Table of Contents

- [Introduction](#introduction)
- [What Does a Customer Success Specialist Do?](#what-does-a-customer-success-specialist-do)
- [Average Customer Success Specialist Salary: A Deep Dive](#average-customer-success-specialist-salary-a-deep-dive)
- [Key Factors That Influence Salary](#key-factors-that-influence-salary)
- [Job Outlook and Career Growth](#job-outlook-and-career-growth)
- [How to Get Started in This Career](#how-to-get-started-in-this-career)
- [Conclusion](#conclusion)
Introduction

In the modern business landscape, particularly within the booming technology and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) sectors, the old adage "the customer is king" has evolved. It's no longer enough to simply acquire a customer; the real value lies in retaining them, growing with them, and ensuring they achieve their desired outcomes using your product or service. This is the world of Customer Success, and the Customer Success Specialist (CSS) is its most vital champion. If you're drawn to a career that blends strategic thinking, deep relationship-building, and a direct impact on a company's bottom line, you've found your calling. But beyond the fulfillment, what is the financial reality? A career as a Customer Success Specialist is not only professionally rewarding but also financially lucrative, with an average salary in the United States often landing between $65,000 and $85,000, and senior professionals commanding well over $120,000 annually.
I've spent over a decade analyzing career trajectories, and I remember a pivotal conversation with a VP of Sales a few years ago. He told me, "We used to celebrate the 'close.' Now, we celebrate the 'renewal.' My best salesperson isn't the one who signs the biggest initial deal; it's the Customer Success Specialist who ensures that deal renews and expands year after year." That single comment crystallizes the immense value and growing prestige of this critical role.
This guide is designed to be your definitive resource for understanding the Customer Success Specialist salary. We will dissect national averages, explore the nuanced factors that can dramatically increase your earning potential, and lay out a clear roadmap for how you can enter and thrive in this dynamic field. Whether you're a recent graduate, a professional looking to pivot, or an existing CSS aiming for the next level, this article will provide the data-driven insights and expert advice you need to navigate your career path with confidence.
What Does a Customer Success Specialist Do?

At its core, the role of a Customer Success Specialist is fundamentally proactive, not reactive. This is the single most important distinction between Customer Success and traditional Customer Service. While a customer service agent reacts to problems (e.g., a support ticket, a complaint call), a Customer Success Specialist works proactively to ensure problems never arise in the first place. Their primary goal is to help customers achieve maximum value and success from the product or service they've purchased, thereby ensuring long-term customer loyalty, retention, and growth.
A CSS acts as a trusted advisor and advocate for a portfolio of clients. They are the main point of contact post-sale and are responsible for the entire customer lifecycle, from initial onboarding to renewal and expansion. They build deep, strategic relationships, understanding their clients' business goals, challenges, and definitions of success.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks:
- Customer Onboarding: Guiding new customers through the initial setup, training, and implementation process to ensure a smooth and successful start.
- Relationship Management: Building and maintaining strong, long-lasting relationships with key stakeholders within their client accounts. This involves regular check-ins, strategic calls, and being their go-to resource.
- Health Monitoring: Proactively tracking customer health scores using various metrics (e.g., product usage, engagement levels, support tickets logged). They identify at-risk customers and develop intervention strategies to prevent churn.
- Strategic Business Reviews (QBRs/EBRs): Conducting quarterly or executive business reviews to showcase the value the customer has received, align on future goals, and identify opportunities for deeper engagement.
- Driving Product Adoption: Encouraging customers to use more features and functionalities of the product that will help them achieve their goals, thus embedding the solution deeper into their daily workflows.
- Customer Advocacy: Acting as the "voice of the customer" internally, relaying feedback, feature requests, and pain points to the Product, Marketing, and Engineering teams.
- Renewals and Upselling: While some companies have dedicated Renewal Managers, the CSS is almost always responsible for ensuring the customer is happy and likely to renew. They also identify opportunities for upselling (e.g., more licenses, premium features) or cross-selling (other products).
---
### A Day in the Life of a Customer Success Specialist
To make this tangible, let's walk through a typical day for a CSS named Alex, who works at a mid-sized B2B SaaS company.
