In the ever-expanding world of technology, Quality Assurance (QA) professionals are the unsung heroes. They are the gatekeepers of quality, ensuring that the software, apps, and systems we use daily are reliable, functional, and free of frustrating bugs. But beyond the satisfaction of shipping a perfect product, what is the financial outlook for a career in QA?
The answer is highly encouraging. A career in Quality Assurance offers a stable and rewarding pathway with significant earning potential. Salaries can range from a solid starting point of around $65,000 per year to well over $150,000 for experienced specialists and managers.
This article provides a data-driven breakdown of what you can expect to earn as a QA professional and the key factors that will shape your salary throughout your career.
What Does a Quality Assurance Professional Do?

Before diving into the numbers, it's essential to understand the role. A Quality Assurance professional is responsible for systematically evaluating products and services to ensure they meet specified requirements and quality standards. They are an integral part of the development lifecycle, working closely with developers, product managers, and other stakeholders.
Key responsibilities typically include:
- Developing and executing test plans: Creating detailed strategies to test every facet of a product.
- Manual and automated testing: Running tests by hand to mimic user behavior and writing scripts to automate repetitive tests.
- Bug tracking and reporting: Identifying, documenting, and prioritizing defects for the development team to fix.
- Regression testing: Ensuring that new code changes haven't broken existing functionality.
- Performance and load testing: Verifying that an application can handle expected user traffic and stress.
Average Quality Assurance Salary
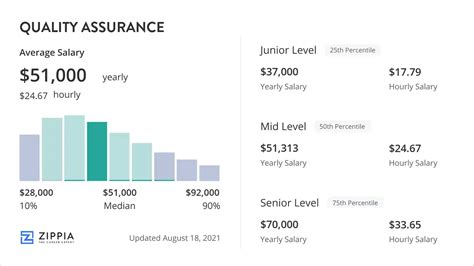
While salary can vary widely, we can establish a strong baseline by looking at data from leading industry sources. According to data aggregated from Payscale, Salary.com, and Glassdoor, the average salary for a Quality Assurance Analyst or Engineer in the United States falls between $78,000 and $90,000 per year.
However, this average figure is just the midpoint. The real story lies in the salary progression based on experience:
- Entry-Level QA Analyst (0-2 years): Typically earns between $60,000 and $75,000. These roles often focus on manual testing and learning the company's products and processes.
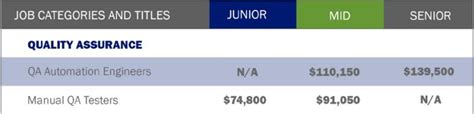
- Mid-Level QA Engineer (3-7 years): Can expect to earn between $75,000 and $110,000. Professionals at this stage often develop automation skills and take on more complex testing projects.
- Senior QA Engineer / QA Lead (8+ years): Salaries frequently range from $110,000 to $140,000+. These roles involve designing test architecture, mentoring junior analysts, and leading strategy for major projects.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your base salary is not set in stone. Several key factors can significantly increase your earning potential. Understanding them is the first step toward maximizing your income.
###
Level of Education and Certification
While a four-year degree in Computer Science, Information Technology, or a related field is the most common entry point, it's not always a strict requirement. However, a relevant bachelor's degree provides a strong foundation and is often preferred by employers.
More impactful than an advanced degree are professional certifications. They validate your skills and demonstrate a commitment to the profession. Key certifications that can boost your resume and salary include:
- ISTQB Certified Tester (International Software Testing Qualifications Board): A globally recognized standard with different levels (Foundation, Advanced, Expert).
- Certified Software Test Engineer (CSTE): Offered by the Quality Assurance Institute (QAI), this certification focuses on QA principles and practices.
- Certified Associate in Software Testing (CAST): Also from QAI, this is an excellent entry-level certification.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the most significant driver of salary in QA. As you progress in your career, you move from executing test cases to designing complex test strategies and leading teams, which commands a higher salary.
- Entry-Level: Focus on execution and learning.
- Mid-Level: Begin specializing (e.g., in automation or performance) and take ownership of testing for specific features or products.
- Senior/Lead: Define testing frameworks, implement QA best practices across the organization, and mentor others.
- QA Manager/Director: Move into a leadership role, managing budgets, hiring, and setting the overall quality vision for the company. Managerial roles can easily push salaries above $150,000.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Major tech hubs and cities with a high cost of living consistently offer higher salaries to attract and retain talent. According to data from Salary.com, a QA professional in San Jose, CA, or New York, NY, can expect to earn 20-35% more than the national average.
High-Paying Metropolitan Areas:
- San Francisco Bay Area, CA
- Seattle, WA
- New York, NY
- Boston, MA
- Washington, D.C.
The rise of remote work has introduced more flexibility, but many companies still adjust salaries based on the employee's location, so this factor remains critical.
###
Company Type
The size and type of company you work for will also influence your compensation package.
- Large Tech Companies (e.g., Google, Apple, Microsoft): These firms typically offer the highest base salaries, generous bonuses, and extensive benefits packages.
- Startups: May offer a lower base salary but compensate with potentially lucrative stock options. The environment is often fast-paced with opportunities for rapid growth.
- Established Companies in Other Industries (e.g., Finance, Healthcare, Retail): These companies have a growing need for robust QA and offer competitive, stable salaries and strong benefits, though they may not always match the peaks of Big Tech.
###
Area of Specialization
Generalist QA roles are valuable, but specialization is the key to unlocking the highest salary brackets. The most significant pay differentiator is manual vs. automated testing.
- Automation Engineering: Professionals skilled in writing test scripts using tools like Selenium, Cypress, or Playwright are in high demand and command a significant salary premium. A "Software Development Engineer in Test" (SDET) often earns a salary comparable to a software developer.
- Performance Testing: Specialists who can use tools like JMeter or LoadRunner to test system stability and scalability are highly sought after.
- Security Testing: As cybersecurity threats grow, QA professionals with skills in identifying security vulnerabilities (sometimes called "QAsec") are becoming invaluable and are compensated accordingly.
Job Outlook

The future for Quality Assurance professionals is bright. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) groups QA analysts with software developers in its occupational outlook. For the category of "Software Developers, Quality Assurance Analysts, and Testers," the BLS projects a job growth of 25% from 2022 to 2032, which is vastly faster than the average for all occupations.
This exceptional growth is driven by the increasing reliance on software in every aspect of business and life, from mobile banking apps to complex enterprise systems. As long as new software is being created, there will be a critical need for skilled professionals to ensure it works flawlessly.
Conclusion

A career in Quality Assurance is a stable, in-demand, and financially rewarding choice. While a mid-career professional can expect an average salary in the $78,000 to $90,000 range, this is only a starting point.
To maximize your earning potential, focus on continuous learning and strategic specialization. By building expertise in high-demand areas like test automation, gaining relevant certifications, and targeting roles in high-paying locations or industries, you can build a career path that is not only intellectually challenging but also leads to a six-figure income. For those with a meticulous eye for detail and a passion for technology, the future in quality assurance is a bright one.