Ever stood at an airport window, watching a 300-ton marvel of engineering like a Delta Airbus A350 push back from the gate, and felt a sense of awe? It’s a breathtaking sight, a testament to human ingenuity. But behind that awe-inspiring moment of takeoff are the unseen heroes on the ground: the highly skilled, meticulously trained Aircraft Maintenance Technicians (AMTs), more commonly known as aircraft mechanics. They are the guardians of safety, the professionals whose expertise and diligence ensure every single flight is airworthy.
This isn't just a job with a wrench; it's a high-stakes, high-demand career that offers immense professional pride, exceptional stability, and significant financial rewards. For those with a passion for mechanics and a calm, focused demeanor under pressure, a career as a Delta Aircraft Mechanic is one of the most respected and lucrative paths in the skilled trades. The salary potential is substantial, with experienced technicians at major airlines like Delta often earning well into the six-figure range when factoring in overtime and bonuses.
I once spoke with a veteran Delta AMT with over 20 years of experience in the hangars at Atlanta's Hartsfield-Jackson International Airport. He described the feeling of signing his name in a maintenance logbook after a major engine repair as "a profound weight of responsibility and an undeniable badge of honor." That sentiment perfectly encapsulates the gravity and prestige of this vital profession. It’s a career where your work has a direct and tangible impact on the safety of hundreds of people every single day.
This comprehensive guide will serve as your flight plan to understanding and achieving a career as a Delta Aircraft Mechanic. We will perform a deep-dive analysis into the Delta Aircraft Mechanic salary, explore the myriad factors that influence your earning potential, break down the job outlook, and provide a clear, step-by-step roadmap to getting started.
### Table of Contents
- [What Does a Delta Aircraft Mechanic Do?](#what-does-a-delta-aircraft-mechanic-do)
- [Delta Aircraft Mechanic Salary: A Deep Dive](#delta-aircraft-mechanic-salary-a-deep-dive)
- [Key Factors That Influence an Aircraft Mechanic's Salary](#key-factors-that-influence-salary)
- [Job Outlook and Career Growth for Aircraft Mechanics](#job-outlook-and-career-growth)
- [How to Become a Delta Aircraft Mechanic: Your Step-by-Step Guide](#how-to-get-started-in-this-career)
- [Conclusion: Is a Career as a Delta AMT Right for You?](#conclusion)
What Does a Delta Aircraft Mechanic Do?

A Delta Aircraft Mechanic is a highly specialized professional responsible for ensuring the safety and airworthiness of Delta Air Lines' entire fleet. This is far more than just "fixing" planes; it involves a rigorous and legally mandated schedule of inspections, maintenance, troubleshooting, and repair on some of the most sophisticated machinery in the world. Their work environment can range from a climate-controlled hangar where massive, scheduled overhauls take place, to the fast-paced environment of the flight line, where they act as first responders to address issues between flights.
Their core mission is to maintain aircraft in perfect compliance with the strict standards set by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and the manufacturer's specifications. The work is precise, documented, and critical. There is no room for error.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks:
An AMT's duties are varied and depend on their specific role (line vs. hangar maintenance) and area of specialization. However, some universal tasks include:
- Inspections: Performing routine checks (daily and pre-flight) and more intensive, scheduled heavy maintenance checks (known as A, C, and D checks) that can involve taking large sections of the aircraft apart.
- Troubleshooting: Using advanced diagnostic equipment, technical manuals, and deep system knowledge to diagnose and resolve complex mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, and electronic issues reported by flight crews or discovered during inspections.
- Repair and Replacement: Repairing or replacing a vast array of components, from simple items like tires and brakes to complex systems like engines, landing gear, flight control surfaces, and advanced avionics.
- Preventative Maintenance: Conducting proactive maintenance to prevent future problems, including lubrication, component testing, and system calibrations.
- Documentation: Meticulously documenting every single task performed in the aircraft's official maintenance logbook. This record-keeping is a legal requirement and serves as a complete history of the aircraft's maintenance life.
- Collaboration: Working closely with other mechanics, avionics technicians, engineers, maintenance control, and flight crews to ensure a seamless and safe operation.
### A Day in the Life of a Hangar Maintenance Mechanic
To make this role more tangible, let’s walk through a hypothetical day for an AMT working on a heavy maintenance check at one of Delta's TechOps facilities:
- 5:45 AM: Arrive at the facility, change into your uniform, and grab a coffee.
- 6:00 AM: Attend the pre-shift briefing with your crew lead. The lead outlines the day's primary objectives for the Boeing 757 currently undergoing a C-check. Your specific task is to assist with the landing gear inspection and operational tests.
- 6:30 AM: You and a senior mechanic head to the aircraft. You review the specific work cards (job instructions) for the task, gather the required tools and specialized equipment, and follow all safety procedures (like tagging out circuit breakers) before beginning work.