- 8:30 AM - 9:30 AM: Morning Triage & Health Check. Alex starts the day by logging into the Customer Success platform (like Gainsight or ChurnZero) and reviewing the health dashboard for their portfolio of 60 accounts. They notice a key account's usage has dropped significantly in the past week. Alex flags this for immediate follow-up and sends a quick, friendly email: "Hey Sarah, noticed things have been a bit quiet on the platform. Just wanted to check in and see if there's anything I can help with."
- 9:30 AM - 11:00 AM: New Client Onboarding Call. Alex leads a kickoff call with a new client that signed last week. They walk the client's team through the implementation plan, set expectations for the first 90 days, schedule key training sessions, and, most importantly, ask, "What does a successful outcome look like for you in six months?"
- 11:00 AM - 12:00 PM: Internal Sync. Alex joins a weekly meeting with the Product team to share feedback gathered from clients. They advocate for a feature request that three of their largest clients have mentioned, providing specific use cases to build a strong business case.
- 12:00 PM - 1:00 PM: Lunch & Learn. Alex attends a company-wide session on a new product feature, taking detailed notes to be able to explain its value and functionality to clients.
- 1:00 PM - 2:30 PM: Preparing for a QBR. Alex has a Quarterly Business Review tomorrow with a major client. They spend this time pulling data, analyzing usage trends, and building a presentation that demonstrates the ROI the client has achieved over the last three months. The goal is to reinforce value and set the stage for a conversation about upgrading to the premium tier.
- 2:30 PM - 4:00 PM: Proactive Outreach & Strategic Check-ins. Alex dedicates a block of time to proactive communication. They send a "best practice" tip to a few clients who could be using a specific feature more effectively. They also call two of their "healthy" but quiet accounts just to maintain the relationship and see if they have any upcoming strategic initiatives where the product could help.
- 4:00 PM - 5:00 PM: Closing Loops & Admin. Alex responds to various client emails that came in throughout the day. They update the CRM (like Salesforce) with notes from all their calls and meetings, ensuring a clean record of all customer interactions. They get a response from Sarah (the at-risk account from the morning), who explains her team was tied up on a priority project but is ready to re-engage next week. Alex schedules a call to help them get back on track.
This "day in the life" illustrates the highly varied, strategic, and relationship-driven nature of the Customer Success Specialist role. It's a blend of data analysis, project management, teaching, and strategic consulting.
Average Customer Success Specialist Salary: A Deep Dive

Understanding the compensation for a Customer Success Specialist requires looking beyond a single number. The salary is a composite of base pay, variable compensation like bonuses, and a range of other benefits that contribute to the total earnings package. Here, we will break down the salary expectations based on data aggregated from authoritative sources like Glassdoor, Payscale, Salary.com, and industry-specific reports from firms like Gainsight and Catalyst. Please note that these figures represent a snapshot in time (late 2023/early 2024) and can fluctuate with market conditions.
### National Average and Salary Ranges
Across the United States, the average base salary for a Customer Success Specialist typically falls in a robust range.
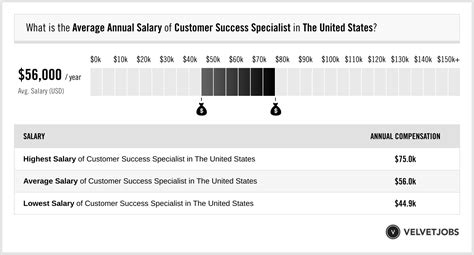
- National Average Base Salary: Approximately $75,000 per year.
- Typical Salary Range: Most Customer Success Specialists can expect to earn between $58,000 and $96,000 in base salary.
However, this broad range is heavily influenced by experience. The journey from an entry-level position to a senior, strategic role is accompanied by significant financial growth.
