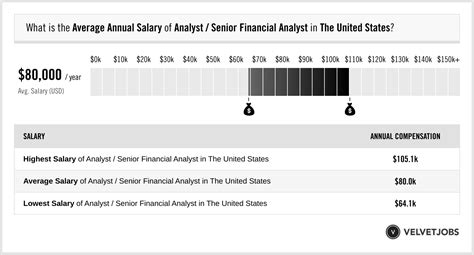
A career as a Senior Financial Analyst is a highly sought-after path for professionals with a knack for numbers and a passion for strategy. It's a role that places you at the heart of a company's decision-making process, offering both intellectual challenges and significant financial rewards. If you're considering this career, one of your primary questions is likely about compensation. The great news is that Senior Financial Analysts are well-compensated, with average salaries often breaking the six-figure mark and offering substantial room for growth.
This in-depth guide will break down the typical salary for a Senior Financial Analyst, explore the key factors that drive earning potential, and provide a clear outlook on the future of this dynamic profession.
What Does a Senior Financial Analyst Do?

Before diving into the numbers, it's essential to understand the value a Senior Financial Analyst brings to an organization. This is not an entry-level position. A "Senior" analyst has moved beyond basic data entry and reporting. They are experienced professionals who:
- Develop Complex Financial Models: They build sophisticated models to forecast revenue, predict the profitability of new projects, and analyze potential mergers or acquisitions.
- Lead Budgeting and Forecasting: They often take a lead role in the annual budgeting process, working with department heads to create and manage budgets that align with corporate goals.
- Provide Strategic Insights: They analyze financial data to identify trends, risks, and opportunities. Their key role is to translate complex numbers into actionable business intelligence for senior leadership.
- Mentor Junior Staff: As senior members of the team, they are expected to guide and mentor junior analysts, helping to develop the next generation of financial talent.
In essence, a Senior Financial Analyst acts as a crucial internal consultant, using financial expertise to guide the company toward profitable growth.
Average Senior Financial Analyst Salary
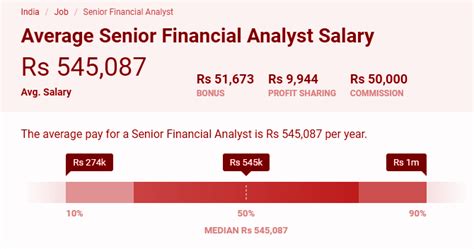
The compensation for a Senior Financial Analyst is competitive and reflects the high level of skill and responsibility required. While figures vary, a clear consensus emerges from authoritative data sources.
According to data from major salary aggregators like Salary.com, Payscale, and Glassdoor, the average base salary for a Senior Financial Analyst in the United States typically falls between $95,000 and $115,000 per year.
- Salary.com reports a median base salary of $101,570 as of early 2024, with the typical range falling between $92,798 and $111,547.
- Payscale notes an average salary of around $92,500, with significant upward variance based on bonuses and profit-sharing, which can add another $10,000 or more to total pay.
It's crucial to look beyond the base salary. The full salary spectrum can range from approximately $85,000 for those newer to the senior title or in lower cost-of-living areas, to well over $130,000 for top performers in high-demand industries. Furthermore, total compensation, which includes annual bonuses, stock options, and profit-sharing, can significantly increase these figures, often pushing total earnings into the $120,000 to $150,000+ range.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary as a Senior Financial Analyst isn't determined by a single number. It's a complex calculation influenced by several key factors. Understanding these variables is the first step toward maximizing your earning potential.
###
Level of Education
Your educational background provides the foundation for your career. A bachelor's degree in finance, accounting, economics, or a related field is the standard requirement. However, advanced credentials can provide a significant salary premium.
- Master's Degree: An MBA (Master of Business Administration) or a specialized Master's in Finance (MSF) is highly valued. Employers often see these candidates as having a broader strategic mindset and leadership potential, which can lead to higher starting salaries and faster promotions.
- Professional Certifications: Earning a prestigious certification is one of the most effective ways to increase your salary. The Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) designation is the gold standard for investment analysis, while the Certified Public Accountant (CPA) is invaluable for roles with a heavy accounting focus. These certifications signal a high level of expertise and dedication to the field.
###
Years of Experience
The "Senior" title inherently implies experience. The salary jumps significantly as you move from a junior to a senior role. Here is a typical progression:
- Financial Analyst (0-3 Years): Focuses on data gathering, report building, and supporting senior staff.
- Senior Financial Analyst (4-8+ Years): Takes ownership of complex projects, leads forecasting cycles, and presents findings to management. This leap is where you see a substantial salary increase.
- Finance Manager / Director (8+ Years): Moves into a leadership role, managing a team of analysts and setting financial strategy. Compensation at this level often includes a larger bonus structure and greater long-term incentives.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work matters—a lot. Salaries are adjusted for the local cost of living and the demand for financial talent. Major financial and technology hubs consistently offer the highest salaries.
- Top-Tier Cities: Metropolitan areas like New York City, San Francisco, Boston, and San Jose offer the highest salaries to attract top talent in a competitive market. It is common for salaries in these cities to be 15-30% above the national average.
- Mid-Tier and Lower-Cost Cities: While cities in the Midwest and Southeast may offer lower base salaries, the reduced cost of living can mean your money goes further. The rise of remote work is also starting to flatten these regional differences slightly, but location remains a powerful factor.
###
Company Type
The industry and size of your employer have a massive impact on compensation.
- Investment Banking and Private Equity: These fields offer the highest potential earnings, with very large performance bonuses, but are known for extremely long hours and high-pressure environments.
- Technology: Large tech firms (e.g., Google, Apple, Meta) pay top-tier salaries and often offer lucrative stock options as part of the total compensation package.
- Fortune 500 Companies: Large, established corporations across sectors like healthcare, consumer goods, and manufacturing offer competitive salaries, strong benefits, and greater job stability.
- Startups: Compensation can be a mix of a potentially lower base salary and a significant equity stake. The risk is higher, but the potential reward from a successful exit can be immense.
- Government and Non-Profit: These sectors typically offer lower salaries but compensate with excellent benefits, job security, and a better work-life balance.
###
Area of Specialization
Not all Senior Financial Analyst roles are the same. Specializing in a high-demand area can dramatically increase your value.
- Financial Planning & Analysis (FP&A): This is the most common path, focusing on internal budgeting, forecasting, and strategic planning.
- Investment Analysis: Working for a buy-side (e.g., mutual fund) or sell-side (e.g., investment bank) firm, these analysts evaluate securities and markets. This is often one of the most lucrative specializations.
- Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A) / Corporate Development: These analysts model the financial impact of potential acquisitions and divestitures. Due to the high-stakes nature of the work, these roles are compensated very well.
- Treasury: Treasury analysts manage a company's cash, debt, and investment portfolios to ensure liquidity and financial stability.
Job Outlook

The future for financial analysts is bright. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), employment for financial analysts is projected to grow 8 percent from 2022 to 2032, which is much faster than the average for all occupations.
The BLS cites that this strong growth is driven by the increasing complexity of the global financial landscape and a greater need for in-depth analysis to guide investment decisions and manage risk. This sustained demand ensures that skilled Senior Financial Analysts will remain valuable and highly sought-after professionals for the foreseeable future.
Conclusion

A career as a Senior Financial Analyst offers a powerful combination of intellectual stimulation, strategic influence, and robust financial rewards. With average salaries comfortably in the six-figure range and significant upside potential, it is an excellent goal for aspiring finance professionals.
Your ultimate earning potential will be shaped by your proactive decisions. By investing in advanced education and certifications like the CFA, gaining diverse experience, targeting high-paying industries and locations, and developing a valuable specialization, you can position yourself at the top end of the pay scale. For those with a strong analytical mindset and a drive to succeed, this career path is a clear road to professional and financial success.