Introduction

Are you drawn to a career that sits at the dynamic intersection of business strategy, relationship building, and technology? Do you find satisfaction not just in solving problems, but in proactively preventing them and helping others thrive? If so, the role of a Client Success Specialist might be your ideal professional calling. In today's subscription-based economy, where customer retention is paramount, this profession has moved from a niche function to a critical pillar of corporate growth, offering a career path that is both financially rewarding and deeply fulfilling.
The Client Success Specialist (CSS) is the guardian of the customer relationship. They are the strategic partner who ensures clients not only receive value from a product or service but are so successful with it that they become loyal advocates for the brand. This vital role comes with significant responsibility and, consequently, competitive compensation. Across the United States, the average client success specialist salary typically falls between $65,000 and $85,000 per year, with entry-level positions starting around $55,000 and experienced senior specialists commanding salaries well over $120,000, especially when factoring in bonuses and commissions.
I once worked with a SaaS company that was on the brink of losing its largest client—a seven-figure account. Panic was setting in until a senior Client Success Specialist, armed with deep product knowledge and an even deeper understanding of the client's business goals, orchestrated a complete turnaround plan. Her blend of empathy, strategic thinking, and technical acumen not only saved the account but expanded it, single-handedly proving the immense ROI of a truly elite client success function. It’s this blend of human connection and business impact that makes the field so compelling.
This comprehensive guide will serve as your roadmap to understanding every facet of a Client Success Specialist's career, with a laser focus on salary potential. We will dissect the role, explore the national salary landscape, and unpack the critical factors that can significantly increase your earning power. Whether you are a recent graduate exploring your options or a seasoned professional looking to transition into a more strategic role, this article will provide you with the data, insights, and actionable advice you need to build a successful and lucrative career in client success.
### Table of Contents
- [What Does a Client Success Specialist Do?](#what-does-a-client-success-specialist-do)
- [Average Client Success Specialist Salary: A Deep Dive](#average-client-success-specialist-salary-a-deep-dive)
- [Key Factors That Influence Salary](#key-factors-that-influence-salary)
- [Job Outlook and Career Growth](#job-outlook-and-career-growth)
- [How to Get Started in This Career](#how-to-get-started-in-this-career)
- [Conclusion](#conclusion)
---
What Does a Client Success Specialist Do?

At its core, the role of a Client Success Specialist is fundamentally proactive, a stark contrast to the traditionally reactive nature of customer service. While customer service excels at resolving immediate, incoming issues, client success aims to anticipate needs, mitigate risks, and drive long-term value to ensure a client never has a reason to leave. They are the client's internal champion, their strategic advisor, and their primary point of contact post-sale.
The ultimate goal of a CSS is to ensure that clients achieve their desired outcomes while using a company's product or service. This mission is driven by the understanding that a successful client is a loyal client. A loyal client not only renews their contract but is also more likely to upgrade, expand their usage, and become a powerful source of referrals. This directly impacts key business metrics like Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), Net Revenue Retention (NRR), and churn rate.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks:
A Client Success Specialist's day is a multifaceted blend of communication, analysis, and strategic planning. Their responsibilities can be broken down into several key areas:
1. Onboarding and Implementation: When a new client signs on, the CSS takes the lead. They are responsible for a smooth and efficient onboarding process, which includes setting up accounts, providing initial training, and ensuring the client understands how to use the product to meet their specific goals from day one.
2. Relationship Management: The CSS builds and nurtures strong, long-term relationships with a dedicated portfolio of clients. This involves regular check-ins, business reviews, and being a consistent, reliable resource. They learn the client's business inside and out to become a trusted advisor.
3. Proactive Engagement and Education: Rather than waiting for a problem to arise, a CSS proactively reaches out with tips, best practices, and information about new features that could benefit the client. They might host webinars, create educational content, or conduct personalized training sessions.
4. Data Analysis and Health Scoring: A significant part of the role involves monitoring client usage data and health scores. By tracking key metrics, a CSS can identify at-risk clients who show signs of disengagement or dissatisfaction and intervene before they churn. Conversely, they can identify healthy, successful clients who are prime candidates for upselling or advocacy programs.
5. Driving Renewals and Identifying Expansion Opportunities: The CSS is directly responsible for customer retention. They manage the renewal process and actively look for opportunities to grow the account, whether through upselling to a higher-tier plan or cross-selling additional products or services.
