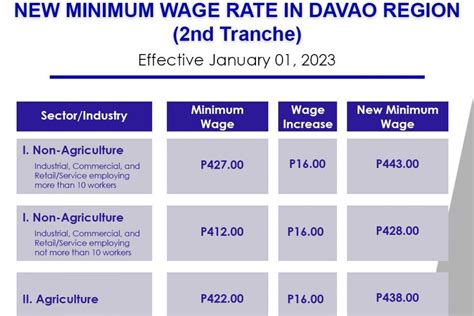
For anyone starting a career or running a business in the Philippines, one of the most critical pieces of information is the minimum wage. It's the legal floor for employee compensation and a key indicator of the economic landscape. While the daily minimum wage can range from approximately PHP 361 to PHP 610 depending on various factors, understanding the system behind these numbers is crucial for career planning and financial goal-setting.
This guide will break down the complexities of the Philippine minimum wage, explain how it's determined, and discuss what it means for your professional journey.
What is the Minimum Wage in the Philippines?

Unlike a single federal minimum wage in countries like the United States, the minimum wage in the Philippines is not one specific number. It is a regionally determined daily rate that represents the lowest legal amount an employer can pay a worker for a standard eight-hour workday.
This system is designed to account for the vast economic differences across the country's diverse regions. The government body responsible for this is the National Wages and Productivity Commission (NWPC), which operates through Regional Tripartite Wages and Productivity Boards (RTWPBs) in each region. These boards are composed of representatives from the government, the labor sector, and the employer sector, who collectively assess and decide on appropriate wage levels.
The primary goal of the minimum wage is to provide a basic safety net, ensuring that workers can afford a minimum standard of living based on the cost of necessities in their specific location.
Average Minimum Wage Rates in the Philippines


As of early 2024, the minimum wage rates are set by "Wage Orders" issued by the regional boards. The highest minimum wage is in the National Capital Region (NCR), which serves as the country's economic hub.
- National Capital Region (Metro Manila): The daily minimum wage is PHP 610 for the non-agriculture sector and PHP 573 for the agriculture sector.
- Other Regions: Rates vary significantly. For example, in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM), the non-agriculture minimum wage is PHP 361, while in CALABARZON (Region IV-A), it ranges up to PHP 520.
According to the National Wages and Productivity Commission (NWPC), these rates are the absolute floor. It is illegal for an employer to pay covered workers less than the mandated minimum wage for their region and sector.
It's important to distinguish the legal minimum wage from the average market salary. Salary aggregators show what people *actually* earn, which is often much higher. For instance, Payscale reports the average base salary in the Philippines to be approximately PHP 326,000 per year, which translates to a daily rate far exceeding the minimum wage, reflecting the earnings of a wide range of skilled professionals.
Key Factors That Influence Salary


While the NWPC sets the legal minimum, several factors determine both the official minimum wage rate and your potential to earn significantly more.
###
Geographic Location
This is the single most important factor in determining the legal minimum wage. The RTWPBs set rates based on the local cost of living, economic development, and poverty threshold. High-cost, highly urbanized areas like Metro Manila have the highest rates, while more rural, agricultural regions have lower rates to reflect their different economic realities. For professionals, this also means that jobs in major cities typically offer higher salaries to compensate for higher living expenses.
###
Company Type and Sector
The official Wage Orders differentiate between sectors. The two primary categories are:
- Non-Agriculture: Includes manufacturing, retail, services, and most office-based work. This sector consistently has a higher minimum wage.
- Agriculture: Covers plantation and non-plantation farm work. These rates are typically lower.
Furthermore, some wage orders may provide different rates based on the size of the establishment (e.g., companies with 10 or more employees vs. smaller enterprises). For professionals, company type (e.g., multinational corporation vs. local startup) and industry (e.g., Tech vs. Retail) will have a massive impact on salary, far beyond the minimum wage floor.
###
Level of Education
Your level of education does not change the legal minimum wage you are entitled to. However, it is a primary driver of your ability to earn a salary *above* the minimum. A bachelor's degree is often a minimum requirement for entry-level professional roles, which command salaries well above the minimum wage. Advanced degrees (Master's, Ph.D.) or specialized certifications can lead to senior and executive positions with significantly higher compensation packages.
###
Years of Experience
Similar to education, experience doesn't alter the legal minimum wage but is crucial for salary growth. An entry-level employee might start at a salary close to or slightly above the minimum wage. However, as noted by data from salary platforms like Glassdoor, a professional with 5-10 years of experience in a skilled field like marketing or IT can expect their salary to double or triple from their starting point. Experience demonstrates proven value, leadership potential, and specialized skills, all of which employers are willing to pay a premium for.
###
Area of Specialization
Your chosen field is a powerful determinant of your earning potential. High-demand specializations command top-tier salaries. For example, a role in a BPO (Business Process Outsourcing) might have a starting salary of PHP 20,000-25,000/month, well above the minimum wage. In contrast, a specialized professional like a Software Engineer or a Data Scientist in the Philippines can command a starting salary upwards of PHP 40,000-60,000/month or more, depending on skills. The legal minimum wage is a baseline, but specialization creates your market value.
Job Outlook


It is important to note that the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) does not track job outlook data for the Philippines. However, economic indicators from institutions like the World Bank and the Asian Development Bank project continued economic growth for the Philippines. This growth is a positive sign for the job market, particularly in sectors like:
- Information Technology and Business Process Management (IT-BPM)
- Healthcare and Wellness
- Construction and Real Estate
- Tourism and Hospitality
Ongoing discussions about inflation and the cost of living mean that petitions for minimum wage increases are a regular occurrence. Professionals can expect the legal wage floor to continue rising over time. More importantly, the demand for skilled, educated, and experienced workers in growth sectors ensures that the outlook for earning a competitive, professional-level salary remains strong.
Conclusion


Understanding the minimum wage in the Philippines is the first step in navigating its job market. Here are the key takeaways:
- It's a Regional Floor, Not a National Standard: The minimum wage you're entitled to depends entirely on your work location and industry sector.
- It’s a Starting Point: The minimum wage is a legal safety net, not a target for a long-term career.
- Growth Comes from Value: Your true earning potential is unlocked by factors you control: education, continuous learning, gaining valuable experience, and choosing a high-demand specialization.
For anyone planning their career, the minimum wage is a crucial piece of context. Use it as a baseline, but focus your energy on building the skills and experience that will allow you to command a salary that reflects your professional value, far exceeding the legal minimum.