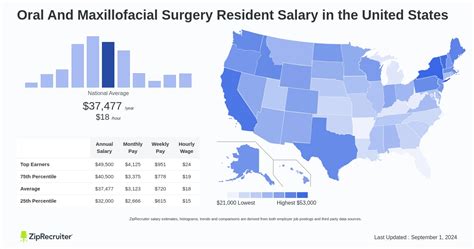
Embarking on the path to becoming a surgeon is a journey of immense dedication, long hours, and rigorous training. While the ultimate financial rewards for a board-certified surgeon are significant, the salary during the residency period is a frequent and important question for aspiring medical professionals. This article provides a data-driven look into what a surgical resident can expect to earn, the factors that influence their pay, and the promising outlook for this demanding career.
While a surgical resident's salary, more accurately a stipend, may seem modest, typically ranging from $60,000 to $85,000 per year, it is the critical stepping stone to a career that is both professionally fulfilling and financially lucrative.
What Does a Surgical Resident Do?

A surgical resident is a physician who has graduated from medical school (with an M.D. or D.O. degree) and is now undergoing a specialized, hands-on training program in a surgical field at a hospital or clinic. This is not a student role; it is a full-time, intensive job.
Residency can last anywhere from five years for general surgery to seven years or more for specialties like neurosurgery or plastic surgery. During this time, residents are responsible for:
- Managing all aspects of patient care, from pre-operative diagnosis to post-operative follow-up.
- Assisting senior surgeons in the operating room and gradually taking the lead on more complex procedures under supervision.
- Performing procedures, managing patient floors, and handling on-call duties, which often involve working nights, weekends, and holidays.
- Continuously learning advanced surgical techniques, anatomy, and critical decision-making skills.
In essence, residency is where a medical school graduate transforms into a competent, independent surgeon.
Average Surgical Resident Salary
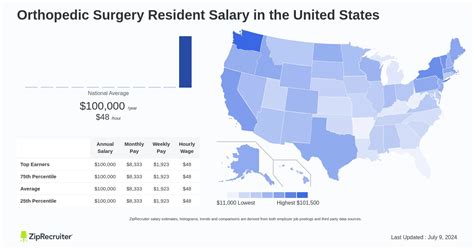

A resident's salary is typically paid by the hospital or institution where they train. It is crucial to understand that these salaries are not determined by the revenue a resident generates but are structured stipends that increase incrementally with each year of training.
According to the Medscape Resident Salary & Debt Report 2023, the average salary for all medical residents in the United States is $67,400. This figure provides a strong baseline, as most institutions pay residents similar amounts regardless of their specialty (e.g., surgery, internal medicine, pediatrics) at the same training level.
Salary aggregators provide a similar view, with a slightly broader range reflecting different locations and training years:
- Salary.com reports the average Medical Resident salary falls between $62,852 and $76,144 as of late 2023.
- Glassdoor lists the average total pay for a Surgical Resident at approximately $74,000 per year, including potential additional pay.
This salary is a stipend meant to cover living expenses during the training period, which is why it is significantly lower than the six-figure salary of a fully licensed attending surgeon.
Key Factors That Influence Salary


While resident salaries are more standardized than in other professions, several key factors create variation in earnings.
###
Years of Experience (Post-Graduate Year)
This is the single most significant factor influencing a resident's salary. "Experience" in this context is measured by the Post-Graduate Year (PGY) of training. A PGY-1 resident (an intern) will earn the least, and a PGY-6 or PGY-7 resident (a chief resident) will earn the most. The salary increases predictably each year to reflect the resident's growing experience and level of responsibility.
For example, a typical progression at a single institution might look like this:
- PGY-1: $62,000
- PGY-2: $64,500
- PGY-3: $67,000
- PGY-4: $70,000
- PGY-5 (Chief): $73,000
*Source: Data modeled after stipend reports from the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) and various university residency programs.*
###
Geographic Location
Where you complete your residency plays a major role in your salary. Hospitals in high-cost-of-living metropolitan areas (like New York City, Boston, or San Francisco) typically offer higher stipends to help offset steep housing and living expenses. Conversely, programs in the Midwest or Southeast may offer lower nominal salaries, but the resident's purchasing power might be equivalent or even greater.
For example, a PGY-3 resident might earn $75,000 in a major Northeastern city but only $65,000 in a smaller Midwestern city. While the first number is higher, the second may afford a higher quality of life due to lower costs.
###
Company Type (Institution)
The type of institution hosting the residency program can influence pay. Large, university-affiliated academic medical centers, especially those in major cities, often have slightly higher pay scales than smaller, private, or community-based hospitals. This can be due to several factors, including:
- Larger institutional budgets.
- The presence of resident unions or associations that negotiate for higher pay and better benefits.
- Competition for the best resident candidates.
###
Area of Specialization
This is a key point of clarification. During residency, your specialty generally does not impact your base salary. Within a given hospital, a PGY-2 surgical resident will earn the same as a PGY-2 internal medicine resident. The salary is tied to the institution and your PGY level, not your chosen field.
However, specialization becomes the dominant factor in salary *after* residency. Once you are a board-certified attending physician, a neurosurgeon's salary will be vastly different from a general surgeon's, which will be different from a family medicine physician's. This future earning potential is the long-term financial reward for completing a demanding surgical residency.
Job Outlook


The career outlook for surgeons is excellent. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that employment for all physicians and surgeons will grow by 3% from 2022 to 2032. This stable growth is driven by several factors, including the healthcare needs of an aging population and the retirement of a significant number of current physicians.
Surgery is a field that will always require highly skilled human experts. This ensures that upon completing a residency, a surgeon will enter a job market with strong, stable, and persistent demand for their services.
Conclusion


Choosing to become a surgeon is a commitment to a life of service, learning, and skill. While the salary during the 5-7 year residency period is a modest stipend, it is important to view it as a paid, intensive apprenticeship for an incredibly rewarding career.
For aspiring surgeons, the key takeaways are:
- Expect a Livable Stipend: A surgical resident's salary, typically $60,000 to $85,000, is designed to cover living expenses during your training.
- Salary Grows with Experience: Your pay will increase reliably each year you advance in your PGY level.
- Focus on the Program, Not Just the Pay: The quality of training, mentorship, and operative experience a residency program offers is far more critical to your future success than a few thousand dollars of difference in annual salary.
- The Ultimate Reward is Substantial: The temporary financial sacrifice of residency paves the way for a career as a surgeon, which is one of the highest-paying professions in the world, with strong job security and the profound satisfaction of saving and improving lives.