6. Acting as the Voice of the Customer: The CSS gathers client feedback, both positive and negative, and funnels it back to the product, marketing, and sales teams. This crucial feedback loop helps the entire company improve its offerings and better meet market needs.
---
### A Day in the Life of a Client Success Specialist
To make this more tangible, let's walk through a typical day for a CSS named Alex, who works at a B2B software company.
- 9:00 AM - 10:00 AM: Morning Triage & Health Score Review. Alex starts the day by logging into the company’s Client Success platform (like Gainsight or ChurnZero) and CRM (Salesforce). She reviews her portfolio of 50 accounts, checking for any red flags—clients with low product usage, unresolved support tickets, or a declining health score. She flags three at-risk accounts for immediate outreach.
- 10:00 AM - 11:00 AM: Proactive Outreach. Alex drafts personalized emails to the three at-risk clients. For one, she offers a 30-minute strategy session to review their goals. For another with low usage, she shares a link to a new webinar on an advanced feature she knows would be valuable to them.
- 11:00 AM - 12:30 PM: Quarterly Business Review (QBR). Alex leads a video call with a key client. She presents a report showing their ROI and progress toward the goals they set three months ago. They discuss upcoming business initiatives and how the software can support them, identifying a potential upsell opportunity.
- 12:30 PM - 1:30 PM: Lunch & Professional Development. During lunch, Alex listens to an episode of the "Gain, Grow, Retain" podcast to stay current on industry trends.
- 1:30 PM - 2:30 PM: New Client Onboarding Call. Alex welcomes a new client who just signed their contract last week. She walks them through the implementation timeline, sets expectations, and schedules their team's first training session. Her goal is to ensure they feel supported and confident from the very beginning.
- 2:30 PM - 4:00 PM: Internal Collaboration. Alex meets with the product team to share feedback from her QBR. She explains that several clients have been requesting a specific integration. She then syncs with an Account Executive to discuss the upsell opportunity she identified earlier, strategizing the best way to approach the client.
- 4:00 PM - 5:00 PM: Prep & Planning. Alex spends the last hour of her day preparing for tomorrow's meetings, updating client notes in the CRM, and planning her outreach cadence for the rest of the week. She ends the day with a clear plan, having moved the needle on retention, expansion, and client advocacy.
---
Average Client Success Specialist Salary: A Deep Dive
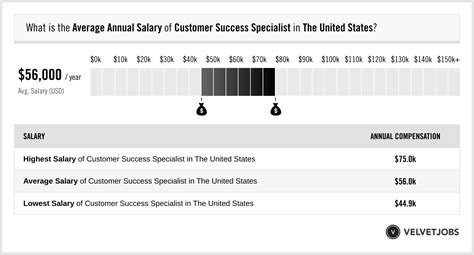
The salary for a Client Success Specialist is a reflection of the role's growing importance and direct impact on a company's bottom line. While compensation can vary widely based on several factors we'll explore in the next section, it's essential to first establish a solid baseline understanding of the national landscape.
According to recent data from leading salary aggregators, the compensation for a Client Success Specialist in the United States is highly competitive.
- Salary.com reports the median salary for a Client Success Specialist I (entry-level) is $61,865, with a typical range between $53,249 and $71,280. For a more experienced Client Success Specialist II, the median jumps to $72,581. (Source: Salary.com, 2024).
- Glassdoor indicates a national average base pay of $75,214 per year, with a "likely range" of $58,000 to $98,000. This figure is compiled from thousands of anonymously submitted salaries. (Source: Glassdoor, 2024).
- Payscale provides a slightly more conservative average base salary of $68,103 per year, with a reported range from $51,000 to $94,000. (Source: Payscale, 2024).
Synthesizing this data, a reasonable expectation for the national average salary for a Client Success Specialist is between $68,000 and $75,000 per year. However, this base salary is often just one piece of the total compensation puzzle.
### Salary by Experience Level
As with any profession, experience is a primary driver of earning potential. The career path in client success is well-defined, with clear salary increases at each stage.
