In the intricate world of technology, systems engineers are the master architects. They design, integrate, and manage the complex computer systems and networks that form the backbone of modern business. If you're drawn to a career that blends big-picture thinking with deep technical expertise, systems engineering is a compelling choice—and one that is both intellectually and financially rewarding.
But what does "financially rewarding" actually mean? A career in systems engineering offers a robust salary, often starting strong and growing to well over six figures with experience and specialization. This guide will break down exactly what you can expect to earn and, more importantly, how you can maximize your salary potential in this dynamic field.
What Does a Systems Engineer Do?
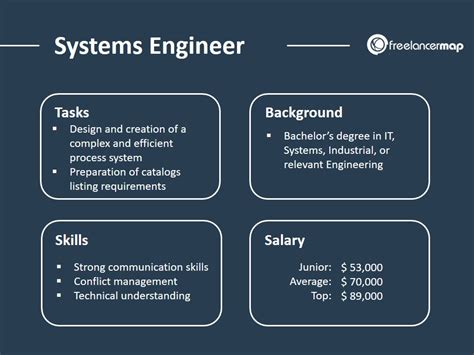
Before we dive into the numbers, let's clarify the role. A systems engineer is a multidisciplinary expert responsible for the entire lifecycle of a complex system. Think of them as the glue that holds a technological project together. Their responsibilities often include:
- Designing and modeling complex systems, from computer networks to cloud infrastructure.
- Integrating hardware and software components to ensure they work together seamlessly.
- Overseeing the installation, maintenance, and upgrading of systems.
- Troubleshooting and problem-solving at a high level to ensure system reliability and performance.
- Managing project requirements and ensuring the final system meets the needs of the business or client.
They work across virtually every industry, from aerospace and defense to finance, healthcare, and big tech.
Average Systems Engineer Salary
The compensation for a systems engineer is highly competitive, reflecting the critical nature of their work. While figures vary based on several factors, we can establish a strong baseline from leading data sources.
According to Salary.com, the median salary for a Systems Engineer in the United States is approximately $108,619 as of early 2024. The typical salary range falls between $98,211 and $119,773.
Other authoritative sources provide a similar picture:
- Payscale reports a median salary of $94,037, with a common range from $67,000 for entry-level roles to over $135,000 for experienced professionals.
- Glassdoor lists an average total pay (including bonuses and other compensation) of $119,895 per year.
This data paints a clear picture: a mid-career systems engineer can comfortably expect to earn a six-figure salary. However, this number is just a starting point. Several key variables can significantly increase your earning potential.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your salary isn't set in stone. By understanding the factors that employers value, you can strategically position yourself for higher compensation.
Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the single most significant driver of salary growth in systems engineering. As you gain expertise in designing, managing, and troubleshooting complex systems, your value to an organization skyrockets.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): Professionals starting their careers can expect a salary in the range of $70,000 to $85,000. In this phase, the focus is on learning core principles and supporting senior engineers.
- Mid-Career (3-8 years): With solid experience, systems engineers take on more responsibility and can expect to earn between $90,000 and $125,000. They can independently manage significant projects and integrations.
- Senior/Principal (8+ years): Highly experienced engineers who lead teams, design enterprise-level architecture, and serve as subject matter experts command top-tier salaries, often ranging from $130,000 to $165,000+.
Geographic Location
Where you work matters—a lot. Salaries are adjusted based on the cost of living and the concentration of tech jobs in a particular region. Major tech hubs consistently offer the highest pay.
Here are some of the top-paying metropolitan areas, which often offer salaries 15-30% above the national average:
- San Jose, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Boston, MA
- Washington, D.C.
- New York, NY
Conversely, salaries in smaller cities and regions with a lower cost of living will likely be closer to or slightly below the national median. However, with the rise of remote work, some companies are offering competitive salaries regardless of location to attract top talent.
Level of Education
A strong educational foundation is standard for this field. A bachelor's degree in computer science, engineering, information technology, or a related field is typically the minimum requirement.
However, advanced education can provide a significant salary bump. A Master of Science in Systems Engineering or a related technical field can not only open doors to more senior and specialized roles but can also increase starting salaries by 5-15%, according to various university and industry reports. Furthermore, professional certifications (e.g., AWS Certified Solutions Architect, CompTIA Security+, Certified Systems Engineering Professional - CSEP) demonstrate specialized expertise and can directly translate to higher pay.
Company Type and Industry
The type of company you work for plays a crucial role in your compensation package.
- Big Tech (e.g., Google, Amazon, Microsoft): These companies are known for offering the highest base salaries and supplementing them with substantial stock options and bonuses, pushing total compensation well above industry averages.
- Aerospace & Defense (e.g., Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman): This is a traditional and highly stable sector for systems engineers. Salaries are very competitive, though they may not always reach the peaks of Big Tech's total compensation packages.
- Finance and Banking: Financial institutions rely on robust, secure, and highly available systems, and they pay premium salaries to the engineers who can build and maintain them.
- Startups: While base salaries at early-stage startups might be lower, they are often compensated with significant equity (stock options), which can lead to a massive financial windfall if the company succeeds.
Area of Specialization
"Systems engineer" is a broad title. Specializing in a high-demand niche is one of the most effective ways to boost your salary. In-demand specializations include:
- Cloud Systems Engineering (AWS, Azure, GCP): As companies migrate to the cloud, engineers who can design and manage scalable cloud infrastructure are in extremely high demand and command top salaries.
- Cybersecurity Systems Engineering: With the rising threat of cyberattacks, engineers who specialize in building secure systems and integrating security protocols are critical assets.
- DevOps Engineering: This specialization bridges the gap between development and IT operations, focusing on automation and CI/CD pipelines. It is a highly sought-after and well-compensated role.
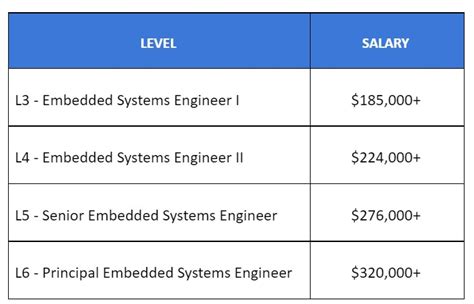
- Embedded Systems Engineering: For those interested in the intersection of hardware and software, specializing in the systems that run on devices (from cars to medical equipment) is a lucrative path.
Job Outlook

The future for systems engineers is bright. Technology is only becoming more complex and integrated, increasing the need for professionals who can manage that complexity.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects job growth for related fields to be strong. For instance, the outlook for Network and Computer Systems Administrators is projected to grow 2% from 2022 to 2032. However, this broad category may underrepresent the explosive growth in specialized areas. For Information Security Analysts, a closely related field, the BLS projects a staggering 32% growth over the same period, indicating massive demand for security-focused systems experts.
This demonstrates that while the overall field is stable, those who specialize in high-growth areas like cloud and cybersecurity will find themselves in an exceptionally strong job market for years to come.
Conclusion: A Career Built for Growth

A career as a systems engineer offers a powerful combination of intellectual challenge, professional impact, and financial security. With a median salary that comfortably sits in the six-figure range and a clear path for advancement, it stands out as a top-tier choice in the tech landscape.
Your earning potential is not a fixed number—it is a reflection of your experience, location, and, most importantly, your specialized skills. For aspiring students and current professionals, the key takeaway is clear: invest in continuous learning. By focusing on high-demand specializations like cloud computing and cybersecurity, pursuing advanced education or certifications, and strategically positioning yourself in a major tech market, you can ensure your career trajectory—and your salary—are constantly on the rise.