Skilled industrial mechanics are the backbone of modern industry, ensuring that the machinery powering manufacturing, production, and logistics runs smoothly and efficiently. This career not only offers hands-on, problem-solving work but also provides a stable and competitive salary. If you're considering a future in this essential trade, understanding your potential earnings is a crucial first step.
On average, industrial mechanics in the United States can expect to earn a median salary of over $60,000 per year. However, with the right combination of experience, specialization, and location, top earners can command salaries well over $85,000 annually. This guide will break down what an industrial mechanic does, analyze average salaries, and explore the key factors that will shape your earning potential.
What Does an Industrial Mechanic Do?

An industrial mechanic, also known as an industrial machinery mechanic or millwright, is a highly skilled technician responsible for the installation, maintenance, repair, and troubleshooting of stationary industrial equipment and production machinery. Their work is critical to preventing costly downtime in facilities like factories, manufacturing plants, and power generation stations.
Key responsibilities include:
- Installing and Assembling: Setting up new, complex machinery according to technical manuals and blueprints.
- Preventative Maintenance: Performing regular inspections, cleaning, and lubrication to keep equipment in peak condition.
- Diagnosing and Troubleshooting: Using diagnostic tools and their expertise to identify the root cause of mechanical, hydraulic, or pneumatic problems.
- Repairing and Replacing: Disassembling machinery to repair or replace broken parts, and reassembling it to perfect working order.
- Reading Technical Documents: Interpreting blueprints, schematics, and service manuals to understand how equipment operates.
Average Industrial Mechanic Salary
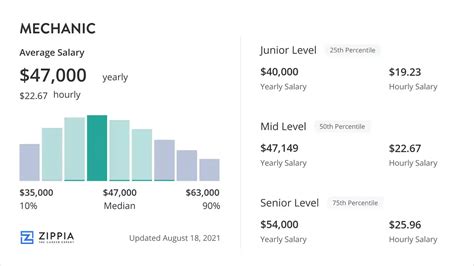
Salary data shows that a career as an industrial mechanic is financially rewarding. The most reliable figures come from government agencies and reputable salary aggregators.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for industrial machinery mechanics was $60,390 as of May 2023. This means half of all mechanics earned more than this amount, and half earned less. The BLS also provides a detailed salary range:
- Lowest 10%: Earned less than $40,650 (typical for entry-level positions)
- Median (50%): $60,390
- Highest 10%: Earned more than $85,690 (typical for senior, specialized, or lead mechanics)
Data from other top sources provides a similar picture:
- Salary.com reports a median salary of $65,568 as of May 2024, with a typical range between $57,847 and $74,013.
- Payscale notes an average base salary of $27.05 per hour, which translates to an annual salary of approximately $56,264, with a total pay range from $45,000 to $82,000 when including bonuses and overtime.
This data illustrates that while a solid base salary is standard, there is significant room for financial growth throughout your career.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary as an industrial mechanic will depend on several key variables. Focusing on these areas is the best way to maximize your earning potential.
### Level of Education
While a high school diploma is the minimum requirement, formal training significantly boosts earning potential. Employers highly value candidates with postsecondary education, such as:
- Vocational School Certificates: Programs in industrial maintenance technology or mechatronics provide foundational hands-on skills that make you job-ready.
- Associate's Degrees: A two-year degree in industrial maintenance or a related field provides a deeper theoretical and practical understanding, often leading to higher starting salaries and faster advancement.
- Certifications: Professional certifications demonstrate proven expertise. Credentials like the Certified Maintenance & Reliability Technician (CMRT) or specialized vendor certifications (e.g., for Allen-Bradley PLCs or Fanuc robotics) can make you a more valuable asset and justify higher pay.
### Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the most significant factor in salary growth. A typical career progression looks like this:
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): In this phase, you are learning from senior mechanics and focusing on routine maintenance and basic repairs. Your salary will be in the lower end of the range, likely between $40,000 and $50,000.
- Mid-Career (3-9 years): With several years of experience, you can troubleshoot complex issues independently and are trusted with critical machinery. Your salary will align with or exceed the median, often falling between $55,000 and $70,000.
- Senior/Lead (10+ years): Highly experienced mechanics often specialize in the most complex systems, lead teams of other technicians, or move into supervisory roles. These professionals command top-tier salaries, frequently exceeding $75,000 to $85,000 or more.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries vary based on local demand for skilled labor and the cost of living. According to the BLS, some of the top-paying states for industrial machinery mechanics are:
- Alaska: ($80,340 annual mean wage)
- District of Columbia: ($79,640)
- Hawaii: ($76,000)
- Wyoming: ($75,020)
- Nevada: ($74,480)
Metropolitan areas with a high concentration of manufacturing, shipping, or energy production also tend to offer higher wages to attract top talent.
### Company Type
The industry you work in has a direct impact on your salary. Industries that rely heavily on expensive, complex, or mission-critical machinery typically pay more to minimize downtime. Top-paying industries include:
- Aerospace and Automotive Manufacturing: The high cost of production stoppage means employers invest heavily in top maintenance talent.
- Power Generation and Utilities: These facilities are critical infrastructure and offer high, stable wages.
- Natural Gas Distribution and Pipeline Transportation: Specialized and often remote work in this sector commands premium pay.
- Large Corporations vs. Small Shops: Larger, multinational corporations generally have more structured pay scales, better benefits, and higher overall compensation compared to smaller, local operations.
### Area of Specialization
Developing a niche skillset is a powerful way to increase your value. While generalist mechanics are always needed, specialists are in high demand and can command higher salaries. High-value specializations include:
- PLC and Automation: Mechanics who can diagnose and work with Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and automated robotic systems are at the forefront of modern manufacturing.
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics: Expertise in fluid power systems is a highly sought-after and well-compensated skill.
- Millwrights: This specialized subset of mechanics focuses on the precision installation, alignment, and assembly of heavy industrial machinery, often earning more than general maintenance mechanics.
- Predictive Maintenance (PdM): Using tools like vibration analysis and thermal imaging to predict failures before they happen is a cutting-edge skill that companies pay a premium for.
Job Outlook

The future for industrial mechanics is bright. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that employment for industrial machinery mechanics will grow by 5% from 2022 to 2032, which is faster than the average for all occupations.
This growth is driven by two main factors:
1. Increasing Automation: As factories and plants adopt more sophisticated machinery and robotics, the need for skilled technicians to install and maintain them will continue to grow.
2. Retiring Workforce: A significant portion of the current skilled trade workforce is nearing retirement age, creating numerous openings for new mechanics to fill their roles.
This strong demand ensures excellent job security and continued wage growth for qualified professionals in the years to come.
Conclusion

A career as an industrial mechanic is an excellent choice for individuals who enjoy technical challenges, hands-on work, and want a profession with strong financial stability and growth prospects. While the national median salary provides a solid benchmark, your personal earnings are directly in your control.
By pursuing formal education, gaining years of valuable experience, choosing a high-demand location or industry, and developing a specialized skillset, you can build a career that is not only fulfilling but also highly lucrative. For those ready to power the future of industry, the path of an industrial mechanic offers a rewarding and financially stable future.
