Thinking about a high-impact career in finance? The role of a Financial Controller is one of the most critical and rewarding positions within any company's leadership structure. It's a role that demands sharp analytical skills, strategic thinking, and impeccable integrity. But what does that level of responsibility mean for your earning potential?
A career as a financial controller is not only intellectually stimulating but also financially lucrative, with top professionals earning well into the six-figure range. In this detailed guide, we will break down the salary you can expect as a financial controller, the key factors that drive your compensation, and the bright future this career path holds.
What Does a Financial Controller Do?
Before we dive into the numbers, let's clarify the role. A financial controller is the head of the accounting department, responsible for ensuring the accuracy and integrity of a company's financial records. They are the tactical leaders who manage the day-to-day accounting operations, acting as the financial backbone of the organization.
Key responsibilities often include:
- Overseeing all accounting operations (Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, General Ledger, Payroll).
- Preparing and publishing timely monthly, quarterly, and annual financial statements.
- Managing the budgeting and financial forecasting processes.
- Developing and maintaining internal control policies and procedures.
- Ensuring compliance with GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) and other regulatory requirements.
- Coordinating with external auditors and providing necessary information.
While a Chief Financial Officer (CFO) focuses on long-term financial strategy and investor relations, the controller ensures the underlying data is pristine and the financial house is in perfect order.
Average Financial Controller Salary
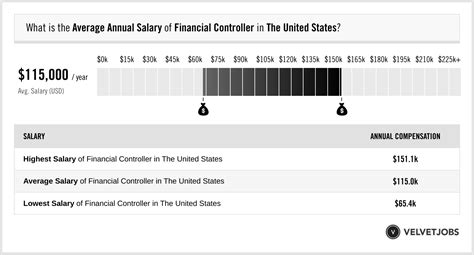
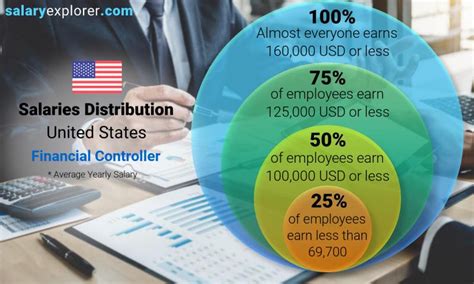
The salary for a financial controller can vary significantly, but it is consistently a high-paying profession. Data from multiple authoritative sources paints a clear picture of a robust compensation package.
- According to Salary.com, the median salary for a Financial Controller in the United States is approximately $160,571 as of early 2024. The typical salary range falls between $136,198 and $187,032, but this can expand significantly based on the factors we'll discuss below.
- Payscale reports a slightly more conservative average base salary of around $103,000 per year, but notes that total pay, including bonuses and profit-sharing, can push the figure much higher, often reaching up to $150,000 or more for experienced professionals.
- The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) groups financial controllers under the broader category of "Financial Managers." For this group, the median annual wage was $139,890 in May 2023. The top 10% of financial managers earned more than $239,200.
This wide range highlights that "Financial Controller" is not a one-size-fits-all role. Your compensation is directly tied to a combination of your qualifications, responsibilities, and where you work.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Understanding what drives salary is crucial for maximizing your earning potential. Here are the five most significant factors that determine how much a financial controller makes.
###
Level of Education
Your educational background and professional certifications lay the foundation for your career.
- Bachelor's Degree: A bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, or a related field is the standard entry requirement.
- Master's Degree: An advanced degree, such as a Master of Business Administration (MBA) with a finance concentration or a Master's in Accounting (MAcc), can provide a significant salary boost and open doors to more senior roles. It signals a higher level of specialized knowledge.
- Professional Certifications: This is arguably the most important educational differentiator. The Certified Public Accountant (CPA) license is the gold standard for controllers. It is often a prerequisite for positions at public companies and large corporations. The Certified Management Accountant (CMA) is another highly respected credential that demonstrates expertise in corporate finance and accounting. Holding a CPA or CMA can increase your salary by 10-20% or more.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is a primary driver of salary growth. The path to controller is a progressive one, and compensation reflects that journey.
