Are you a meticulous problem-solver with a passion for technology? Do you get satisfaction from ensuring a product is flawless before it reaches users? If so, a career as a Test Engineer, also known as a Quality Assurance (QA) Engineer, might be the perfect fit. This critical role is not only intellectually stimulating but also offers a lucrative and stable career path.
In this guide, we'll break down everything you need to know about a Test Engineer's salary, from the national average to the key factors that can significantly increase your earning potential.
What Does a Test Engineer Do?

Before we dive into the numbers, let's clarify the role. A Test Engineer is the guardian of software quality. They are highly skilled professionals responsible for designing and implementing strategies to test software applications and systems. Their goal is to identify bugs, performance issues, and usability problems before a product is released to the public.
Key responsibilities include:
- Developing and executing detailed test plans and test cases.
- Writing and maintaining automated test scripts to improve efficiency.
- Identifying, recording, and tracking defects in bug-tracking systems.
- Collaborating closely with software developers and product managers.
- Performing various types of testing, including functional, regression, performance, and security testing.
In essence, they ensure that the technology you use every day—from your banking app to your video games—works as expected.
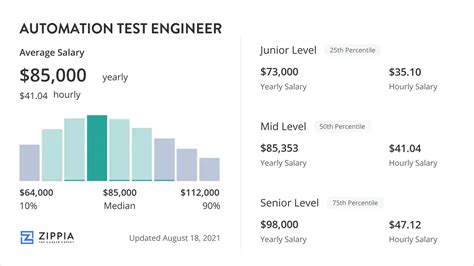
Average Test Engineer Salary
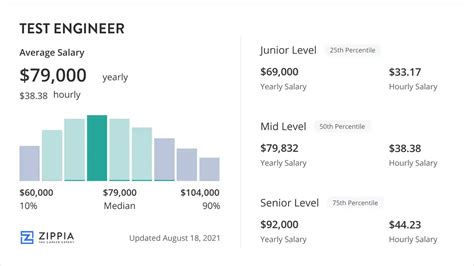
A career as a Test Engineer is financially rewarding. While salaries can vary widely, the national average provides a strong benchmark.
According to data from major salary aggregators, the average base salary for a Test Engineer in the United States typically falls between $90,000 and $105,000 per year.
Let's look at the data from reputable sources:
- Salary.com reports the median salary for a Test Engineer I (entry-level) is around $77,901, while a Senior Test Engineer can earn a median of $116,400.
- Glassdoor lists the average base pay for a Test Engineer at $95,011 per year, with a "most likely range" between $76,000 and $120,000.
- Payscale shows an average salary of $88,500 per year, with a typical range from $65,000 for entry-level roles to over $124,000 for experienced professionals.
This data illustrates a clear path for salary growth. Entry-level professionals can expect to earn a competitive starting salary, while senior and lead engineers with specialized skills can command compensation well into the six figures.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your salary isn't set in stone. Several key factors can dramatically influence how much you earn. Understanding these variables is crucial for maximizing your income throughout your career.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the most significant driver of salary in the tech industry. As you gain more skills and a deeper understanding of testing methodologies and software development lifecycles, your value to an employer skyrockets.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): You can expect a starting salary in the $70,000 to $85,000 range. The focus is on learning manual testing processes, understanding bug reporting, and possibly starting with basic automation.
- Mid-Level (3-5 years): With solid experience, salaries often rise to the $85,000 to $110,000 range. At this stage, engineers are proficient in test automation, have a strong grasp of testing frameworks, and can work more independently.
- Senior/Lead (5+ years): Senior Test Engineers and QA Leads can command salaries of $110,000 to $150,000+. These roles involve architecting test strategies, mentoring junior engineers, and specializing in high-impact areas like performance or security testing.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Major technology hubs have a higher cost of living but also offer significantly higher salaries due to intense competition for talent.
Here are some of the top-paying metropolitan areas for Test Engineers:
- San Francisco Bay Area, CA: Consistently offers the highest salaries, often exceeding the national average by 20-30% or more.
- Seattle, WA: Home to Amazon and Microsoft, Seattle is another high-paying market.
- New York, NY: A major hub for both tech and finance (FinTech), driving up demand and salaries.
- Boston, MA: A strong East Coast tech hub with competitive compensation.
- Austin, TX: A rapidly growing tech city with salaries that are rising to compete with established hubs.
Working remotely has changed this dynamic slightly, but companies still often adjust salaries based on the employee's location.
###
Area of Specialization
Not all testing is created equal. Specializing in a high-demand area is a powerful way to increase your salary.
- Manual vs. Automation: The biggest pay differentiator. A Test Automation Engineer, who writes code to automate tests, will consistently earn more than a manual tester.
- Software Development Engineer in Test (SDET): This is a hybrid role that blends software development with testing. SDETs have strong coding skills (often in Python, Java, or C#) and build sophisticated testing frameworks. They are highly sought after and command premium salaries.
- Performance Testing: These engineers specialize in testing an application's speed, scalability, and stability under load. It's a niche skill that is critical for user-facing applications, making it a high-value specialization.
- Security Testing: With the rising threat of cyberattacks, engineers who can identify and test for security vulnerabilities (sometimes called "pen testers") are in extremely high demand and can earn top-tier salaries.
###
Company Type
The type of company you work for plays a major role in your total compensation.
- Big Tech (e.g., Google, Meta, Apple, Amazon): These companies typically offer the highest compensation packages, which include a high base salary, annual bonuses, and significant stock grants (RSUs) that can dramatically increase your total earnings.
- Established Enterprises: Large, non-tech corporations (e.g., banks, healthcare providers, retailers) have a growing need for test engineers and offer competitive salaries and stable work environments, though their total compensation may not match Big Tech.
- Startups: A startup might offer a lower base salary but compensate with potentially valuable stock options. This is a higher-risk, higher-reward scenario that appeals to those who want to be part of building a product from the ground up.
###
Level of Education
For most Test Engineer roles, a Bachelor's degree in Computer Science, Engineering, or a related field is the standard requirement. However, experience and skills often weigh more heavily than education. Certifications in testing tools (like ISTQB) or cloud platforms (AWS, Azure) can also provide a competitive edge. A Master's degree may be beneficial for highly specialized or research-focused roles but is generally not a requirement for most positions.
Job Outlook

The future for Test Engineers is incredibly bright. As technology becomes more integrated into every aspect of our lives, the need for quality assurance has never been greater.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that employment for "Software Quality Assurance Analysts and Testers" will grow 25 percent from 2022 to 2032. This is described as "much faster than the average for all occupations." This incredible growth rate translates to approximately 15,900 new job openings each year over the decade, driven by the expanding need for new software across all industries.
Conclusion

A career as a Test Engineer offers a powerful combination of intellectual challenge, career stability, and excellent financial rewards. The path forward is clear: with a national average salary approaching six figures and significant growth potential, it's a field ripe with opportunity.
To maximize your earning potential, focus on building in-demand skills, particularly in test automation. Gaining experience, considering a move to a tech hub, and specializing in areas like performance or security testing will place you in the top tier of earners. Given the outstanding job outlook projected by the BLS, now is an excellent time to enter or advance your career in software quality assurance.