Industrial engineering is a dynamic and essential field, serving as the critical link between business objectives and technical execution. For those with a mind for optimizing systems and eliminating waste, it offers a financially rewarding and intellectually stimulating career path. But what exactly can you expect to earn?
The answer is promising. Industrial engineers are in high demand across nearly every sector, and their compensation reflects this value. While the national average salary hovers near six figures, your personal earning potential can be significantly higher based on a few key factors.
This guide will break down the salary for an industrial engineer, exploring the data from authoritative sources and detailing the variables that will shape your career and your paycheck.
What Does an Industrial Engineer Do?

Before we dive into the numbers, it's important to understand the role. Industrial engineers are the efficiency experts of the modern world. Their primary goal is to design, improve, and manage integrated systems of people, money, knowledge, information, and equipment.
In short, they figure out how to do things better. This can involve:
- Optimizing a factory assembly line to reduce production time.
- Redesigning a hospital's patient intake process to minimize wait times.
- Streamlining a company's supply chain to cut transportation costs.
- Developing quality control standards to prevent defects in a product.
- Using data analytics to forecast demand and manage inventory.
Because these skills are universally valuable, industrial engineers are not limited to a single industry; they work in manufacturing, healthcare, tech, finance, logistics, and even entertainment.
Average Industrial Engineer Salary
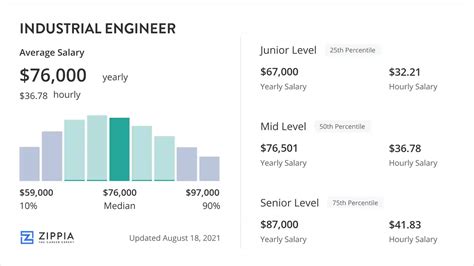
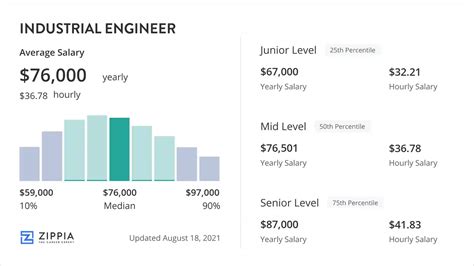
So, what does this critical work pay? The compensation for industrial engineers is strong, even at the start of their careers, with significant growth potential over time.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for industrial engineers was $96,350 as of May 2022. This means half of all industrial engineers earned more than this amount, and half earned less.
However, a single number doesn't tell the whole story. Salary aggregators provide a more detailed look at the typical range:
- Salary.com reports that the core salary range for an industrial engineer in the U.S. typically falls between $88,590 and $109,790 (as of early 2024).
- Payscale highlights the progression with experience, showing an average entry-level salary around $71,000, with experienced engineers earning well over $120,000.
- Glassdoor lists a total pay average of around $95,000 per year, combining base salary and additional compensation like bonuses.
This data paints a clear picture: while a starting salary is very competitive, choices you make throughout your career in education, location, and specialization will have a profound impact on your ability to reach the upper end of this range.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your salary isn't set in stone. It’s a dynamic figure influenced by your unique professional profile. Here are the most significant factors that determine how much you can earn as an industrial engineer.
### Level of Education
A bachelor's degree in industrial engineering or a related field is the standard entry requirement. However, advanced education can unlock higher-level roles and significantly boost your earning potential.
- Master of Science (M.S.) in Industrial Engineering: An M.S. deepens your technical expertise in areas like operations research, data analytics, or supply chain management. This specialization often leads to higher starting salaries and qualifies you for senior technical or research-focused roles.
- Master of Business Administration (MBA): Combining an engineering background with an MBA is a powerful combination. It positions you for leadership and management tracks, where salaries are substantially higher. Many senior managers and executives in manufacturing and tech firms started as engineers.
- Professional Certifications: Certifications demonstrate mastery of a specific skill set. Key certifications for an industrial engineer include the Six Sigma Black Belt (for quality management), the Project Management Professional (PMP), and the Certified Professional in Engineering Management (CPEM). These can make you a more competitive candidate and justify a higher salary.
### Years of Experience
Experience is one of the most direct drivers of salary growth. As you move from theory to application and demonstrate a track record of successful projects, your value to an employer increases.
