In a world where data is the new currency and digital infrastructure is the backbone of every business, ensuring its security and integrity is paramount. This is where the Information Technology (IT) Auditor comes in—a critical role at the intersection of technology, business, and security. If you're considering this dynamic career path, you're likely wondering about its financial potential.
The great news is that the demand for skilled IT auditors translates into a highly competitive and rewarding salary. On average, professionals in this field can expect to earn a robust salary, typically ranging from $85,000 to over $130,000 annually, depending on a variety of key factors. This article will break down what an IT auditor does, the salary you can expect, and how you can maximize your earning potential.
What Does an Information Technology Auditor Do?

Think of an IT Auditor as a detective for an organization's digital systems. Their primary mission is to examine and evaluate an organization's information technology infrastructure, policies, and operations. They are responsible for ensuring that IT systems are secure, efficient, and in compliance with internal policies and external regulations (like Sarbanes-Oxley, GDPR, and HIPAA).
Key responsibilities include:
- Assessing Risks: Identifying potential threats to the company's IT systems, from cybersecurity breaches to data loss.
- Evaluating Controls: Testing the strength of security measures, backup systems, and access controls.
- Ensuring Compliance: Verifying that the organization adheres to legal and regulatory standards for data protection and privacy.
- Reporting Findings: Communicating audit results to management and providing recommendations for improvement.
Average Information Technology Auditor Salary
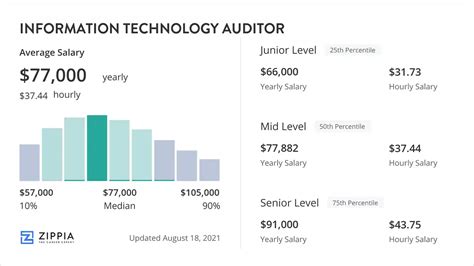
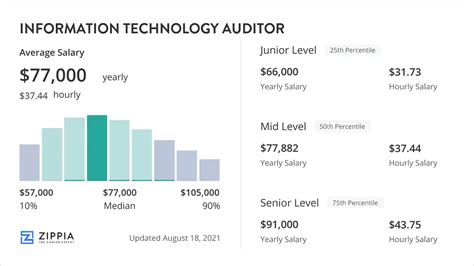
The compensation for an IT auditor is strong, reflecting the specialized skills required for the job. While salaries vary, we can establish a reliable baseline by looking at data from authoritative sources.
Across the United States, the average salary for an Information Technology Auditor falls into a consistent range:
- Salary.com reports the median salary for an IT Auditor is $96,590 as of late 2023, with a typical range falling between $88,081 and $105,712.
- Payscale lists a similar average base salary of around $82,000, with a reported range from $61,000 to $116,000.
- Glassdoor states a national average total pay of approximately $99,000 per year, which includes base salary and additional compensation like bonuses.
Typically, you can expect a salary progression that looks something like this:
- Entry-Level IT Auditor: $70,000 - $85,000
- Mid-Career IT Auditor: $85,000 - $115,000
- Senior/Managerial IT Auditor: $115,000 - $140,000+
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your final salary offer will depend on a combination of your qualifications, background, and where you work. Here are the most significant factors that influence an IT auditor's earnings.
### Level of Education
A bachelor's degree is the standard entry requirement for an IT auditor position. Common fields of study include Information Technology, Computer Science, Management Information Systems (MIS), or Accounting with an IT focus. While a bachelor's degree will get you in the door, a master's degree in a relevant field like Cybersecurity, Information Assurance, or an MBA with a technology concentration can provide a significant salary boost and open doors to leadership positions more quickly.
### Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the most critical factor in determining your salary. Employers pay a premium for auditors who have a proven track record of identifying risks and strengthening controls.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): Professionals starting out focus on learning standard audit procedures and assisting senior auditors. They can expect a salary at the lower end of the range.
- Mid-Career (3-7 years): With several years of experience, auditors can lead smaller projects, handle more complex systems, and operate with greater autonomy. This is where salaries see a significant jump into the six-figure range.
- Senior or Managerial (8+ years): Senior IT auditors and managers oversee entire audit programs, manage teams, and present findings to executive leadership. Their compensation reflects this high level of responsibility, often exceeding $130,000.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries are adjusted to the cost of living and local market demand. Major metropolitan areas and tech hubs typically offer higher salaries to attract top talent.
Cities known for offering top-tier IT auditor salaries include:
- San Jose, CA
- New York, NY
- Washington, D.C.
- Boston, MA
- Seattle, WA
Working in these high-cost-of-living areas can result in a salary that is 15-30% higher than the national average.
### Company Type
The type and size of the company you work for also play a role.
- "Big Four" Accounting Firms (Deloitte, PwC, EY, KPMG): These firms are a common starting point for many IT auditors. While starting salaries might be competitive, the real value comes from the world-class training and rapid career progression, which leads to high earning potential after a few years.
- Large Corporations (Fortune 500): Major companies across finance, healthcare, and retail have large in-house audit teams and pay competitively to protect their vast IT infrastructure.
- Tech and Financial Services Companies: These sectors often pay a premium for IT auditors due to the critical nature of their technology and the strict regulatory environment they operate in.
### Area of Specialization and Professional Certifications
Specializing in a high-demand area is one of the fastest ways to increase your value. Furthermore, professional certifications are the gold standard in the audit world and are often required for senior roles.
The premier certification is the Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) offered by ISACA. Holding a CISA is a clear signal to employers that you possess a high level of expertise. According to the Robert Half Salary Guide, professionals with in-demand certifications like CISA can earn 5% to 15% more than their non-certified peers.
Other valuable certifications include:
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
- Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC)
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
Specializing in areas like cybersecurity audit, cloud computing audit, or data analytics can also lead to higher-paying, niche opportunities.
Job Outlook

The future for IT auditors is exceptionally bright. While the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) does not have a separate category for IT auditors, the role is a hybrid of two fields with strong growth projections.
1. Accountants and Auditors: This field is projected to grow 4% from 2022 to 2032, about as fast as the average for all occupations.
2. Information Security Analysts: This closely related field is projected to grow a staggering 32% over the same period.
IT auditors, especially those with strong cybersecurity skills, are perfectly positioned to benefit from the explosive growth in the information security sector. As long as businesses rely on technology, there will be a strong and growing need for professionals who can protect it.
Conclusion

A career as an Information Technology Auditor offers a clear path to a financially rewarding and stable profession. With an impressive average salary and a robust job outlook, it's an excellent choice for detail-oriented individuals with a passion for technology.
To maximize your earning potential, focus on these key takeaways:
- Build a Solid Foundation: Gain relevant experience and never stop learning.
- Get Certified: Earning your CISA is a non-negotiable step for serious career advancement.
- Specialize: Develop expertise in high-demand areas like cybersecurity or cloud systems.
- Be Strategic: Consider how location and company type align with your career goals.
For those ready to embrace the challenge, a career as an IT auditor is not just a job—it's a critical role in protecting the digital future.