technical skill, patience, and strong communication.
Average Metro Bus Driver Salary
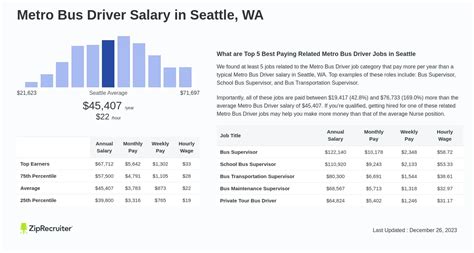
Salary data from multiple authoritative sources paints a clear picture of the earning potential for metro bus drivers.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for "Bus Drivers, Transit and Intercity" was $55,420 in May 2023. The BLS provides a detailed range for earnings:
- Lowest 10%: Earned less than $38,270
- Median 50%: Earned $55,420
- Highest 10%: Earned more than $81,350
Data from salary aggregators provides further context. Salary.com reports that the typical salary range for a City Bus Driver in the United States falls between $46,801 and $61,701 as of early 2024. Meanwhile, Glassdoor estimates the total pay (including base salary and additional pay like overtime and bonuses) for a Metro Bus Operator to be around $65,496 per year.
This variation highlights that your exact salary will depend on several key factors.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Not all bus driver positions are created equal. Your location, experience, and employer play a significant role in determining your final paycheck.
Level of Education
A four-year college degree is not required to become a metro bus driver. The standard educational requirement is a high school diploma or equivalent. However, all drivers must obtain a Commercial Driver's License (CDL) with a Passenger (P) endorsement. This involves passing a written knowledge test and a skills test. While this specialized training doesn't necessarily increase your base salary, it is the fundamental, non-negotiable requirement for entering the profession. Most large transit authorities provide paid, on-the-job training to help new hires obtain their CDL and learn specific routes and procedures.
Years of Experience
Experience is a primary driver of salary growth in this field. Most public transit agencies have a structured pay scale based on seniority.
- Entry-Level (0-3 Years): New drivers typically start at a lower "training" or probationary wage. Once they complete their initial training period, they move to the first step of the official pay scale.
- Mid-Career (4-9 Years): With several years of experience, drivers advance through the pay scale, receiving regular, incremental wage increases as outlined in union contracts or company policy.
- Senior-Level (10+ Years): Veteran drivers are at the top of the pay scale. They often get first pick of routes and shifts, which can lead to more opportunities for predictable hours and lucrative overtime pay.
According to Payscale, an entry-level bus driver earns less than a driver with significant experience, who often sees a notable increase in their hourly wage over their career.
Geographic Location
Where you work is arguably the most significant factor influencing your salary. High cost-of-living areas and cities with large, well-funded public transit systems offer the highest wages to attract and retain drivers.
The BLS identifies the top-paying states for transit and intercity bus drivers as:
1. Washington: Average annual salary of $78,890
2. California: Average annual salary of $71,330
3. New York: Average annual salary of $69,450
4. Massachusetts: Average annual salary of $68,360
5. Colorado: Average annual salary of $64,180
Metropolitan areas like San Francisco-Oakland-Hayward, CA, and Seattle-Tacoma-Bellevue, WA, are among the highest-paying in the nation. In contrast, drivers in smaller cities or rural areas will likely earn closer to the lower end of the national average.
Company Type
The type of organization you work for heavily impacts both your salary and your benefits package.
- Local Government (Public Sector): This is typically the highest-paying sector for metro bus drivers. Employees of city or state transit authorities (like MTA in New York, LA Metro, or King County Metro in Seattle) often benefit from strong union representation, which negotiates for higher wages, robust health insurance, pension plans, and generous paid time off. The BLS reports that drivers employed by local government earned a median annual wage of $64,420 in 2023.
- Private Transit Companies: Some cities contract their transit services out to private companies. While pay can be competitive, it may not always match the levels and benefits offered by direct government employment.
- Intercity and Charter Bus Services: Companies like Greyhound or charter bus lines have different pay structures, often based on mileage or tours, which can differ from a metro driver's hourly wage.
Area of Specialization
Within the field, certain specializations can lead to higher pay or provide opportunities for career advancement.
- Paratransit Services: Drivers who operate smaller buses to transport passengers with disabilities (paratransit) may require additional certifications or training. The added responsibility can sometimes come with a pay premium.
- Driver Trainer: Experienced, senior drivers can be promoted to become trainers for new hires. This role typically includes a pay differential to compensate for the added teaching and leadership responsibilities.
- Specialized Vehicles: Operating more complex vehicles, such as articulated (or "bendy") buses, may also come with slightly higher pay in some transit systems.
Job Outlook

The future for metro bus drivers is bright. The BLS projects that employment for all bus drivers will grow 6 percent from 2022 to 2032, which is faster than the average for all occupations.
This growth is driven by several factors:
- Population Growth: As urban areas expand, the demand for public transportation increases.
- Environmental Concerns: Cities are investing in public transit to reduce traffic congestion and air pollution.
- Retirements: A significant portion of the current workforce is nearing retirement age, creating a steady stream of job openings for new drivers.
This projected growth indicates strong job security for those entering or continuing in the profession.
Conclusion

A career as a metro bus driver offers a stable, respectable, and essential role in society. With a median salary around $55,420 and the potential to earn over $80,000 in high-paying regions, it provides a solid middle-class income without the need for a college degree.
Your earning potential will be most heavily influenced by your geographic location, years of experience, and employer type. By targeting positions in major metropolitan areas with strong public transit authorities, you can maximize your salary and access excellent benefits, including pensions and healthcare. With a positive job outlook and a clear path for salary progression, becoming a metro bus driver is a rewarding and financially viable career choice for the right individual.