- Entry-Level (0-4 Years): In the initial years, you’ll focus on applying your academic knowledge to real-world problems. Expect a salary in the $70,000 to $85,000 range as you learn the ropes.
- Mid-Career (5-10 Years): With solid experience, you begin to lead projects, mentor junior engineers, and tackle more complex challenges. Your salary will typically move into the $90,000 to $115,000 range.
- Senior/Experienced (10+ Years): Senior engineers often serve as subject-matter experts, project leaders, or department managers. At this stage, salaries frequently exceed $125,000, with principal engineers and senior managers earning significantly more.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries for industrial engineers vary considerably based on the state and metropolitan area, driven by local industry demand and cost of living.
According to BLS data, the top-paying states for industrial engineers include:
- California: Average annual salary of $122,810
- Washington: Average annual salary of $118,520
- Alaska: Average annual salary of $117,140
- Texas: Average annual salary of $111,810
- New Mexico: Average annual salary of $111,350
Conversely, states in the Southeast and parts of the Midwest may offer salaries closer to or slightly below the national median. However, it's crucial to balance salary data with the local cost of living; a lower salary in a more affordable city might offer greater purchasing power.
### Company Type and Industry
The universal applicability of industrial engineering is a strength, but not all industries pay equally. Your earning potential can be significantly higher in high-margin or technically complex sectors.
The BLS identifies the top-paying industries for industrial engineers as:
- Computer and Electronic Product Manufacturing: These companies rely on hyper-efficient supply chains and manufacturing processes.
- Aerospace Product and Parts Manufacturing: A high-tech industry with complex quality and production standards.
- Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services: This includes consulting firms, where engineers are hired to solve problems for a diverse range of clients.
- Oil and Gas Extraction: A capital-intensive industry that heavily rewards efficiency experts.
Working for a large, multinational corporation will generally offer a higher salary and more robust benefits package than a smaller, local firm or a government agency.
### Area of Specialization
Within the broad field of industrial engineering, certain specializations are in particularly high demand, commanding premium salaries.
- Supply Chain Management & Logistics: In the age of e-commerce, experts who can optimize the flow of goods from a warehouse to a customer's doorstep are invaluable.
- Data Analytics & Operations Research: Companies are drowning in data. Engineers who can use this data to model systems, predict outcomes, and drive decisions are highly sought after.
- Healthcare Systems Engineering: As healthcare costs rise, hospitals and healthcare networks are hiring industrial engineers to improve patient flow, manage resources, and increase operational efficiency.
- Quality & Reliability Engineering: In manufacturing, ensuring a product is reliable and free of defects is paramount. Specialists in this area, particularly those with Six Sigma expertise, are essential.
Job Outlook

The future for industrial engineers is exceptionally bright. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that employment for this profession will grow by 12% from 2022 to 2032, which is much faster than the average for all occupations.
This robust growth is fueled by the relentless pursuit of efficiency across all industries. From building sustainable energy grids to designing automated warehouses and streamlining software development, the need to reduce costs, improve quality, and increase productivity is constant. This ensures a stable and growing demand for industrial engineering talent for the foreseeable future.
Conclusion

A career as an industrial engineer offers a powerful combination of financial reward, professional stability, and intellectual challenge. While the national median salary provides a strong baseline of nearly $97,000, your earning potential is truly in your hands.
For aspiring students and professionals, the path to a top-tier salary involves a strategic approach:
- Pursue advanced education or valuable certifications to deepen your expertise.
- Gain experience and seek out roles with increasing responsibility.
- Be mindful of geographic and industry-specific salary trends.
- Develop a specialization in a high-demand area like data analytics or supply chain management.
By focusing on these factors, you can build a fulfilling and lucrative career, shaping the future of industries by making them smarter, faster, and more efficient.