### Salary by Experience Level
The career ladder in Customer Success is well-defined, and compensation scales accordingly. Here’s a detailed breakdown of what you can expect to earn at different stages of your career.
| Experience Level | Years of Experience | Typical Base Salary Range | Key Responsibilities |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Entry-Level (Associate CSS) | 0 - 2 years | $55,000 - $70,000 | Learning the product, managing a smaller/less complex book of business, handling basic onboarding, responding to inbound client queries. |
| Mid-Career (CSS) | 2 - 5 years | $70,000 - $90,000 | Managing a full portfolio of clients, conducting QBRs, proactive health monitoring, identifying upsell opportunities, mentoring junior team members. |
| Senior (Senior CSS/Strategic CSS)| 5 - 8+ years | $90,000 - $125,000+ | Managing the most strategic/high-value accounts, handling complex renewals and escalations, developing CS playbooks, acting as a subject matter expert. |
| Team Lead / Manager | 6 - 10+ years | $110,000 - $150,000+ | Managing a team of CSSs, setting team KPIs, hiring and training, managing the overall health of a large customer segment. |
| Director / VP of Customer Success | 10+ years | $160,000 - $250,000+ | Setting the entire CS strategy for the company, managing a large department, reporting to the C-suite, owning net revenue retention (NRR) goals. |
*Source: Data compiled and synthesized from Glassdoor, Payscale, and recent tech industry salary surveys.*
As you can see, the growth potential is substantial. A professional who starts as an Associate CSS can realistically double their base salary within 5-7 years by demonstrating value, developing key skills, and taking on more strategic responsibility.
### Deconstructing the Compensation Package: Beyond the Base Salary
The base salary is only one piece of the puzzle. A significant portion of a Customer Success Specialist's total compensation often comes from variable pay and other benefits. It's crucial to evaluate the entire offer when considering a role.
1. Bonuses and Variable Compensation:
Unlike traditional sales roles that are heavily commission-based, Customer Success compensation is often tied to retention and growth metrics. This aligns the CSS's goals with the company's long-term health.
- Bonus Structure: Most CSS roles include a quarterly or annual bonus, which can range from 10% to 25% of the base salary.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Bonuses:
- Gross Revenue Retention (GRR): The percentage of revenue retained from existing customers, not including upsells. A common target is 90%+.
- Net Revenue Retention (NRR): This is the holy grail. It includes revenue from renewals *plus* revenue from expansion (upsells/cross-sells), minus revenue churn. A world-class NRR is above 120%.
- Customer Health Score: A composite score based on product usage, survey responses, and other engagement metrics.
- Logo Retention: The percentage of customers (by logo/name) that renew their contracts.
Example: A mid-career CSS with an $80,000 base salary and a 15% bonus target could earn an additional $12,000 per year, bringing their total cash compensation to $92,000 if they hit their targets.
2. Stock Options / Equity:
Particularly prevalent in startups and pre-IPO tech companies, equity can be a highly lucrative component of the compensation package.
- Startups: Often offer a lower base salary but compensate with a more significant grant of stock options (e.g., ISOs or RSUs). This is a high-risk, high-reward proposition that could be worth a substantial amount if the company is successful (i.e., gets acquired or goes public).
- Public Companies: May offer Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) as part of an annual compensation package, which vest over a period of several years. This is a more stable and predictable form of equity compensation.
3. Standard Benefits:
Beyond cash and equity, a comprehensive benefits package adds significant value. When comparing offers, look for:
- Health Insurance: Medical, dental, and vision coverage. Look at the quality of the plans and the percentage of the premium covered by the employer.
- Retirement Savings: A 401(k) plan, ideally with a company match. An employer match is essentially free money and should be factored into your total compensation analysis.
- Paid Time Off (PTO): Generous vacation, sick leave, and holiday policies. Some progressive companies now offer unlimited PTO.
- Professional Development: A budget for courses, certifications, and conferences. This is a huge perk, as it allows you to invest in the skills that will increase your future earning potential.
- Other Perks: Remote work flexibility, commuter benefits, wellness stipends, parental leave, and more.
In summary, when evaluating a Customer Success Specialist salary, it's essential to look at the Total Rewards Statement. A role with a $75,000 base salary, a 20% bonus potential, a strong 401(k) match, and a good professional development budget can be far more valuable than a role with a flat $85,000 base salary and minimal benefits.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

While the national averages provide a useful benchmark, a Customer Success Specialist's salary is not a one-size-fits-all number. Several key factors can dramatically influence your earning potential, pushing your compensation well above or below the median. Understanding these levers is the key to maximizing your income throughout your career. This is the most critical section for anyone looking to strategically build their career and command a top-tier salary.
