For those drawn to a career in federal law enforcement that combines high-stakes security with national and international travel, the role of a Federal Air Marshal is a compelling choice. These highly-trained, undercover professionals are the last line of defense in our nation's skies. But beyond the demanding mission, what is the financial reality of this career?
A position as a Federal Air Marshal (FAM) offers a competitive and structured salary, with significant potential for growth. While entry-level salaries are robust, experienced and senior-level marshals can earn well over $100,000 to $170,000 annually, depending on a combination of factors we'll explore below. This guide will break down the salary you can expect and the key drivers that will influence your earnings throughout your career.
What Does a Federal Air Marshal Do?

Federal Air Marshals are federal law enforcement officers working for the Transportation Security Administration (TSA), a component of the Department of Homeland Security. Their primary mission is to detect, deter, and defeat hostile acts targeting U.S. aircraft, airports, passengers, and crews.
Their responsibilities include:
- Flying anonymously on domestic and international flights.
- Identifying and responding to security threats in the air and on the ground.
- Liaising with other law enforcement agencies.
- Participating in ground-based task forces and investigative assignments.
The role demands exceptional judgment, rigorous physical and firearms proficiency, and the ability to operate discreetly under immense pressure.
Average Federal Air Marshal Salary
Unlike private-sector jobs, the salary for a Federal Air Marshal is not arbitrary. It is dictated by the federal government's structured pay system. FAMs are typically hired under the SV pay system, which corresponds to the federal government's General Schedule (GS) pay scale.
New hires often begin at the G pay band, which is equivalent to GS-11. Upon successful completion of training and a probationary period, they can advance to higher pay bands like H and I, which correspond to GS-12 and GS-13.
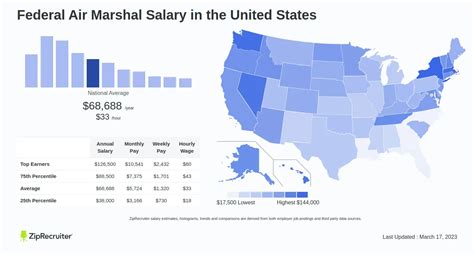
According to reputable salary aggregators, the real-world average reflects this structured growth:
- Salary.com reports the average Federal Air Marshal salary in the United States is approximately $104,500 as of early 2024, with a typical range falling between $87,034 and $125,123.
- Glassdoor estimates a total pay range of $111,000 to $188,000 per year, which includes base salary and potential additional pay.
It's crucial to understand that these are averages. Your precise salary is determined by a clear set of factors defined by the federal government.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your earning potential as a Federal Air Marshal is influenced by several concrete factors. Here’s a detailed breakdown of what matters most.
### The Federal Pay System and Years of Experience
Federal Air Marshals work for a single employer: the TSA. Therefore, "company type" isn't a factor. Instead, the entire pay structure is based on the government's General Schedule (GS) system. This system has two components that determine your base pay:
- Grade (Pay Band): This represents the level of responsibility and complexity of the job. New FAMs typically start at the G pay band (GS-11). As you gain experience and take on more responsibility, you can be promoted to higher pay bands like H (GS-12) and I (GS-13) for senior or supervisory roles.
- Step: Within each grade, there are 10 "steps." These steps are incremental pay increases that you earn based on your time in service and successful performance. It typically takes 1-3 years to advance to the next step.
For example, a new FAM starting at GS-11, Step 1 will earn less than a FAM with 5 years of experience at GS-11, Step 3. A promotion to a Supervisory Air Marshal at the GS-13 level would result in a significant salary jump.
### Geographic Location
This is one of the most significant factors in determining your final salary. The federal government provides a pay adjustment known as "locality pay" to account for the varying costs of living across the United States. This is a percentage added on top of your base GS salary.
For 2024, locality pay adjustments range from 16.82% for the "Rest of U.S." category to 44.15% for the San Francisco-Oakland-Hayward, CA, area.
Let's see how this works using the 2024 OPM pay tables for a starting FAM at the GS-11, Step 1 level (base salary $72,553):
- Dallas-Fort Worth, TX (26.69% locality pay): $91,917
- Washington D.C.-Baltimore, MD (33.26% locality pay): $96,737
- New York, NY (37.24% locality pay): $99,566
- Los Angeles, CA (36.17% locality pay): $98,795
- San Francisco, CA (44.15% locality pay): $104,574
(Source: U.S. Office of Personnel Management, 2024 GS Pay Tables)
Your assigned field office location will directly and substantially impact your take-home pay.
### Level of Education
To qualify for a FAM position, candidates typically need a bachelor's degree OR a minimum of three years of relevant work experience in areas like law enforcement, investigations, or the military.
While a specific degree is not required, having a bachelor's or master's degree in a relevant field like Criminal Justice, Homeland Security, or Criminology can make you a more competitive applicant. It fulfills the primary qualification requirement and demonstrates a foundational knowledge relevant to the role. However, it does not typically result in a higher starting salary, as most new hires begin at the same G pay band regardless of their educational background.
### Area of Specialization and Career Progression
While all FAMs are trained for the core mission, career progression offers a form of "specialization" that leads to higher pay. Instead of specializing in a narrow field, you advance into roles with greater responsibility. These roles correspond to higher GS grades:
- Supervisory Federal Air Marshal: Leading teams of FAMs, responsible for operations and personnel management. These roles are typically at the GS-13 pay band or higher.
- Training Instructor: Serving at the FAMS training center, responsible for preparing new recruits.
- Field Office Roles: Working on ground-based assignments, intelligence, or administrative functions within one of the FAMS field offices.
Each promotion to a higher GS grade (e.g., from GS-12 to GS-13) comes with a significant increase in base pay and, consequently, a higher locality-adjusted salary.
Job Outlook

The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) does not provide a separate outlook for Federal Air Marshals. They are grouped within the broader category of "Police and Detectives."
For this category, the BLS projects a job growth of 3% from 2022 to 2032, which is about as fast as the average for all occupations. The BLS notes that the need for public safety is constant, but employment levels often depend on government funding. For a specialized federal role like an Air Marshal, hiring is directly tied to national security priorities and congressional budgets. Demand remains steady, but hiring cycles can be competitive.
(Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Police and Detectives)
Conclusion: A Rewarding Career Path

Choosing a career as a Federal Air Marshal is a commitment to public service in a demanding and critical field. The compensation structure reflects the significance of the role, offering a strong, transparent, and rewarding financial path.
Here are the key takeaways:
- Strong Starting Salary: Expect a starting salary well above the national average, heavily influenced by your assigned geographic location.
- Structured Growth: Your salary will increase predictably through promotions (higher grades) and time-in-service (higher steps).
- Six-Figure Potential: It is common for experienced Federal Air Marshals to earn well over $100,000, with senior and supervisory roles in high-cost-of-living areas potentially reaching upwards of $170,000 or more.
For individuals seeking a challenging career with purpose, stability, and excellent earning potential, the Federal Air Marshal Service presents an outstanding opportunity to protect the nation while building a secure financial future.