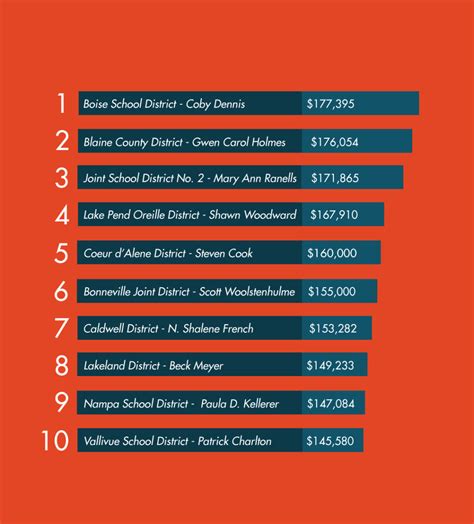
The role of a school superintendent is one of the most demanding and impactful in the field of education. As the chief executive officer of a school district, a superintendent's leadership affects students, teachers, and the entire community. For those aspiring to this pinnacle of educational administration, the career offers not only immense responsibility but also significant financial rewards.
While salaries can vary dramatically, it is a high-paying profession, with many experienced leaders earning well into the six-figure range, and top administrators in large, urban districts commanding salaries exceeding $300,000. This article will provide a data-driven, in-depth look at what you can expect to earn as a school superintendent and the key factors that will shape your compensation.
What Does a School Superintendent Do?

Before diving into the numbers, it's essential to understand the scope of the role. A school superintendent is the top executive of a school district, hired by and reporting to an elected school board. They are responsible for the day-to-day operations and long-term strategic vision of the district. Key responsibilities include:
- Strategic Leadership: Setting academic goals and a vision for the district.
- Financial Management: Developing and managing multi-million or even billion-dollar budgets.
- Human Resources: Overseeing the hiring, evaluation, and development of principals, teachers, and other district staff.
- Policy and Governance: Implementing policies set by the school board and ensuring compliance with state and federal regulations.
- Community Relations: Serving as the public face of the district, communicating with parents, community leaders, and the media.
In essence, a superintendent is the CEO of an educational enterprise, balancing educational priorities with complex operational and political demands.
Average School Superintendent Salary
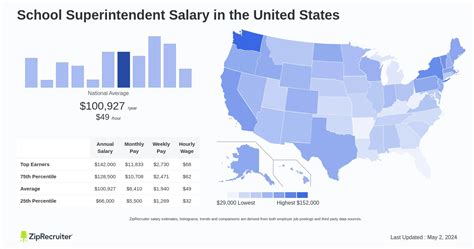
Given the complexity of the role, compensation for school superintendents is substantial. However, averages can be misleading without context. Different sources report slightly different figures based on their methodology.
- Salary.com reports that the median annual salary for a School Superintendent in the United States is approximately $178,590, with a typical range falling between $145,890 and $215,790 as of late 2023.
- Payscale provides a slightly lower average base salary of around $130,788 per year, with their reported range spanning from $88,000 on the low end to $182,000 on the high end.
- Glassdoor lists a national average salary of $139,150 per year, based on user-submitted data.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) groups superintendents under the broader category of "Elementary and Secondary School Education Administrators," which also includes principals and other administrative staff. For this group, the BLS reported a median annual wage of $107,430 in May 2023. This lower figure reflects the inclusion of other administrative roles; superintendent-specific salaries are consistently higher.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your earning potential as a superintendent isn't determined by a single number. It’s a dynamic figure influenced by several critical factors.
###
Level of Education
A master's degree is the standard entry-level requirement for nearly all educational administration positions, including superintendent. However, to be a competitive candidate for larger, higher-paying districts, a doctoral degree is often expected. Possessing a Doctor of Education (Ed.D.) or a Ph.D. in educational leadership signals a high level of expertise and commitment to the field, which can directly translate into a higher salary offer and greater career opportunities.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is paramount. A first-time superintendent in a small district will earn significantly less than a seasoned veteran with a proven track record of leading multiple districts. Salary progression is often steep.
- Early Career (0-5 years): Superintendents at this stage, often leading smaller districts, can expect to earn on the lower end of the national range, typically from $90,000 to $130,000.
- Mid-Career (5-15 years): With a solid track record of improving student outcomes and managing budgets, superintendents can move to larger, more complex districts and see their salaries increase to the $150,000 - $200,000 range.
- Late Career (15+ years): Highly experienced superintendents who are sought after for their expertise in areas like financial turnarounds or academic reform can command top-tier salaries, often exceeding $250,000, particularly in large districts.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work is one of the biggest determinants of your salary. Compensation is generally higher in states with a higher cost of living and in major metropolitan areas. For instance, superintendents in states like California, New York, Illinois, and Texas often earn some of the highest salaries in the nation, especially in their large suburban and urban districts. Conversely, salaries in more rural states in the South and Midwest tend to be lower, though the cost of living is also proportionally less.
###
Company Type (District Size, Wealth, and Type)
In this context, "company type" translates to the characteristics of the school district you lead. This is arguably the most significant factor.
- District Enrollment: The larger the student body, the greater the complexity and responsibility, and the higher the pay. A 2022-23 survey by the American Association of School Administrators (AASA) highlighted this disparity: superintendents in districts with fewer than 300 students earned a median salary of $125,000, while those in districts with 25,000 or more students earned a median of $301,656.
- District Budget and Wealth: Districts funded by a strong local property tax base can often afford to pay their leaders more. A wealthy suburban district may offer a higher salary than a large urban district with a much tighter per-pupil budget.
- District Type (Urban vs. Suburban vs. Rural): Large urban districts present unique challenges and often offer very high salaries to attract top talent. However, affluent suburban districts are also known for offering highly competitive compensation packages to maintain strong leadership. Rural districts typically offer the lowest salaries.
###
Area of Specialization (Specialized Skills and Reputation)
While a superintendent is a generalist, having a strong reputation in a high-demand area can make you a more valuable and higher-paid candidate. A superintendent known for successfully turning around academically failing schools, navigating a district out of a financial crisis, or effectively implementing large-scale technology initiatives can command a premium salary. This reputation allows a leader to be recruited nationally, rather than just locally, which increases their bargaining power.
Job Outlook

The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that employment for Elementary and Secondary School Education Administrators will grow by 1% from 2022 to 2032, which is slower than the average for all occupations.
However, this statistic should not be discouraging. The role of superintendent is a top-tier position, and there are a limited number of districts. Job openings are not created by industry growth but primarily arise from retirements or other forms of turnover. With a significant portion of current superintendents nearing retirement age, a steady stream of opportunities is expected to become available for qualified, experienced, and well-educated professionals ready to step into these leadership roles.
Conclusion

The path to becoming a school superintendent is a long and challenging one, requiring advanced education, extensive experience, and a deep commitment to public service. However, for those who reach this career pinnacle, the rewards are substantial.
Key Takeaways:
- High Earning Potential: This is a six-figure profession with the potential to earn over $300,000.
- Experience and Education Matter: A doctorate and a proven track record are your keys to higher earnings.
- Location and District are Crucial: The single biggest factor in your salary will be the size, wealth, and location of the district you lead.
- Stable Demand: While overall job growth is slow, consistent opportunities will arise from turnover and retirements.
For dedicated educational leaders aiming to make a broad and lasting impact, the role of school superintendent offers a unique opportunity to shape the future of thousands of students while achieving significant professional and financial success.