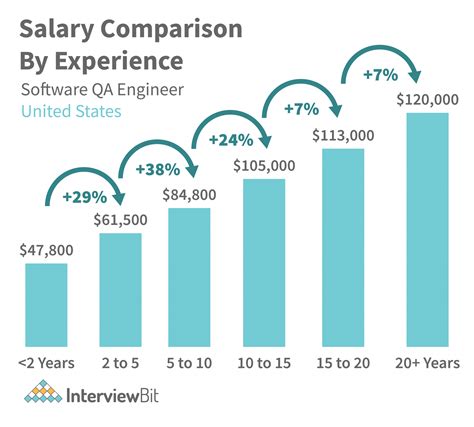
In today's digital-first world, a flawless user experience isn't a luxury—it's a necessity. This has catapulted Quality Assurance (QA) professionals from a background role to a critical position on the front lines of software development. But beyond its importance, is a career in QA financially rewarding?
The answer is a resounding yes. With roles ranging from manual testing to sophisticated automation engineering, a career in Quality Assurance offers a robust and scalable salary path. Depending on factors like specialization, location, and experience, a QA professional's salary can range from an entry-level starting point of around $65,000 to well over $150,000 for senior and management positions.
This guide will break down the Quality Assurance salary landscape, explore the key factors that dictate your earning potential, and provide a look at the future of this dynamic profession.
What Does a Quality Assurance Professional Do?

