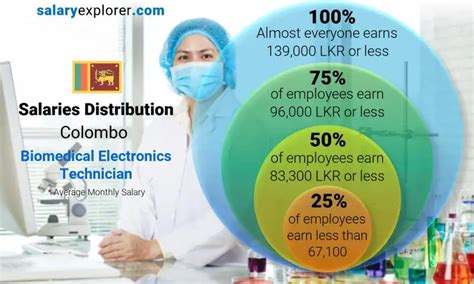
In the rapidly advancing world of healthcare, the line between medicine and technology is increasingly blurred. At this critical intersection works the Biomedical Electronics Technician, a highly skilled professional responsible for keeping life-saving medical equipment running flawlessly. If you're drawn to a career that combines technical expertise with a direct impact on patient care, this role is a compelling choice. But what is the earning potential?
A career as a Biomedical Electronics Technician (BMET), also known as a Medical Equipment Repairer, offers not only a stable and rewarding job but also a competitive salary. Nationally, you can expect an average salary in the range of $60,000 to $70,000, with entry-level positions starting around $55,000 and senior specialists earning well over $90,000 annually.
This article provides a data-driven breakdown of a biomedical electronics technician's salary, the factors that influence it, and the bright future this career holds.
What Does a Biomedical Electronics Technician Do?
Think of a BMET as a first responder for medical technology. When a patient monitor, infusion pump, defibrillator, or ventilator malfunctions, these are the experts who are called in to diagnose and fix the problem. Their core responsibilities are vital to the daily operations of any hospital or clinical setting and include:
- Installation and Calibration: Setting up new, complex medical devices and ensuring they are calibrated to precise manufacturer specifications for patient safety.
- Preventive Maintenance: Performing routine inspections and service to prevent equipment failures before they happen.
- Troubleshooting and Repair: Diagnosing electronic, mechanical, and software issues and performing intricate repairs on a wide array of devices.
- Documentation: Keeping meticulous records of maintenance schedules, repairs, and equipment performance for regulatory compliance.
Their work ensures that doctors, nurses, and other healthcare providers have reliable tools to diagnose, treat, and monitor patients, making them an indispensable part of the healthcare team.
Average Biomedical Electronics Technician Salary
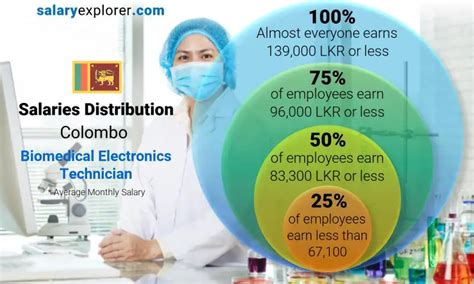
To understand your potential earnings, it's best to look at data from several authoritative sources.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for medical equipment repairers was $59,960 in May 2023. This is the midpoint, meaning half of the technicians earned more than this amount and half earned less. The BLS also provides a broader range: the lowest 10% earned less than $39,230, while the highest-earning 10% brought in more than $96,010.
Reputable salary aggregators provide a similar and often slightly higher snapshot, reflecting real-time market data:
- Salary.com reports a median salary of approximately $68,850 as of late 2024. Their data shows a typical range between $61,715 and $76,711, with more senior roles (Biomedical Equipment Technician III) having a median salary of over $87,000.
- Payscale.com places the average base salary around $64,000 per year.
- Glassdoor.com aggregates user-submitted data to report a total pay average of around $67,000 per year in the United States.
These figures confirm a strong and stable salary base, but your personal earnings will be shaped by several key variables.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary as a BMET isn't a single number—it’s a range influenced by your unique background, skills, and work environment. Here are the most significant factors.
### Level of Education
While a high school diploma is the minimum requirement, most employers demand postsecondary education.
- Associate's Degree: This is the standard and most common entry point. An Associate of Applied Science (A.A.S.) in Biomedical Equipment Technology or Electronics Technology provides the foundational knowledge needed for the job and is typically required for entry-level positions.