Level of Education
While Customer Success is a field that values experience and skills over rigid academic credentials, your educational background still plays a role, particularly in opening doors and setting your initial salary baseline.
- Bachelor's Degree (The Standard): A bachelor's degree is typically the minimum requirement for most CSS roles. There isn't one "correct" major, but degrees in Business Administration, Marketing, Communications, or Psychology are highly valued. They provide a strong foundation in commercial acumen, interpersonal skills, and understanding human behavior—all core tenets of Customer Success. An entry-level candidate with a relevant degree from a reputable university may be able to negotiate a salary at the higher end of the entry-level bracket.
- Master's Degree (The Accelerator): A Master's in Business Administration (MBA) or a related field is generally not required for an individual contributor CSS role. However, it becomes a significant advantage for those aspiring to leadership positions (Manager, Director, VP). An MBA can fast-track your path to management and command a significantly higher salary, often a 15-20% premium, as it equips you with advanced strategic, financial, and operational skills.
- Certifications (The Differentiator): In the world of Customer Success, industry-recognized certifications are arguably more impactful on salary than an advanced degree for non-leadership roles. They signal to employers that you have specific, practical knowledge and are committed to the profession. Holding certifications can be a powerful negotiation tool.
- Top Certifications:
- Gainsight Admin Certification: For the leading CS platform, this is highly sought after.
- SuccessHACKER's Certified Customer Success Manager (CCSM): A well-respected, foundational certification program.
- SuccessCOACHING Certifications: Offers various levels, from foundational to leadership.
- Cisco Customer Success Manager (DTCSM): A globally recognized certification.
- Salary Impact: Possessing one or more of these certifications can add $5,000 to $15,000 to your annual salary, as it reduces the training burden on the employer and demonstrates proven expertise.
Years of Experience
Experience is, without a doubt, the single most significant factor determining a CSS's salary. The profession rewards those who have a track record of retaining and growing accounts. The career and salary progression is often steep and rewarding.
- 0-2 Years (Associate/Entry-Level): *Salary Range: $55,000 - $70,000.* At this stage, you are learning the ropes. Your focus is on executing plays defined by others, managing smaller accounts, and mastering the product and basic CS motions like onboarding. Your value is in your potential and ability to learn quickly.
- 2-5 Years (Mid-Career): *Salary Range: $70,000 - $90,000.* You've proven yourself. You can now manage a full portfolio of mid-market or even some enterprise accounts independently. You're trusted to run QBRs, manage minor escalations, and think strategically about your book of business. Employers are paying for your proven ability to prevent churn and drive positive outcomes.
- 5-8+ Years (Senior/Strategic): *Salary Range: $90,000 - $125,000+.* You are no longer just managing accounts; you are a strategic partner to your clients and a leader within your team. You handle the most complex, high-value, and at-risk accounts. You may be involved in creating CS strategies, mentoring junior CSSs, and working cross-functionally to improve the overall customer experience. Your salary reflects your ability to protect and grow millions of dollars in annual recurring revenue (ARR).
- Leadership (Manager/Director): *Salary Range: $110,000 - $250,000+.* At this level, your compensation is tied to the performance of your entire team and department. Your experience is leveraged to build and scale a world-class Customer Success organization. Your salary reflects your impact on the company's most important metric: Net Revenue Retention.
Geographic Location
Where you live and work has a profound impact on your salary, largely due to variations in cost of living and the concentration of tech companies. The rise of remote work has started to flatten these differences slightly, but geographic pay differentials remain a major factor.
High-Paying Metropolitan Areas:
These cities are major tech hubs with high demand for CS talent and a correspondingly high cost of living.
| City | Average CSS Base Salary | Why It's High |
| :--- | :--- | :--- |
| San Francisco Bay Area, CA | $95,000 - $130,000+ | The epicenter of the global tech industry; intense competition for talent. |
| New York, NY | $85,000 - $120,000+ | Major hub for tech (especially FinTech and AdTech) and finance; high cost of living. |
| Boston, MA | $80,000 - $110,000+ | Strong biotech and tech scene, fueled by world-class universities. |
| Seattle, WA | $80,000 - $110,000+ | Home to tech giants like Amazon and Microsoft and a thriving startup ecosystem. |
| Austin, TX | $75,000 - $105,000+ | A rapidly growing tech hub attracting companies from California; "Silicon Hills." |
Mid-Tier & Lower-Paying Areas:
Salaries in smaller cities or regions with a lower cost of living will be closer to or slightly below the national average.