At its core, a Quality Assurance professional is the guardian of the user experience. They are meticulous, detail-oriented experts responsible for ensuring that software, applications, and digital products meet the highest standards of quality before they reach the end-user. Their goal is to identify bugs, defects, and inconsistencies that could negatively impact functionality, performance, or security.
Key responsibilities often include:
- Developing and executing test plans and test cases.
- Performing manual and automated tests to check for functionality and usability.
- Identifying, documenting, and tracking bugs in systems like Jira or Azure DevOps.
- Collaborating with developers and product managers to resolve issues.
- Conducting regression testing to ensure new changes haven't broken existing features.
Think of them not just as "testers," but as advocates for quality throughout the entire development lifecycle.
Average Quality Assurance Salary
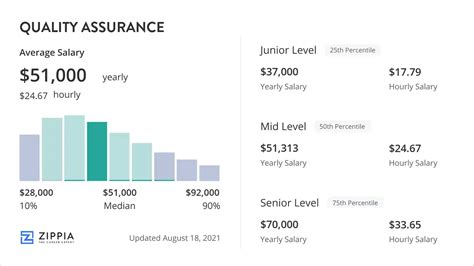
While salaries can vary widely, we can establish a strong baseline by looking at data from leading salary aggregators.
According to Payscale.com, the average salary for a Quality Assurance Engineer in the United States is approximately $82,000 per year. Similarly, Salary.com reports the median salary for a mid-level Software Quality Assurance Analyst at around $88,500.
However, the "average" only tells part of the story. A more realistic picture is a salary range that reflects different career stages:
- Entry-Level (QA Analyst/Tester): Typically ranges from $65,000 to $80,000.
- Mid-Level (QA Engineer): Typically ranges from $80,000 to $110,000.
- Senior/Lead (Senior QA Engineer/QA Lead): Typically ranges from $110,000 to $140,000+.
- Management (QA Manager/Director of QA): These roles often command salaries of $140,000 to $180,000 and higher.
These figures represent a national average and are heavily influenced by the factors we'll explore next.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary within these ranges is not arbitrary. It is determined by a combination of your skills, background, and where you choose to work. Understanding these factors is key to maximizing your earning potential.
###
Level of Education
While a formal degree isn't always a strict requirement, a Bachelor's degree in Computer Science, Information Technology, or a related field is the most common educational background and often sets the salary floor. However, two other elements are arguably more impactful:
- Certifications: Industry-recognized certifications can significantly boost your credibility and salary. Certifications like the ISTQB (International Software Testing Qualifications Board) are globally recognized and demonstrate a formal understanding of testing principles. More advanced certifications in test automation (e.g., vendor-specific certifications for tools like Selenium or Tricentis) or security testing can lead to higher pay.
- Advanced Degrees: A Master's degree may provide an edge for leadership or highly specialized roles (like research-focused testing in AI/ML), but for most QA positions, demonstrable experience and specialized skills will have a greater impact on salary than an advanced degree.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the single most significant driver of salary growth in QA. As you progress in your career, your value to an organization increases exponentially.
- Entry-Level (0-2 Years): At this stage, you are learning the fundamentals of testing methodologies and company processes. Your focus is on executing test cases and accurately reporting bugs.
- Mid-Level (3-7 Years): You are now a fully independent contributor. You may be leading small projects, designing test strategies, and beginning to mentor junior analysts. This is often where professionals specialize in automation, which brings a significant pay increase.
- Senior/Lead (8+ Years): Senior professionals are expected to have deep technical expertise. They often design the entire testing framework for a product, lead automation initiatives, and mentor the entire QA team. Their salary reflects their high-level strategic impact.
###
Geographic Location
Where you live and work plays a massive role in your compensation due to variations in cost of living and demand for tech talent. Major tech hubs consistently offer the highest salaries.
Based on data from aggregators like Glassdoor and Salary.com, top-paying metropolitan areas include:
- San Francisco Bay Area, CA
- Seattle, WA
- New York, NY
- Boston, MA
- Washington, D.C.
Salaries in these regions can be 20-40% higher than the national average. Conversely, salaries in lower cost-of-living areas in the Midwest and South will typically be closer to or slightly below the national average. The rise of remote work has introduced more flexibility, though some companies adjust salaries based on an employee's location rather than the company's headquarters.
###
Company Type
The size and type of company you work for directly influence your compensation package.
- Large Tech Companies (e.g., Google, Apple, Microsoft): These companies offer the highest base salaries, significant bonuses, and valuable stock options. The work is often at a massive scale, and the hiring bar is extremely high.
- Startups: A startup may offer a lower base salary but compensate with potentially lucrative stock options. The environment is fast-paced, and you may have a broader range of responsibilities.
- Established Non-Tech Companies (e.g., Banking, Healthcare, Retail): These companies offer competitive and stable salaries but may not reach the peaks of the top tech firms. Job security is often a significant benefit.
###
Area of Specialization
Moving from a generalist to a specialist is the fastest way to accelerate your salary. The demand for certain niche skills is incredibly high.
- Test Automation Engineer: This is the most common and impactful specialization. Professionals who can write code (using Python, Java, or JavaScript) and build/maintain automated testing frameworks using tools like Selenium, Cypress, or Playwright are in constant demand and command a salary premium of 15-25% over their manual testing counterparts.
- Performance and Load Testing Engineer: These specialists focus on a system's speed, stability, and scalability under load. Expertise in tools like JMeter and LoadRunner is highly valued.
- Security Tester (Penetration Tester): A highly specialized and lucrative field, security testers proactively look for vulnerabilities in a system. This role often overlaps with cybersecurity and commands top-tier salaries.
Job Outlook

The future for Quality Assurance professionals is exceptionally bright. As software continues to integrate into every facet of our lives, the need for quality assurance will only grow.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that employment for "Software Developers, Quality Assurance Analysts, and Testers" is projected to grow 25 percent from 2022 to 2032. This is categorized as "much faster than the average for all occupations."
This incredible growth is driven by:
- The increasing complexity of software and applications.
- The critical importance of cybersecurity.
- The widespread adoption of Agile and DevOps methodologies, which integrate QA into every step of the development cycle.
Conclusion

A career in Quality Assurance is more than just a job; it's a stable, in-demand, and financially rewarding profession with a clear path for growth. While a national average salary provides a helpful starting point, your ultimate earning potential is in your hands.
The key takeaways for maximizing your QA salary are clear:
1. Gain Experience: Stick with it, as each year of experience brings significant financial rewards.
2. Specialize, Specialize, Specialize: Master test automation. It is the single most valuable skill you can develop to increase your market value.
3. Keep Learning: Pursue relevant certifications and stay current with new tools and methodologies.
For those with a keen eye for detail and a passion for technology, the path to a lucrative and impactful career in Quality Assurance is not just possible—it's waiting for you.