- 7:00 AM - 11:30 AM: You spend the morning performing a detailed visual inspection of the landing gear struts, wheels, and braking systems. You assist the senior mechanic in rigging the aircraft on jacks to perform a gear swing test, ensuring the retraction and extension mechanisms function flawlessly. You identify a hydraulic line that shows early signs of wear and flag it for replacement.
- 11:30 AM - 12:00 PM: Lunch break with your team.
- 12:00 PM - 3:00 PM: You work on replacing the flagged hydraulic line, which involves draining the local hydraulic fluid, carefully removing the old line, fabricating a new one to exact specifications, and installing it. You then perform a leak check to ensure the integrity of the new installation.
- 3:00 PM - 3:30 PM: The most critical part of the day: paperwork. You meticulously document every step you took, including the part numbers used and the specifications followed. A senior mechanic or inspector reviews and signs off on your work, and you sign for the work you performed. This "signing your name" is the ultimate act of accountability.
- 3:30 PM: You clean your tools, tidy the workspace, and attend a brief hand-off meeting with the next shift, informing them of the progress made and any outstanding tasks. Your day is done, knowing you've made a direct contribution to the safety of a future flight.
Delta Aircraft Mechanic Salary: A Deep Dive
Now, let's get to the core of the query: the financial compensation for this critical role. A Delta Aircraft Mechanic salary is among the most competitive in the industry, reflecting the high level of skill, responsibility, and demand for these professionals. It's important to understand that compensation is a package, composed of a base hourly wage, significant overtime opportunities, and industry-leading benefits.
According to data from salary aggregator Glassdoor, the estimated total pay for an Aircraft Mechanic at Delta Air Lines ranges from $83,000 to $136,000 per year, with an estimated average base pay of around $99,500 per year (as of late 2023). Payscale.com reports a similar average base salary of approximately $98,000 per year, with a typical range from $70,000 to $139,000. It's crucial to note these figures often blend different experience levels.
For broader context, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports that the median annual wage for all Aircraft and Avionics Equipment Mechanics and Technicians was $70,010 in May 2022. However, the BLS notes that mechanics working for scheduled air transportation (the category for major airlines like Delta) earn significantly more, with a median annual wage of $99,020. This aligns perfectly with the data reported for Delta, confirming its position as a top-tier employer in the field.
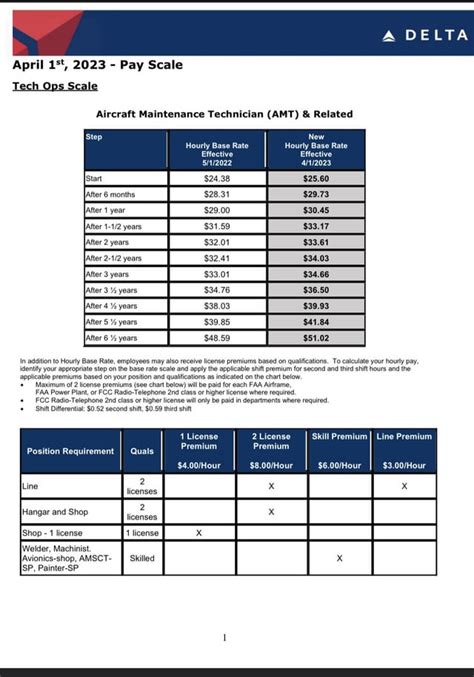
### Salary Progression by Experience Level
At a unionized airline like Delta, pay is not arbitrary; it's structured and based on a negotiated scale that increases with years of service. A new hire will start at a specific rate and receive scheduled pay increases until they reach the top of the scale (TOS).
Here is a representative breakdown of what salary progression looks like. (Note: These are estimates for total compensation, including a moderate amount of overtime and potential profit sharing, to reflect real-world earnings.)
| Experience Level | Years of Service | Typical Base Hourly Rate (Estimate) | Estimated Annual Compensation Range (incl. OT/Bonuses) |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Entry-Level Mechanic | 0 - 2 Years | $30 - $40 / hour | $65,000 - $85,000 |
| Mid-Career Mechanic| 3 - 7 Years | $45 - $55 / hour | $90,000 - $120,000 |
| Senior / Top of Scale (TOS) Mechanic | 8+ Years | $58 - $65+ / hour | $120,000 - $160,000+ |
| Lead / Inspector | 10+ Years | $65 - $70+ / hour (plus premium) | $140,000 - $200,000+ |
*Sources: Data compiled and synthesized from Glassdoor, Payscale, BLS reports, and industry forums discussing union pay scales.*
### Beyond the Base Salary: Unpacking Total Compensation
The base salary is only one part of the equation. To truly understand a Delta AMT's earning potential, you must consider the entire compensation package, which is one of the best in the business.
