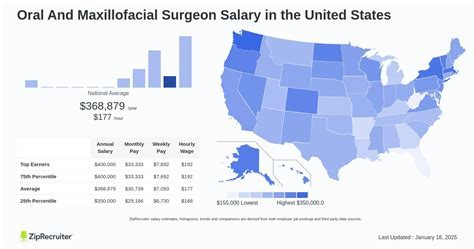
Pursuing a career in healthcare often involves a delicate balance between passion, dedication, and financial viability. For those drawn to the highly specialized field of oral and maxillofacial surgery (OMS), the rewards are substantial on all fronts. This career path is not only intellectually stimulating and impactful but also stands as one of the most financially lucrative professions in the medical and dental worlds, with top earners commanding salaries well over $400,000 annually.
This guide provides a comprehensive analysis of an oral and maxillofacial surgeon's salary, explores the factors that influence earning potential, and examines the career outlook for this demanding yet rewarding profession.
What Does an Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon Do?
An Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon is a dental specialist who has completed extensive surgical training, bridging the gap between dentistry and medicine. Their expertise lies in diagnosing and performing surgical procedures on the hard and soft tissues of the face, mouth, and jaw (the maxillofacial region).
Their responsibilities are diverse and highly complex, including:
- Dentoalveolar Surgery: Complex tooth extractions, including impacted wisdom teeth.
- Dental Implant Surgery: Placing implants to support prosthetic teeth.
- Corrective Jaw Surgery (Orthognathic Surgery): Realigning jaws to correct functional and aesthetic issues.
- Facial Trauma Repair: Treating fractures of the jaw, cheekbones, and eye sockets.
- Pathology & Reconstructive Surgery: Diagnosing and treating cysts, tumors, and cancers of the head and neck, followed by reconstruction.
- Cleft Lip and Palate Surgery: Performing corrective procedures for congenital deformities.
- Facial Cosmetic Surgery: Offering procedures like rhinoplasty, facelifts, and more.
Average Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon Salary
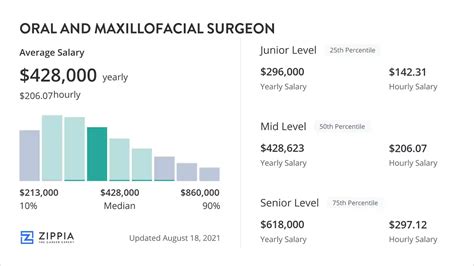
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery is consistently ranked among the highest-paying professions. Due to the extensive training required and the complexity of the procedures performed, compensation is exceptionally strong.
While figures vary slightly between reporting agencies based on their methodologies, they all point to a significant income.
- Salary.com: As of early 2024, the median annual salary for an Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon in the United States is approximately $309,799. The typical salary range falls between $290,123 and $330,958, with the top 10% of earners exceeding $351,000.
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS): The BLS provides a median pay figure for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons that is listed as greater than $239,200 per year as of May 2022. The ">" symbol indicates that the median salary is so high it exceeds the upper limit of the BLS's standard reporting wage interval, confirming its position as a top-earning field.
- Payscale: This platform reports an average base salary of around $290,000 per year, with total pay packages often increasing substantially with bonuses and profit-sharing, especially for practice owners.
It's clear that a starting salary comfortably in the low-to-mid $200,000s is standard, with a rapid ascent toward and beyond $300,000 with experience.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