- Bachelor's Degree: A four-year degree in Biomedical Engineering Technology can lead to higher starting salaries and a faster track to advanced roles, such as a BMET III, supervisor, or clinical engineer.
- Certifications: Professional certifications are a major factor in salary growth. The most recognized is the Certified Biomedical Equipment Technician (CBET) credential offered by the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI). Earning a CBET demonstrates your expertise and commitment, and many employers offer a pay increase or bonus for certified technicians.
### Years of Experience
Like most professions, experience is a primary driver of income growth. The career path is often structured in tiers (BMET I, II, III).
- Entry-Level (BMET I, 0-2 years): Technicians just starting out can expect a salary in the range of $50,000 to $60,000. They typically handle routine maintenance and less complex repairs under supervision.
- Mid-Career (BMET II, 3-5 years): With a few years of experience, technicians can work independently, tackle more complex equipment, and may begin to specialize. Salaries typically climb to the $60,000 to $75,000 range.
- Senior/Specialist (BMET III, 5+ years): Senior technicians with extensive experience, certifications, and often a specialization (like imaging or anesthesia equipment) hold the highest earning potential. Their salaries frequently exceed $75,000 and can push into the $90,000s or higher.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries for BMETs vary significantly by state and even by metropolitan area due to differences in the cost of living and demand for healthcare services.
According to BLS data, the top-paying states for medical equipment repairers are:
1. Oregon
2. Washington
3. California
4. Nevada
5. Connecticut
Working in a major metropolitan area with a high concentration of hospitals and a high cost of living will almost always result in a higher salary than working in a rural community.
### Company Type
The type of organization you work for has a direct impact on your paycheck.
- In-House Hospital Teams: This is the most common employment setting. You work directly for a hospital or healthcare system. The work is stable, and benefits are often excellent, with salaries generally aligning with the national averages.
- Independent Service Organizations (ISOs): These are third-party companies that hold service contracts with multiple healthcare facilities. These roles may offer higher base pay and overtime opportunities but often require travel between different sites.
- Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs): Working for a manufacturer like GE Healthcare, Siemens, or Philips often represents the highest earning potential. These roles are typically field service engineer positions that require deep, specialized knowledge of that company's products. They often involve extensive travel but come with top-tier salaries and benefits.
### Area of Specialization
While many BMETs are generalists, those who develop expertise in high-tech, complex systems can command a premium salary. High-demand specializations include:
- Diagnostic Imaging: Servicing MRI, CT scanners, PET scanners, and X-ray machines.
- Sterilization Equipment: Maintaining autoclaves and other critical sterilization systems.
- Laboratory Equipment: Repairing complex analytical and diagnostic lab instruments.
- Anesthesia and Respiratory: Working on ventilators, anesthesia machines, and other life-support equipment.
These specializations require advanced training and often manufacturer-specific certifications, making these technicians highly valuable assets.
Job Outlook

The future for biomedical electronics technicians is bright and stable. The BLS projects that employment for medical equipment repairers will grow 5% from 2022 to 2032, which is faster than the average for all occupations.
This growth is driven by two key trends:
1. An Aging Population: As the baby-boomer generation ages, the demand for healthcare services and the medical devices that support them will continue to increase.
2. Technological Advancement: Medical equipment is becoming more complex and integrated, requiring a steady stream of skilled technicians to install, maintain, and repair it.
Conclusion

Choosing a career as a biomedical electronics technician is a smart move for anyone with an aptitude for technology and a desire to contribute to the healthcare field. The role offers a clear path for professional growth and a strong, competitive salary that rewards expertise and dedication.
Your earning potential starts with a solid educational foundation and grows significantly with experience, professional certification, and strategic specialization. With a national median salary comfortably above $60,000 and a pathway to earning over $90,000, coupled with excellent job security, the BMET profession is a fantastic and fulfilling career choice in today's technology-driven world.