1. Overtime Pay:
This is arguably the most significant factor that boosts an AMT's total income. The aviation industry operates 24/7/365. Maintenance needs can arise at any time, and there is always a need for mechanics to work beyond their standard 40-hour week. Overtime is typically paid at 1.5x the base hourly rate, with work on holidays or specific days sometimes earning double-time (2x). A senior mechanic with a base rate of $60/hour would earn $90/hour for overtime, meaning a single 8-hour overtime shift adds $720 to their paycheck. It is not uncommon for dedicated mechanics to increase their base salary by 30-50% or more through overtime alone.
2. Profit Sharing:
This is a massive benefit at Delta. Each year, Delta shares a portion of its pre-tax profits with its employees. In recent years, this has resulted in bonus checks equivalent to a significant percentage of an employee's annual earnings. For example, in early 2023, Delta paid out over $560 million in profit sharing, which for many employees equated to over 5% of their 2022 salary. For a mechanic earning a base of $100,000, that's an extra $5,000+ check. In bumper years, this percentage has been much higher, sometimes exceeding 15%. This program directly links employees' success to the company's performance and can dramatically increase total annual compensation.
3. License Premiums:
Delta, like other major airlines, pays a premium hourly rate to mechanics who hold specific, valuable certifications. The standard FAA Airframe and Powerplant (A&P) license is a requirement for the job, but additional premiums are often paid for:
- Holding both an Airframe and a Powerplant license.
- Holding an FCC (Federal Communications Commission) license for avionics work.
- Possessing specialized certifications like Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) qualifications.
These premiums might add an extra $1 to $5+ per hour to the base rate.
4. Shift Differentials:
To compensate employees for working less desirable hours, airlines pay a shift differential. This is an extra hourly amount paid for working evening shifts, overnight (graveyard) shifts, or weekends. This premium encourages staffing around the clock and can add a few thousand dollars to an annual salary for those who consistently work off-hours.
5. Unmatched Benefits Package:
The value of Delta's benefits cannot be overstated and should be considered part of the total compensation.
- Flight Privileges: This is the most famous perk. Employees (and their eligible family members) receive free or heavily discounted standby travel on Delta flights worldwide. For those with a passion for travel, this benefit is invaluable and can be worth tens of thousands of dollars per year.
- Health Insurance: Comprehensive medical, dental, and vision plans for employees and their families.
- Retirement Savings: A robust 401(k) plan with a generous company match, helping employees build long-term wealth.
- Paid Time Off: Generous vacation, holiday, and sick leave policies.
When you combine a top-tier base salary with substantial overtime, profit sharing, and a world-class benefits package, the total value proposition of being a Delta Aircraft Mechanic becomes one of the most compelling in any skilled trade industry.
Key Factors That Influence an Aircraft Mechanic's Salary

While the union pay scale at Delta provides a structured salary progression, several key factors can influence a mechanic's career trajectory, specialization, and overall long-term earning potential. Understanding these factors is crucial for anyone looking to maximize their income in this field.
### `
`Level of Education & Certification`
`Education and certification are the bedrock of an aircraft mechanic's career. They are not just boxes to check; they are the foundation of your authority and trustworthiness as a technician.
- The FAA Airframe & Powerplant (A&P) Certificate: This is the non-negotiable, mandatory license to work on aircraft in the United States. It is issued by the FAA after an applicant demonstrates proficiency through rigorous written, oral, and practical examinations. Without an A&P certificate, you cannot be an aircraft mechanic. Holding both the Airframe and Powerplant ratings is the industry standard and a prerequisite for working at a major airline like Delta. The base pay scales are built around having this license.
- Associate of Applied Science (A.A.S.) Degree: Many aspiring mechanics attend an FAA-approved Part 147 school, which can be a technical college that also offers an A.A.S. degree. While not strictly required to get a job on the floor, earning an associate's degree can be highly beneficial for long-term career advancement. It provides a broader educational foundation, enhances critical thinking and communication skills, and makes a candidate more competitive for future leadership roles (e.g., Supervisor, Manager, Director of Maintenance). An A.A.S. degree signals a higher level of commitment and can be a tie-breaker when competing for promotions.
- Advanced Certifications and Type Ratings: This is where you can significantly increase your value and earning potential.
- FCC General Radiotelephone Operator License (GROL): This license, issued by the FCC, is often required for technicians who work on and repair advanced communication and navigation equipment (avionics). Avionics specialists are in high demand, and holding an FCC license can command an additional hourly pay premium.
- NCATT Certifications: The National Center for Aerospace & Transportation Technologies offers specialized certifications, such as the Aircraft Electronics Technician (AET) certification, which is becoming a recognized standard for avionics expertise.