While the baseline salary is high, several key factors can significantly impact an oral surgeon's total compensation. Understanding these variables is crucial for anyone planning a career in this field.
### Level of Education
The educational pathway to becoming an oral surgeon is one of the longest and most rigorous in healthcare. After completing a bachelor's degree, candidates must attend dental school to earn a Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) or Doctor of Dental Medicine (DMD). Following this, they must complete a demanding 4-to-6-year surgical residency in a hospital-based setting.
Some surgeons opt for a 6-year residency program that also grants a medical degree (MD). While not always a direct cause for higher base pay, holding dual degrees (DDS/MD) can open doors to more complex hospital-based cases, academic leadership roles, or specialized procedures (like major facial reconstruction or oncology), which can lead to higher overall earnings.
### Years of Experience
As with most professions, experience is a primary driver of salary growth.
- Entry-Level (0-5 years): A surgeon fresh out of residency, typically working as an associate in a group practice or hospital, can expect to earn at the lower end of the range, often between $220,000 and $280,000.
- Mid-Career (6-15 years): With a proven track record, established patient base, and refined surgical skills, a mid-career surgeon's salary will align with or exceed the national median, often in the $300,000 to $380,000 range. Many in this stage become partners in their practice.
- Senior/Experienced (15+ years): Highly experienced surgeons, especially those who own a successful private practice, represent the top earners in the field. Their income can easily surpass $400,000 or even $500,000 annually, driven by practice profitability, efficiency, and reputation.
### Geographic Location
Where you practice matters immensely. Compensation varies based on regional market demand, the cost of living, and the number of competing surgeons.
- High-Demand States: States with a favorable ratio of patients to surgeons or a strong market for dental implants and cosmetic procedures often offer higher salaries. States like North Carolina, Minnesota, Texas, and Alaska frequently appear on lists of top-paying locations for surgeons.
- Metropolitan vs. Rural Areas: Major metropolitan areas like New York City or Los Angeles may offer higher absolute salaries to offset a significantly higher cost of living. Conversely, practicing in an underserved rural or suburban area can be extremely lucrative. With less competition, a surgeon can become the primary provider for a large population, leading to a high volume of cases and significant income potential.
### Company Type
The type of practice setting is arguably the most significant factor determining earning potential.
- Private Practice (Owner/Partner): This offers the highest earning potential. Practice owners not only earn a salary for their clinical work but also share in the profits of the business. They have control over fees, expenses, and strategic growth, leading to incomes at the very top of the scale.
- Private Practice (Associate): An associate works for a practice owner or a group. They typically receive a guaranteed base salary or a percentage of the revenue they generate (production), whichever is higher. This provides a secure, high income without the administrative burdens of ownership.
- Hospital Setting: Surgeons employed by hospitals receive a fixed salary and benefits. While this salary may be slightly lower than private practice potential, it often comes with less administrative work, no overhead costs, and access to complex, academically interesting trauma and reconstructive cases.
- Academia: Working at a university or teaching hospital involves training residents, conducting research, and clinical practice. Compensation is generally lower than in private practice, but the role offers excellent benefits, a different work-life balance, and the fulfillment of shaping the next generation of surgeons.
### Area of Specialization
While OMS is already a specialty, surgeons can develop sub-specialty focuses that boost their income. Procedures with high reimbursement rates or those that are cash-based (not covered by insurance) can significantly increase revenue. A practice that heavily focuses on high-value services like full-arch dental implants ("all-on-4") or facial cosmetic surgery will often generate more revenue than one focused primarily on insurance-based tooth extractions.
Job Outlook

The future for oral and maxillofacial surgeons is exceptionally bright. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects a 4% growth for dentists overall from 2022 to 2032, which is as fast as the average for all occupations. The demand for OMS specialists is expected to remain strong for several reasons:
- Aging Population: As the baby boomer generation ages, there is an increased need for advanced dental procedures like dental implants and treatment for oral cancers.
- Technological Advances: Innovations in surgical techniques and diagnostic tools continue to expand the scope of what oral surgeons can treat.
- Public Awareness: Greater awareness of corrective jaw surgery and the life-changing benefits of dental implants fuels consistent patient demand.
Conclusion

A career as an oral and maxillofacial surgeon is a long and challenging journey, demanding years of intense education and training. However, the rewards are commensurate with the effort. This profession offers the unique opportunity to profoundly improve patients' lives by restoring function, relieving pain, and enhancing appearance.
From a financial perspective, it is one of the most stable and high-paying careers available. With a national median salary exceeding $300,000 and a clear path to earning over $400,000 through experience and practice ownership, the financial security is undeniable. For aspiring professionals who possess the required academic aptitude, surgical skill, and unwavering dedication, oral and maxillofacial surgery represents a pinnacle of professional and financial achievement.