| Experience Level | Typical Title(s) | Average Base Salary Range | Key Responsibilities |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Entry-Level (0-2 years) | Client Success Specialist, Customer Success Associate | $55,000 - $70,000 | Manages a portfolio of smaller accounts, handles onboarding, answers day-to-day questions, monitors client health. |
| Mid-Career (3-5 years) | Senior Client Success Specialist, Client Success Manager I | $70,000 - $95,000 | Manages more strategic or higher-value accounts, leads QBRs, mentors junior specialists, handles complex escalations. |
| Senior/Lead (6-9 years) | Lead Client Success Specialist, Client Success Manager II, Team Lead | $95,000 - $125,000+ | Manages the most critical enterprise accounts, develops success playbooks, may have direct reports, influences CS strategy. |
| Management/Director (10+ years) | Director of Client Success, VP of Customer Success | $130,000 - $200,000+ | Oversees the entire Client Success department, sets team-wide goals and KPIs, manages budget, reports to C-suite. |
*(Salary ranges are estimates based on aggregated data and can vary significantly based on the factors discussed in the next section.)*
### Beyond the Base: Understanding Total Compensation
A Client Success Specialist's salary is rarely just a flat number. The total compensation package often includes variable components that can significantly boost overall earnings. It's crucial to understand these elements when evaluating a job offer.
1. Base Salary:
This is the fixed, guaranteed portion of your pay. It's the most stable component and what the figures above primarily represent. A strong base salary provides financial security and is the foundation of your compensation.
2. Bonuses and Commissions (Variable Pay):
This is where the role's performance-based nature truly shines. Variable pay in client success is typically tied to key metrics that you directly influence. Common structures include:
- Retention-Based Bonuses: A bonus paid quarterly or annually for achieving a target Gross Retention Rate (GRR) or Net Revenue Retention (NRR) across your portfolio of clients. NRR is especially common, as it accounts for both renewals and expansion revenue (upsells/cross-sells).
- Upsell/Cross-sell Commission: A percentage of any new revenue you generate from your existing clients. For example, you might earn a 5-10% commission on any contract expansion you facilitate.
- MBOs (Management by Objectives): Bonuses tied to achieving specific, pre-defined goals. These could include improving a client's health score by a certain percentage, successfully onboarding a set number of new clients, or securing a certain number of client case studies.
This variable component can add anywhere from 10% to 30% (or more in high-performance scenarios) to your base salary, making it a powerful motivator and a significant part of your total earnings.
3. Stock Options or RSUs (Restricted Stock Units):
Particularly common in tech startups and publicly traded companies, equity is a form of compensation that gives you ownership in the company.
- Stock Options: Give you the right to buy company stock at a predetermined price in the future. Their value grows as the company's valuation increases.
- RSUs: Are a grant of company shares that vest over time. Once vested, they are yours to keep or sell.
Equity can be an extremely lucrative component of compensation, especially if you join a company that experiences significant growth.
4. Comprehensive Benefits Package:
While not direct cash, the value of a strong benefits package should not be underestimated. This includes:
- Health Insurance: Medical, dental, and vision coverage.
- Retirement Savings: 401(k) or similar plans, often with a company match.
- Paid Time Off (PTO): Vacation days, sick leave, and holidays.
- Professional Development Stipend: Funds for certifications, courses, and conferences to help you grow your skills.
- Other Perks: Remote work flexibility, wellness programs, parental leave, and commuter benefits.
When assessing a job offer, always look at the Total Compensation Package, not just the base salary. A lower base salary with a strong bonus structure and excellent benefits might be more valuable than a higher base salary with limited upside and poor benefits.
---
Key Factors That Influence a Client Success Specialist Salary
While the national averages provide a useful starting point, your actual salary as a Client Success Specialist will be determined by a complex interplay of several key factors. Understanding these variables is the first step toward strategically positioning yourself for maximum earning potential. This is the most critical section for anyone looking to not just enter the field, but to excel and command a top-tier salary.
###
1. Geographic Location
Where you work is one of the single most significant determinants of your salary. Companies in high-cost-of-living (HCOL) areas must offer higher salaries to attract and retain talent. This disparity is especially pronounced in the tech industry, where many Client Success roles are concentrated.
High-Paying Metropolitan Areas:
Tech hubs are notorious for their competitive salaries, driven by high demand and a steep cost of living. Expect salaries here to be 15-30% or more above the national average.
- San Francisco Bay Area, CA: (San Francisco, San Jose, Oakland) - Often the highest-paying region in the country. A mid-career CSS could easily earn $100,000-$130,000+ in base pay.
- New York, NY: A major hub for both tech and finance, offering highly competitive salaries.
- Seattle, WA: Home to Amazon and Microsoft, creating a high-demand environment for tech-adjacent roles.
- Boston, MA: A rapidly growing tech and biotech hub with salaries to match.
Mid-Tier & Emerging Tech Hubs:
These cities offer a better balance of strong salaries and a more manageable cost of living. Salaries here often track closely to or slightly above the national average.