- Aircraft Type Ratings: While more common for pilots, some mechanics pursue specialized training and ratings on specific aircraft models (e.g., Airbus A350, Boeing 787). This deep, specific knowledge makes them invaluable assets, especially as new-generation aircraft are introduced. Delta provides this training internally, and being selected for it is a mark of trust and a step toward becoming a go-to expert.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Certifications: NDT technicians use sophisticated methods like eddy current, ultrasonic, and X-ray to inspect parts for flaws without damaging them. This is a highly specialized and well-compensated niche within aircraft maintenance.
### `
`Years of Experience`
`As detailed in the salary table, experience is the single most direct driver of base pay increases at a unionized airline. The career path is designed to reward loyalty and the accumulation of hands-on expertise.
- Apprentice / New Hire (0-2 Years): During this phase, your primary role is to learn and prove your competence. You'll work under the close supervision of senior mechanics, handling less complex tasks and gradually earning more responsibility. Your pay is at the starting point of the scale, but the real value is the invaluable experience you're gaining on a world-class fleet.
- Journeyman Mechanic (3-8 Years): By this point, you are a fully functional and trusted member of the team. You can work independently on complex systems, troubleshoot difficult problems, and may begin to mentor new hires. You will have received several contractual pay raises, moving you steadily up the salary scale. Your overtime opportunities will also increase as you become qualified on more tasks and aircraft types.
- Top of Scale (TOS) and Lead Mechanic (8+ Years): Reaching the top of the pay scale is a significant milestone. You are now a senior expert. From here, further pay increases come from overtime, lead premiums, and annual cost-of-living adjustments negotiated by the union. Experienced TOS mechanics are often tapped for Lead Mechanic or Inspector roles. Leads are responsible for directing the work of a crew, while Inspectors hold the ultimate authority to sign off that an aircraft is airworthy after major work. These roles carry immense responsibility and come with an additional hourly pay premium, pushing total compensation to the highest levels.
### `
`Geographic Location`
`Unlike many professions where salary varies dramatically by city, the base hourly pay for a Delta mechanic is standardized across the country by the union contract. A TOS mechanic in Atlanta, GA, will have the same base hourly rate as a TOS mechanic in New York, NY, or Los Angeles, CA.
However, the *value* of that salary changes dramatically based on the cost of living. This is a critical factor for aspiring mechanics to consider when thinking about where they want to build their career. Delta's major maintenance hubs are located in:
- Atlanta, GA (ATL)
- Minneapolis-St. Paul, MN (MSP)
- Detroit, MI (DTW)
- Salt Lake City, UT (SLC)
They also have significant line maintenance operations in high-cost-of-living cities like New York (JFK), Los Angeles (LAX), and Seattle (SEA).
A total compensation package of $130,000 provides a vastly different lifestyle in Atlanta compared to Los Angeles. According to Payscale's Cost of Living Calculator, a $130,000 salary in Atlanta has the same buying power as a salary of over $210,000 in Los Angeles. Therefore, mechanics based at hubs in lower-cost-of-living areas like ATL or DTW can build wealth and afford a higher standard of living on the same nominal salary.
### `
`Company Type & Size (Contextualizing Delta)`
`Delta stands at the top of the aviation food chain, but understanding how its compensation compares to other types of aviation employers is key.
- Major/Legacy Airlines (Delta, United, American): These are the top-tier employers. They offer the highest union-negotiated pay scales, best-in-class benefits (especially profit sharing and flight privileges), and the most job security and structured career paths.
- Major Cargo Carriers (FedEx, UPS): These are the other titans of the industry and are often considered the absolute highest-paying jobs for aircraft mechanics. Their compensation packages are legendary, but the positions are intensely competitive. They represent the peak of the profession alongside the major passenger airlines.
- Regional Airlines (Envoy Air, SkyWest, Republic Airways): These airlines operate smaller aircraft on behalf of the majors. Their pay scales are significantly lower than the majors. However, they are a crucial entry point into the industry. Many mechanics work at a regional for a few years to gain valuable experience before applying to a major like Delta.
- MROs (Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul facilities): These are third-party companies that perform heavy maintenance for various airlines. Pay can be competitive but is often more variable and may lack the robust benefits and profit-sharing of a major airline.
- Corporate/Private Aviation: Working on private jets for corporations or wealthy individuals can be very lucrative, sometimes exceeding major airline pay. However, these jobs are far fewer, can have less job security, and may not offer the same level of benefits or retirement plans.
### `
`Area of Specialization`
`Within Delta's TechOps division, mechanics can specialize in different areas. While the base pay scale is often the same, certain specializations can lead to more overtime opportunities, faster promotions, or additional pay premiums.
- Line Maintenance: These mechanics work on the "line" or tarmac, handling rapid turnarounds between flights. The work is fast-paced and high-pressure. They are the first responders for any issues that arise and must make quick, accurate decisions. This role often involves shift work and significant overtime.
- Hangar (Base) Maintenance: These mechanics work in the hangar on scheduled, long-term maintenance checks (