- Cities like Chicago, IL; Denver, CO; and Atlanta, GA often have salaries in the $70,000 - $95,000 range.
- Smaller cities in the Midwest and Southeast might see salaries in the $60,000 - $80,000 range.
The Remote Work Effect: The pandemic accelerated the trend of remote work. Some companies now pay a single "national rate" regardless of location. However, many still use "geo-arbitrage," adjusting salaries based on the employee's location. A CSS working remotely for a San Francisco-based company but living in St. Louis, MO, might earn more than the local St. Louis average but less than their Bay Area counterparts. When applying for remote roles, it is crucial to clarify the company's compensation philosophy regarding location.
Company Type & Size
The type of company you work for—its size, stage, and industry—is another powerful determinant of your salary and overall compensation structure.
- Early-Stage Startups (Seed to Series B):
- Salary: Typically lower base salary.
- Compensation Mix: Heavy on equity (stock options). The philosophy is "build it with us, and we'll all win big."
- Pros: Huge learning opportunity, direct impact, exciting culture, massive potential upside from equity.
- Cons: High risk, long hours, less job security, lower cash compensation.
- Growth-Stage Companies (Series C to Pre-IPO):
- Salary: Competitive base salary, often close to market-rate.
- Compensation Mix: A strong blend of base salary, bonus, and still-meaningful equity.
- Pros: The "sweet spot" for many. The company is established but still growing fast. Processes are being built, offering a chance to make an impact.
- Cons: Can be chaotic as the company scales ("building the plane while flying it").
- Large Public Corporations (e.g., Salesforce, Microsoft, Adobe):
- Salary: High base salary and predictable bonus structure.
- Compensation Mix: Dominated by cash (base + bonus) and RSUs (publicly traded stock).
- Pros: High job security, excellent benefits, structured career paths, brand recognition on your resume.
- Cons: Can be more bureaucratic, slower-paced, and your individual impact may feel smaller.
- Non-Tech Companies: As the CS function expands, industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and finance are hiring CSSs. Salaries may be slightly lower than in pure tech but are often more stable and may offer a better work-life balance.
Area of Specialization
Just as doctors specialize, so too can Customer Success Specialists. Developing expertise in a complex, high-stakes vertical can lead to a significant salary premium.
- Technical/Developer-Focused CS: If you are supporting a highly technical product sold to engineers (e.g., an API, a cloud infrastructure tool), your role requires deep technical acumen. These "Technical Success Manager" roles often command a 15-25% salary premium because the talent pool is much smaller.
- FinTech (Financial Technology): Working with banks, investment firms, and insurance companies requires an understanding of finance, security, and complex regulations. This specialization is highly lucrative.
- HealthTech (Healthcare Technology): Supporting EMR systems or other clinical software requires knowledge of healthcare workflows and regulations like HIPAA. This is a growing and well-compensated field.
- Cybersecurity: Given the mission-critical nature of security products, CS professionals in this space are highly valued and compensated accordingly.
- Enterprise vs. SMB/Mid-Market: A CSS managing a handful of "enterprise" accounts (large corporations with contracts worth $100k+ per year) will almost always earn more than a CSS managing a large volume of "SMB" (small-to-medium business) accounts. The strategic complexity and revenue responsibility are far greater.
In-Demand Skills
Finally, your specific skill set is what makes you valuable. Cultivating high-impact skills is the most direct way to increase your salary.
- Hard Skills (The "What You Can Do"):
- Platform Proficiency: Expertise in CS platforms like Gainsight or ChurnZero and CRM systems like Salesforce is non-negotiable for top roles.
- Data Analysis: The ability to interpret usage data, health scores, and customer feedback to derive actionable insights. Knowing how to use tools like Excel/Google Sheets, and even basic BI tools like Tableau or Looker, is a major plus.
- Project Management: Skills in managing complex onboarding projects or renewal processes, using tools like Asana