A career in teaching in the state of Georgia offers a unique opportunity to shape the future, inspire young minds, and contribute meaningfully to the community. Beyond the intrinsic rewards, teaching also provides a stable and structured career path with a clear, and recently improving, salary framework. For those considering this vital profession, understanding the financial landscape is a crucial first step.
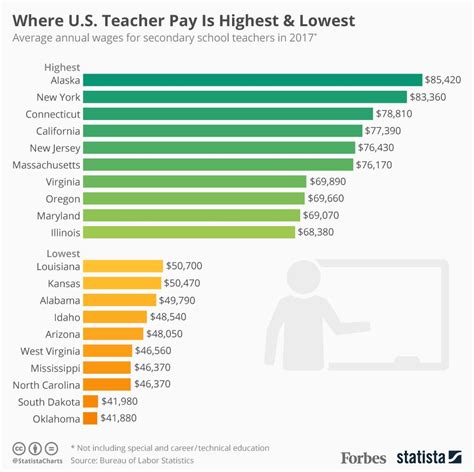
On average, teachers in Georgia can expect to earn a salary ranging from approximately $55,000 to $68,000 per year. However, this figure is just a starting point. An individual teacher's actual earnings are influenced by a transparent set of factors, with highly qualified and experienced educators in high-demand districts earning upwards of $85,000 or more.
This guide will break down the Georgia state teacher salary, explore the key factors that determine your pay, and provide a clear outlook on the profession.
What Does a Teacher in Georgia Do?

A teacher's role extends far beyond the classroom lecture. These dedicated professionals are planners, mentors, analysts, and communicators. Key responsibilities include:
- Instruction and Curriculum Development: Designing and delivering engaging lesson plans that align with the Georgia Standards of Excellence.
- Student Assessment: Creating, administering, and grading assignments and tests to evaluate student progress and tailor instruction.
- Classroom Management: Fostering a safe, inclusive, and productive learning environment for a diverse group of students.
- Parent and Community Communication: Collaborating with parents through conferences and regular updates to support student success.
- Professional Development: Engaging in continuous learning to stay current with the latest teaching strategies, technologies, and subject-matter knowledge.
Average Georgia Teacher Salary
Salary data shows a consistent and competitive range for educators across Georgia. It's helpful to look at averages across different sources and grade levels to get a complete picture.
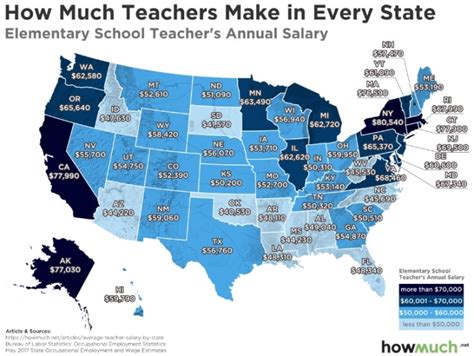
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the mean annual salaries for full-time teachers in Georgia (as of May 2023) are:
- Elementary School Teachers: $63,640
- Middle School Teachers: $65,580
- Secondary (High School) Teachers: $65,500
Reputable salary aggregator Salary.com reports that the average public school teacher salary in Georgia is around $60,801, with a typical range falling between $54,301 and $68,401 (as of May 2024).
It is crucial to understand that these figures represent an average. Entry-level teachers will start at the lower end of this range, while seasoned educators with advanced degrees will earn significantly more.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

In Georgia, teacher pay is not arbitrary. It is primarily determined by a statewide formula, with local districts often adding supplements. Here are the five main factors that will shape your earning potential.
### Level of Education
The Georgia Department of Education (GaDOE) establishes a statewide minimum salary schedule based on a teacher’s "Certificate Level." A higher level of education directly translates to a higher base salary from day one. The certificate levels are:
- T-4: Bachelor's Degree
- T-5: Master's Degree
- T-6: Education Specialist (Ed.S.) Degree
- T-7: Doctorate (Ph.D. or Ed.D.)
The financial impact is significant. According to the official FY 2025 State Salary Schedule, a first-year teacher with a Bachelor's degree (T-4) has a state base salary of $44,795. In contrast, a first-year teacher with a Master's degree (T-5) starts with a base salary of $51,123—an immediate increase of over $6,300 per year.
### Years of Experience
The GaDOE salary schedule is a grid that cross-references your certificate level with your years of creditable service. Each additional year of experience results in a "step increase" in your base pay. This structure rewards longevity and dedication to the profession.
For example:
- A teacher with a Bachelor's degree (T-4) and 10 years of experience has a state base salary of $58,354.
- A teacher with a Master's degree (T-5) and 10 years of experience has a state base salary of $66,610.
- An educator who has earned a Doctorate (T-7) and has over 21 years of experience reaches the top of the state scale at $86,303.
### Geographic Location
While the state sets the minimum salary, individual school districts have the authority to pay more by adding a "local supplement." This is one of the most significant factors in overall compensation.
Districts in metropolitan areas with a higher cost of living, such as Gwinnett County, Cobb County, Fulton County, and Atlanta Public Schools, typically offer substantial local supplements to attract and retain top talent. These supplements can add thousands—or even tens of thousands—of dollars to the state base salary. In contrast, smaller or more rural districts may offer a smaller supplement or none at all. When job searching, always look for a district's specific salary schedule, not just the state minimum.
### School Type
The type of school where you work also impacts your pay structure.
- Traditional Public Schools: Follow the state and district salary schedules described above. This provides a predictable and transparent pay structure.
- Public Charter Schools: While publicly funded, charter schools often have more autonomy. Some may follow the district schedule, while others may implement their own pay systems, which could include performance-based bonuses.
- Private Schools: Private and independent schools are not bound by the state salary schedule. Their pay scales can vary dramatically based on the school's tuition, endowment, and philosophy. While some elite private schools may offer competitive salaries, many pay less than their public school counterparts.
### Area of Specialization
To address teacher shortages in critical fields, many districts offer stipends or bonuses for certain specializations. These financial incentives are offered on top of the regular salary schedule. High-need areas frequently include:
- Special Education (SPED)
- STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math)
- World Languages (especially Spanish)
- Bilingual Education (ESOL)
If you are certified in one of these high-demand areas, you may have a higher total earning potential and more job opportunities.
Job Outlook

The career outlook for teachers remains stable. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the overall employment of elementary, middle, and high school teachers is projected to grow about 1% from 2022 to 2032.
While this growth is slower than the average for all occupations, it does not tell the whole story. The BLS anticipates tens of thousands of job openings each year nationwide due to the need to replace teachers who are retiring or leaving the profession. In a growing state like Georgia, the continued influx of new families and students will ensure a steady demand for qualified educators for years to come.
Conclusion

Choosing a career as a teacher in Georgia means stepping into a role with immense personal and professional rewards. The state's compensation structure is transparent, directly rewarding educators for advancing their education and committing to the profession.
Your salary is not just a single number but a dynamic figure influenced by your:
- Degree level
- Years in the classroom
- Choice of school district
- Area of expertise
With recent statewide pay raises and a clear path for salary growth, Georgia is an increasingly attractive state for new and experienced educators alike. By strategically planning your education and carefully researching specific school districts, you can build a fulfilling and financially secure career while making a lasting impact on the next generation.