For individuals with a passion for cars and a talent for hands-on work, a career in collision repair offers a stable and rewarding path. But beyond the satisfaction of restoring a damaged vehicle to its former glory, what is the earning potential? A collision repair salary is not a single number; it's a dynamic figure influenced by skill, location, and specialization.
While entry-level positions start in a promising range, highly skilled, certified master technicians can earn well over $100,000 annually. This guide will break down the typical salary for a collision repair technician and explore the key factors you can control to maximize your income in this in-demand trade.
What Does a Collision Repair Technician Do?

Often referred to as an auto body technician or automotive body repairer, a collision repair technician is a skilled professional who repairs vehicles after they've been damaged in an accident. This is far more than just fixing dents; the role is increasingly technical and requires a diverse skill set.
Key responsibilities include:
- Assessing Damage: Evaluating the full extent of vehicle damage, from surface-level scratches to complex structural issues.
- Structural Repair: Using sophisticated hydraulic and frame-straightening equipment to restore the vehicle's frame and unibody to factory specifications.
- Body Repair & Replacement: Repairing or replacing damaged body panels, including fenders, doors, and bumpers made from steel, aluminum, plastic, and composites.
- Refinishing: Preparing surfaces and applying multiple layers of paint to perfectly match the original factory finish.
- Systems Diagnosis: Increasingly, this includes working with vehicle electronics, such as recalibrating Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) like cameras and sensors that are disturbed during a repair.
Average Collision Repair Salary
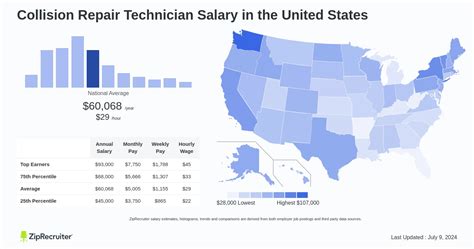
The salary for a collision repair technician can vary significantly, but data from authoritative sources provides a clear picture of the earning landscape.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for automotive body and glass repairers was $51,890 in May 2023. The lowest 10 percent earned less than $34,440, while the top 10 percent earned more than $83,230.
Reputable salary aggregators often report slightly higher averages, reflecting real-time, user-submitted data and the common commission-based pay structures in the industry.
- Salary.com reports that the average Auto Body Repair Technician salary in the United States is $67,610 as of May 2024, with a typical range falling between $58,546 and $76,711.
- Payscale places the average base salary at around $56,500 per year, but notes that total pay, including bonuses and commission, can reach up to $91,000.
It's crucial to understand that many experienced technicians work on a "flat-rate" or commission basis. They are paid a set number of hours for a specific job, regardless of how long it actually takes them. An efficient, skilled technician can complete jobs faster than the allotted time, significantly increasing their hourly and annual earnings.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your starting salary is just that—a start. Several key factors directly impact your ability to climb the income ladder in the collision repair industry.
### Level of Education and Certification
While a four-year degree is not required, formal training and industry certifications are paramount for higher earnings.
- Vocational/Technical School: Graduating from a postsecondary collision repair program provides a strong foundation in modern repair techniques and safety procedures, making you a more attractive candidate than someone with no formal training.
- I-CAR Certifications: The Inter-Industry Conference on Auto Collision Repair (I-CAR) is the gold standard for training. Technicians who achieve "Platinum" status by completing a rigorous series of courses are recognized as experts and are in high demand, commanding top-tier salaries.
- ASE Certifications: Certifications from the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), particularly in Collision Repair and Refinish (B-series), validate your skills and boost your credibility and earning potential.
- Manufacturer-Specific Training: As vehicles become more complex, certifications from manufacturers like Tesla, BMW, Ford (for aluminum), and Honda are highly valuable. Shops that are certified to repair these specific brands require technicians with this training and pay them a premium.
### Years of Experience
Experience is one of the most significant drivers of salary growth. A technician's career and income typically progress along a clear path.
- Entry-Level / Apprentice (0-2 years): In this stage, you are learning the trade, often assisting senior technicians. Salaries typically range from $35,000 to $48,000 as you build your skills and efficiency.
- Mid-Career Technician (3-8 years): With solid experience, you can work independently and efficiently. Technicians at this level have likely earned key certifications and can expect to earn between $55,000 and $75,000, especially if they are on a flat-rate pay system.
- Senior / Master Technician (8+ years): These are the experts in the shop. They often hold multiple I-CAR Platinum and ASE Master certifications and may specialize in complex structural repairs or diagnostics. Their deep expertise and high efficiency can push their annual earnings to $80,000, $90,000, and often well over $100,000.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Demand for skilled technicians and the cost of living can dramatically affect your salary. According to the BLS, the top-paying states for automotive body repairers are:
1. Washington: ($69,820 average)
2. Maryland: ($67,770 average)
3. California: ($67,110 average)
4. Colorado: ($65,160 average)
5. New Jersey: ($65,040 average)
Metropolitan areas with heavy traffic and a higher concentration of vehicles generally offer more job opportunities and higher wages than rural locations.
### Company Type
The type of shop you work for also plays a role in your compensation package and earning ceiling.
- Dealerships: Often offer competitive wages, factory training, and steady work on newer vehicles of a specific brand. They typically have excellent benefits packages.
- National Collision Chains (e.g., Caliber Collision, Gerber): These large companies provide structured career paths, standardized training programs, and comprehensive benefits. Their size can offer stability and consistent workflow.
- Independent Body Shops: Pay can vary widely. High-end, specialty independent shops that work on luxury or classic cars can offer some of the highest earning potentials. Smaller, local shops may offer more flexibility but might have less consistent work or fewer benefits.
### Area of Specialization
Developing expertise in a high-demand niche is one of the fastest ways to increase your value.
- Structural and Frame Repair: This requires immense skill and precision. Technicians who can expertly analyze and repair a vehicle's frame are invaluable and among the highest earners.
- Automotive Refinishing (Painting): A skilled painter who can perfectly match colors and produce a flawless finish is an artist in the trade and is compensated accordingly.
- Aluminum and Advanced Materials: Repairing aluminum and other high-strength, lightweight materials found in modern vehicles requires special tools and training. Technicians with these skills are sought after.
- ADAS Calibration: As nearly all new cars come with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems, technicians who can diagnose, repair, and recalibrate these complex sensor systems are on the cutting edge of the industry and can command a premium salary.
Job Outlook

The future for skilled collision repair technicians is bright. The BLS projects about 11,500 openings for automotive body and glass repairers each year, on average, over the next decade. While overall employment growth is expected to be slower than average, these openings will arise from the need to replace workers who retire or transition to different occupations.
Furthermore, the increasing complexity of vehicles—with their advanced materials, intricate electronics, and sophisticated safety systems—means that the demand for *highly trained and certified technicians* will remain strong. Those who continuously update their skills will be best positioned for career stability and growth.
Conclusion

A career in collision repair offers a direct path to a stable, well-paying profession without the need for a traditional four-year degree. While the median salary provides a solid baseline, your ultimate earning potential is in your hands.
For those considering this field, the message is clear: focus on excellence. Pursue formal training, commit to lifelong learning through certifications like I-CAR and ASE, and develop a specialization. By becoming an expert in your craft, you can build a financially rewarding and personally fulfilling career, turning mangled metal back into a work of art, one vehicle at a time.