- Early Career (0-5 years): Professionals at this stage are typically in roles like Senior Accountant or Accounting Manager, building the foundational skills needed. Assistant Controllers fall into this category, earning on the lower end of the controller salary spectrum.
- Mid-Career (5-15 years): This is the sweet spot where most professionals step into the full controller role. With proven experience managing accounting teams and closing the books, they can command salaries well within the median range ($140,000 - $180,000).
- Senior/Experienced (15+ years): Controllers with extensive experience, particularly those who have managed complex financial systems, led audits, or worked at large corporations, are at the top of the earning pyramid. Senior, Corporate, or Group Controllers at large enterprises can earn over $200,000 - $250,000, especially when bonuses and stock options are included.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work matters—a lot. Salaries are adjusted for local market demand and the cost of living. According to BLS data for Financial Managers, some of the top-paying states and metropolitan areas include:
- High-Paying States: New York ($200,200 average), New Jersey ($181,240), Delaware ($171,840), and California ($169,960).
- High-Paying Metro Areas: Major financial hubs like New York City, San Francisco, San Jose, and Boston offer the highest salaries, often exceeding a $200,000 average to compensate for the high cost of living.
Conversely, salaries in states with a lower cost of living, such as in the Midwest and Southeast, will typically be closer to or slightly below the national median.
###
Company Type
The size, industry, and structure of a company heavily influence a controller's salary.
- Company Size: A controller at a Fortune 500 company with billions in revenue and complex international operations will earn significantly more than a controller at a $20 million private company. More revenue, more employees, and more complexity equal higher pay.
- Industry: Industries with high margins and complex accounting, such as technology, pharmaceuticals, and professional/scientific services, tend to pay the most. The BLS confirms that "Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services" is one of the top-paying industries for financial managers.
- Public vs. Private: Controllers at publicly traded companies command higher salaries due to the added complexity and risk associated with SEC reporting, Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) compliance, and shareholder accountability.
###
Area of Specialization
Within the controller role, certain specialized skills can make you a more valuable—and higher-paid—candidate.
- Technical Accounting: Expertise in complex areas like revenue recognition (ASC 606), lease accounting (ASC 842), or mergers and acquisitions (M&A) is highly sought after.
- SEC Reporting & SOX: For public companies, experience with regulatory filings (10-K, 10-Q) and SOX compliance is non-negotiable and comes with a salary premium.
- Systems Implementation: Controllers who can lead the implementation of new Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems (like SAP, Oracle NetSuite, or Microsoft Dynamics 365) possess a valuable project management skill set that companies will pay for.
Job Outlook

The career outlook for financial controllers and managers is exceptionally strong. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that employment for financial managers will grow 16% from 2022 to 2032, which is much faster than the average for all occupations.
This robust growth is driven by several factors, including the increasing complexity of the global economy, a continued focus on financial regulations, and the need for thorough data analysis to guide business strategy. As long as businesses exist, they will need skilled leaders to manage their finances, making this a very stable career choice.
Conclusion

The role of a financial controller is a challenging and demanding career path, but it offers substantial rewards, both professionally and financially. With a median salary well into the six figures and a clear path for growth, it represents a top-tier destination for ambitious accounting and finance professionals.
To maximize your earning potential, focus on the key drivers: pursue advanced certifications like the CPA, gain experience in complex and high-growth industries, and be strategic about your location. For those with a meticulous eye for detail and a passion for financial leadership, the journey to becoming a financial controller is a strategic and lucrative career to build.
Sources:
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Occupational Outlook Handbook, Financial Managers. [bls.gov](https://www.bls.gov/ooh/management/financial-managers.htm)
- Salary.com, Financial Controller Salary in the United States. [salary.com](https://www.salary.com/research/salary/benchmark/financial-controller-salary)
- Payscale.com, Average Financial Controller Salary. [payscale.com](https://www.payscale.com/research/US/Job=Financial_Controller/Salary)