Hearing Aid Instrument Specialist Salary: A Comprehensive Guide for 2024

Are you looking for a career that blends technical skill, compassionate patient care, and strong earning potential? The role of a Hearing Aid Instrument Specialist might be the perfect fit. This rewarding profession not only helps people reconnect with the world of sound but also offers a stable and competitive salary, with many specialists earning well over $60,000 annually.
This guide provides a data-driven look into the salary you can expect as a Hearing Aid Instrument Specialist, the key factors that influence your income, and the bright future this career path holds.
What Does a Hearing Aid Instrument Specialist Do?

A Hearing Aid Instrument Specialist (also known as a Hearing Instrument Specialist or Hearing Aid Dispenser) is a state-licensed professional trained to evaluate hearing loss and dispense hearing aids. They are on the front lines of non-medical hearing care, working directly with clients to improve their quality of life.
Key responsibilities include:
- Conducting basic hearing tests to determine the extent and type of hearing loss.
- Selecting and recommending appropriate hearing aids and assistive listening devices based on test results, lifestyle, and budget.
- Taking ear impressions and fitting, programming, and adjusting hearing aids for optimal performance.
- Educating clients and their families on how to use and maintain their new devices.
- Performing minor repairs and providing ongoing follow-up care and support.
Unlike an audiologist, who holds a doctoral degree (Au.D.), a Hearing Aid Specialist's training is focused specifically on hearing aid technology and fitting, typically requiring a high school diploma and extensive on-the-job training or an associate's degree, followed by a state licensing exam.
Average Hearing Aid Instrument Specialist Salary
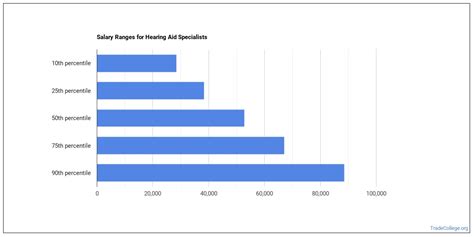
The compensation for a Hearing Aid Instrument Specialist is competitive and often includes a base salary supplemented by commission or bonuses based on sales. This structure allows high-performing specialists to significantly increase their earnings.
According to the most recent data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for hearing aid specialists was $59,010 as of May 2023. This means half of all specialists earned more than this amount, and half earned less.
However, the median only tells part of the story. Let's look at the full range:
- The lowest 10% earned less than $37,880.
- The highest 10% earned more than $93,390.
Reputable salary aggregators provide further insight into the typical salary range:
- Salary.com reports that the average salary for a Hearing Instrument Specialist in the United States falls between $51,699 and $74,801, with a median of around $62,604.
- Payscale notes an average base salary of approximately $53,200, with a total pay range (including bonuses and commission) spanning from $37,000 to $94,000.
This data highlights a crucial point: while the base salary is solid, your potential to earn is heavily influenced by performance and several other key factors.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary as a Hearing Aid Instrument Specialist isn't a single number—it's a range determined by a combination of your qualifications, location, and work environment.
###
Level of Education
While a high school diploma is the minimum requirement for entry in many states, pursuing further education can give you a competitive edge. An associate's degree in Hearing Instrument Sciences or a related field can lead to a higher starting salary and may be required for licensure in some states. Holding a bachelor's degree in a field like communication sciences or business can also be advantageous, particularly if you aspire to move into a management or practice ownership role.
Crucially, all states require specialists to be licensed, which involves passing both written and practical exams. Maintaining this license through continuing education is mandatory and demonstrates a commitment to the profession that employers value.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is one of the most significant drivers of income in this field. As you build your skills and client base, your earning potential grows substantially.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): In the beginning, your focus is on mastering the technical skills of testing, fitting, and programming devices. Your earnings will likely be closer to the lower end of the national range, from $40,000 to $50,000, often with a higher emphasis on base salary over commission.
- Mid-Career (3-9 years): With several years of experience, you become more efficient and effective at meeting patient needs, which directly translates to better sales and service. Mid-career specialists can comfortably earn within the national median range of $55,000 to $70,000.
- Senior/Experienced (10+ years): A seasoned specialist with a strong reputation, loyal client base, and mastery of the latest technology can command top-tier compensation. It's not uncommon for senior specialists to earn $75,000 to $90,000 or more, especially in high-paying locations or roles.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries for Hearing Aid Specialists vary significantly by state and even by metropolitan area due to differences in demand and cost of living.
According to BLS data, some of the top-paying states for this profession include:
- Maine
- New Jersey
- Arizona
- Maryland
- New Hampshire
Working in a major metropolitan area with a high cost of living and a large aging population typically results in higher wages than working in a rural community. Before accepting a position, always research the average salary for that specific city or region on sites like Glassdoor or Salary.com.
###
Company Type
The type of organization you work for has a profound impact on your salary structure and overall earning potential.
- Large Retail Chains (e.g., Costco, Sam's Club): These employers often offer a competitive hourly wage or base salary and benefits. The high volume of customers provides a significant opportunity for commissions, making it a lucrative option for skilled specialists.
- Private Audiology or Hearing Aid Practices: Working in a private clinic offers a more personalized, patient-focused environment. Compensation may include a solid base salary plus a commission structure tied to sales. Successful practices often reward top performers handsomely.
- ENT (Otolaryngology) Physician Offices: In this medical setting, your role is integrated with a broader healthcare team. Compensation is often a stable salary, though it may have less commission-based upside than a retail-focused environment.
- Hospitals: Similar to ENT offices, hospital-based positions provide stable, salaried employment with strong benefits, though they are less common for specialists compared to audiologists.
- Practice Ownership: The path with the highest earning potential is owning your own practice. While it involves the risks of entrepreneurship, successful practice owners can earn well into the six-figure range.
###
Area of Specialization
While the core job is consistent, developing expertise in specific areas can increase your value. Specializing in pediatric fittings, tinnitus management technology, or advanced devices like cochlear implants (in a support role) can make you a sought-after expert. Furthermore, specialists who excel in the "soft skills" of sales and customer service—building trust, understanding patient needs, and providing exceptional follow-up care—are the ones who consistently maximize their commission-based earnings and build a career at the top of the pay scale.
Job Outlook

The future for Hearing Aid Instrument Specialists is exceptionally bright. The BLS projects that employment in this field will grow by 11% from 2022 to 2032, which is much faster than the average for all occupations.
This robust growth is driven by two key factors:
1. An Aging Population: The large baby-boomer generation is entering the age range where hearing loss becomes more prevalent, creating a sustained demand for hearing aids and related services.
2. Increased Awareness: There is a growing public understanding of the health consequences of untreated hearing loss, leading more people to seek help.
This strong demand ensures a high degree of job security and continued opportunities for qualified professionals entering the field.
Conclusion

A career as a Hearing Aid Instrument Specialist offers a powerful combination of personal fulfillment and financial stability. With a median salary around $59,000 and the potential to earn over $90,000 with experience and strong performance, it is an accessible and rewarding profession.
Your earning potential is firmly in your hands, directly influenced by your experience, your choice of employer, your location, and your dedication to patient care. For those looking for a career that makes a tangible difference in people's lives while providing a great living, the path of a Hearing Aid Instrument Specialist is a sound choice.