For anyone starting their career journey or entering the workforce in the Commonwealth of Virginia, understanding the state's minimum wage is a critical first step. While it represents the legal floor for earnings, it's also the launchpad from which countless successful careers begin. As of 2024, Virginia's minimum wage stands at $12.00 per hour, a figure that positions it significantly above the federal minimum.
This article provides a data-driven look at the "salario mínimo en Virginia," exploring not just the current rate but also the key factors that empower workers to earn substantially more.
Understanding the Minimum Wage in Virginia: Who It Affects

The minimum wage is a foundational pay rate that impacts a wide range of professions, particularly those that serve as entry points into the workforce. It is not a career in itself, but rather the starting salary for many essential jobs that form the backbone of Virginia's economy.
Roles that typically start at or near the minimum wage include:
- Retail: Cashiers, stockers, and sales associates.
- Food Service: Fast-food workers, servers, hosts, and dishwashers.
- Hospitality: Hotel front desk clerks, cleaning staff, and event setup crews.
- General Labor: Entry-level construction helpers, warehouse assistants, and cleaners.
- Customer Service: Entry-level call center representatives.
These positions are crucial for developing foundational "soft skills" like communication, teamwork, time management, and problem-solving—all of which are invaluable for future career advancement.
Current and Future Minimum Wage in Virginia

Virginia's minimum wage has seen significant changes in recent years. After being tied to the federal minimum of $7.25 per hour for over a decade, the state legislature passed a law to incrementally increase it.
As of today, the minimum wage in Virginia is $12.00 per hour. This rate went into effect on January 1, 2023.
According to the Virginia Department of Labor and Industry, the planned schedule for future increases is currently paused. Proposed increases to $13.50 in 2025 and $15.00 in 2026 would require another vote and re-enactment by the Virginia General Assembly.
Tipped Employees: For employees who regularly receive tips, such as restaurant servers, the minimum wage calculation is different. Employers can pay a lower cash wage, but they must ensure that the combination of the cash wage and tips equals at least the standard minimum wage of $12.00 per hour.
Key Factors That Influence Earnings Beyond the Minimum Wage
While $12.00 per hour is the legal starting point, it is by no means a ceiling. For ambitious professionals, it's a baseline to be surpassed through strategic career development. Several key factors directly influence your ability to increase your earnings in Virginia.
### Level of Education
Education is one of the most reliable pathways to higher income. While many minimum wage jobs require only a high school diploma or equivalent, pursuing further education opens doors to higher-paying professions.
- Associate's Degree: Can lead to technical roles in healthcare (e.g., medical assistant) or skilled trades with starting salaries well above minimum wage.
- Bachelor's Degree: Unlocks professional careers in business, technology, education, and engineering, where average starting salaries in Virginia often range from $50,000 to $70,000 annually, according to data from sources like Salary.com.
### Years of Experience
Experience, even in an entry-level role, is a powerful salary driver. As you gain expertise and prove your reliability, you become more valuable to an employer.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): Typically earn at or slightly above the minimum wage.
- Mid-Career (2-5 years): An experienced retail associate may be promoted to a shift lead or assistant manager, earning a significantly higher hourly rate or salary. A Payscale report shows that an experienced Retail Store Assistant Manager in Virginia can earn an average of over $18 per hour.
- Senior-Level (5+ years): With substantial experience, one can move into store management or regional oversight roles with much higher compensation packages.
### Geographic Location
Where you work in Virginia matters significantly. The cost of living and demand for labor vary dramatically across the state, which directly impacts wages, even for entry-level jobs.
- Northern Virginia (e.g., Arlington, Alexandria, Fairfax County): This region has a much higher cost of living and a competitive job market due to its proximity to Washington, D.C. Many employers offer starting wages well above the state minimum to attract talent. The MIT Living Wage Calculator estimates that a single adult in Arlington County needs to earn over $28 per hour to cover basic living expenses.
- Southwest Virginia (e.g., Bristol, Wise County): In areas with a lower cost of living, wages tend to be closer to the state minimum. However, the purchasing power of that wage is greater than in more expensive regions.
### Industry and Company Size
The industry you work in and the size of your employer can have a major impact on your starting pay and benefits.
- Industry: An entry-level position in a high-growth sector like logistics (e.g., a warehouse associate for Amazon) or healthcare administration will often pay more than a similar entry-level role in fast food.
- Company Size: Large corporations often have more structured pay scales and may offer higher starting wages and more comprehensive benefits (like health insurance and retirement plans) than small, local businesses.
### Developing Skills and Specializations
This is the most direct way to increase your earning power. Moving beyond a generalist role by acquiring specific, in-demand skills can immediately increase your value.
- Certifications: Obtaining a certification as a forklift operator, a commercial driver (CDL), a pharmacy technician, or in basic IT support (like CompTIA A+) can instantly qualify you for jobs paying $18-$25+ per hour.
- Technical Skills: Learning skills related to software (e.g., Microsoft Excel, Salesforce) or basic coding can open doors to administrative and tech-adjacent roles.
- Bilingualism: In customer-facing roles, fluency in a second language like Spanish is a highly sought-after skill that often comes with a pay premium.
Virginia's Economic Outlook and Its Impact on Wages
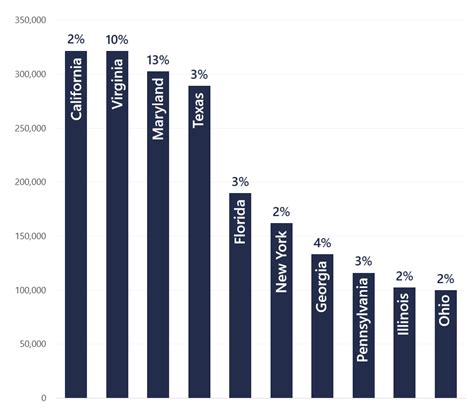
The job outlook in Virginia is strong, providing a fertile ground for career growth. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), Virginia is projected to add over 330,000 new jobs between 2020 and 2030.
The sectors with the strongest projected growth include:
- Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services: Fueling demand in the tech-heavy Northern Virginia corridor.
- Health Care and Social Assistance: Driven by an aging population and advancements in medicine.
- Transportation and Warehousing: Spurred by the growth of e-commerce and Virginia's strategic location with major ports and logistics hubs.
This robust economic growth creates competition for labor, which puts upward pressure on wages at all levels and creates numerous opportunities for workers to move from minimum wage roles into more stable, higher-paying careers.
Conclusion: Your Career Launchpad in Virginia

Understanding the "salario mínimo en Virginia" is essential for anyone entering the job market. At $12.00 per hour, it provides a starting point that is well above the national average.
However, the key takeaway for any aspiring professional is to view this wage not as a destination, but as a starting line. By focusing on the critical factors for advancement—gaining experience, pursuing education, targeting high-growth industries and locations, and developing specialized skills—you can rapidly move beyond the minimum wage. Virginia's diverse and growing economy offers clear and achievable pathways for anyone willing to invest in their own professional development.