- Austin, TX
- Denver, CO
- Chicago, IL
- Atlanta, GA
- Raleigh-Durham, NC (Research Triangle Park)
Lower-Cost-of-Living Areas:
In smaller cities or regions with a lower cost of living, salaries will typically be below the national average. However, your purchasing power may still be quite strong.
The Rise of Remote Work:
The pandemic has dramatically shifted the landscape of compensation for remote workers. Initially, many companies adjusted salaries based on the employee's location. However, a growing number of forward-thinking (often tech) companies are moving toward location-agnostic pay, offering the same salary for a role regardless of where the employee lives to attract the best talent nationwide. When looking for remote roles, be sure to clarify the company's compensation philosophy.
Example Salary Comparison by City (Mid-Career CSS):
| City | Estimated Average Base Salary |
| :--- | :--- |
| San Francisco, CA | $115,000 |
| New York, NY | $105,000 |
| Seattle, WA | $102,000 |
| Austin, TX | $88,000 |
| Chicago, IL | $85,000 |
| Kansas City, MO | $72,000 |
*(Data is illustrative, based on trends from sites like Payscale and Glassdoor.)*
###
2. Years and Quality of Experience
As shown in the salary table earlier, experience is a direct lever for compensation. However, it's not just about the number of years on your resume; it's about the *quality* and *relevance* of that experience.
- 0-2 Years (Entry-Level): At this stage, you're learning the ropes. Your focus is on mastering the fundamentals: onboarding, basic relationship management, and using CS tools. Salary growth comes from proving your competence and reliability.
- 3-5 Years (Mid-Career): You're no longer just executing tasks; you're becoming a strategist. Your value comes from your ability to manage larger, more complex accounts, lead strategic business reviews, and successfully de-escalate difficult situations. You can demonstrate a track record of high retention rates. This is often where the most significant salary jumps occur.
- 6-9 Years (Senior/Lead): You are now a subject matter expert. You not only manage the most critical enterprise-level clients but also contribute to the overall CS strategy. You might be mentoring junior team members, developing new "success plays," or specializing in a particular industry or product line. Your salary reflects your status as a leader and top performer.
- 10+ Years (Management): Moving into a Director or VP role requires a shift from managing clients to managing people and processes. Your salary is based on your ability to build and scale a high-performing team, control churn across the entire company, and align the CS department with executive-level business goals.
Actionable Tip: On your resume and in interviews, don't just list your responsibilities. Quantify your achievements. Instead of "Managed a portfolio of clients," write "Managed a $2M portfolio of 40 enterprise clients, achieving a 98% gross retention rate and 115% net revenue retention in FY2023."
###
3. Industry and Company Type & Size
The context in which you work plays a massive role in your paycheck. A CSS at a fast-growing B2B SaaS company will have a very different compensation structure than one at a stable manufacturing firm.
Industry:
The more complex the product and the higher the contract values, the higher the salary for the CSS who manages those clients.
- Technology (especially B2B SaaS): This is the highest-paying industry for Client Success. The products are complex, contract values are high (often tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars per year), and the impact of churn is enormous. Specialists in technically demanding fields like cybersecurity, enterprise data platforms, or fintech command top dollar.
- Healthcare & MedTech: A growing field for CS, with high-value clients (hospitals, insurance companies) and complex compliance needs. Salaries are very competitive.
- Financial Services: Similar to tech, involves high-stakes client relationships and complex products.
- Marketing & Advertising (Agencies): Salaries can be strong, but may be more variable and tied to client campaign performance.
- Non-Tech Industries (e.g., Manufacturing, CPG): While CS roles are emerging in these areas, salaries may lag behind the tech sector as the function is often less mature.
Company Type & Size:
- Early-Stage Startups (Seed/Series A): Will likely offer a lower base salary but compensate with significant equity (stock options). The risk is high, but the potential reward is immense if the company succeeds. The role is often broad, requiring you to wear many hats.
- Growth-Stage Companies (Series B/C and beyond): Often the "sweet spot." They offer a competitive base salary, a strong bonus structure, and still-meaningful equity. The company has found product-market fit, and you're there to help scale the success function.
- Large Public Corporations (e.g., Microsoft, Salesforce, Oracle): Tend to offer the highest base salaries and most structured bonus plans. They have well-defined career ladders and excellent benefits. The trade-off may be less autonomy and a more siloed role. Equity is often in the form of RSUs, which are less risky than options.
- Non-Profits: Salaries are almost always lower than in the for-profit sector. Professionals choose these roles for mission alignment and personal fulfillment, not maximum financial gain.
###
4. In-Demand Skills and Specializations
The skills you possess directly translate into value for an employer, and high-value skills command high salaries. Cultivating a blend of hard and soft skills is essential for maximizing your income.
High-Value Hard Skills:
- CRM & CS Platform Proficiency: Expertise in tools like Salesforce (CRM) and Gainsight, ChurnZero, or Catalyst (CS Platforms) is non-negotiable. Being a "power user" who can build reports, create automated playbooks, and derive insights from the data is a huge differentiator.
- Data Analysis: The ability to go beyond pre-built dashboards. You should be comfortable using Excel or Google Sheets (pivot tables, VLOOKUPs) and ideally have some familiarity with data visualization tools like Tableau or Power BI. This allows you to tell a compelling, data-backed story about client value.
- Technical Aptitude: You don't need to be a coder, but for tech roles, a solid understanding of the product's architecture, APIs, and integration capabilities is highly valuable. This allows you to troubleshoot more effectively and speak credibly with clients' technical teams.
- Project Management: Skills in managing complex onboarding projects or strategic initiatives, using frameworks like Agile or tools like Asana or JIRA, can justify a higher salary.
Crucial Soft Skills (often more important than hard skills):
- Strategic & Commercial Acumen: Understanding your client's business model, market pressures, and financial goals. This allows you to position your product not as a tool, but as a solution to their core business problems, which is the foundation for upselling and renewal conversations.
- Empathy & Active Listening: The ability to genuinely understand a client's frustrations and aspirations. This builds trust and transforms the relationship from a vendor-client dynamic to a true partnership.
- Negotiation & Influence: Skillfully navigating difficult conversations, from handling contract renewals and price increases to influencing internal product roadmaps based on client feedback.
- Advanced Communication: Being able to clearly articulate value, present compelling business reviews to executives, and de-escalate tense situations with grace and professionalism.
###
5. Level of Education and Certifications
While experience often trumps education in this field, your academic and professional credentials can still have a notable impact, especially early in your career or when moving into leadership.
- Bachelor's Degree: A bachelor's degree is typically a minimum requirement. Degrees in Business Administration, Marketing, Communications, or a related field are most common and provide a strong foundation.
- Master's Degree (e.g., MBA): An MBA is generally not required for a CSS role but can be a significant advantage for those aspiring to leadership positions like Director or VP of Customer Success. It equips you with the high-level financial and strategic thinking skills needed to manage a department and contribute to executive-level strategy.
- Professional Certifications: This is an increasingly important differentiator. Certifications demonstrate a commitment to the profession and a standardized level of expertise. They can directly lead to higher salary offers.
Top Certifications for Client Success Professionals:
- Gainsight Admin Certification: Signals expertise in one of the leading CS platforms.
- Certified Customer Success Manager (CCSM) by SuccessHACKER: A well-respected, multi-level certification program covering the fundamentals and advanced strategies of CS.
- Salesforce Administrator/Consultant Certifications: Highly valuable as Salesforce is the dominant CRM and is often integrated with CS platforms.
- HubSpot Certifications: Relevant for companies using the HubSpot ecosystem.
- Project Management Professional (PMP): Useful for those in roles with heavy implementation or project management components.
By strategically developing these five areas, you can actively steer your career toward higher compensation brackets and create a professional profile that is highly sought after by top-tier employers.
---
Job Outlook and Career Growth

For anyone considering a career as a Client Success Specialist, the future is exceptionally bright. The role is not just a passing trend; it represents a fundamental shift in how businesses operate, moving from a transactional, acquisition-focused model to a relationship-based, retention-focused one. This paradigm shift ensures that the demand for skilled CS professionals will continue to grow robustly for the foreseeable future.
While the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) does not yet have a dedicated category for "Client Success Specialist," we can infer its growth trajectory by looking at related and overarching occupations. The BLS projects that employment for "Customer Service Representatives" is expected to decline slightly, but this category often represents more traditional, reactive support roles. A better proxy is the broader category of "Business and Financial Operations Occupations," which the BLS projects will grow by 7% from 2022 to 2032, faster than the average for all occupations. This will result in about 712,700 new jobs over the decade. (Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2023).
Industry-specific data paints an even more optimistic picture. Reports from Forrester and other market research firms consistently highlight customer retention and experience as the top priorities for C-level executives. A 2022 report by Gainsight, a leading customer success software provider, emphasized
