For decades, working as an aerospace engineer for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has represented the pinnacle of the engineering profession. It’s a career synonymous with pushing the boundaries of human knowledge, from the Apollo moon landings to the intricate dance of the James Webb Space Telescope. But beyond the immense prestige and groundbreaking work, a practical question remains for aspiring engineers: What does a NASA aerospace engineer actually earn?
While the fulfillment of working on history-making missions is a major draw, a career at NASA also offers a competitive and stable financial future. An aerospace engineer's salary at the agency is well-defined, transparent, and can range from approximately $80,000 for an entry-level position to over $180,000 for a senior expert, depending on a clear set of factors.
This guide will break down the salary you can expect, the key factors that influence your earnings, and the overall career outlook for this extraordinary profession.
What Does a NASA Aerospace Engineer Do?

Before diving into the numbers, it's essential to understand the scope of the role. A NASA aerospace engineer is a problem-solver on an interplanetary scale. Their responsibilities are vast and varied, but typically involve:
- Designing and Developing: Conceptualizing, designing, and developing spacecraft, satellites, rovers, and aviation technology. This includes everything from the massive rockets of the Artemis program to delicate scientific instruments.
- Testing and Analysis: Conducting rigorous testing on components and systems to ensure they can withstand the extreme conditions of launch and space. They analyze data to verify performance, identify flaws, and innovate solutions.
- Mission Operations: Supporting active missions by monitoring vehicle health, troubleshooting real-time issues, and planning future operations.
- Research and Innovation: Researching new materials, propulsion systems, and aerodynamic concepts that will enable the next generation of space exploration.
In essence, they turn the theoretical science of space exploration into tangible, working technology.
Average NASA Aerospace Engineer Salary
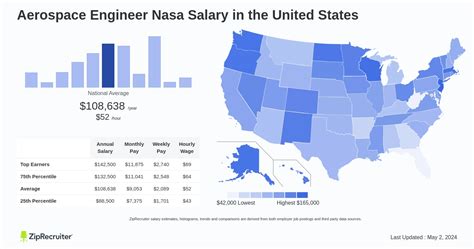
Unlike private companies where salaries can be opaque, NASA is a U.S. federal agency. This means its employee salaries are public information, governed by the federal government's General Schedule (GS) pay scale. An engineer's salary is determined by their GS grade (from GS-1 to GS-15) and their step within that grade (from 1 to 10).
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for all aerospace engineers was $126,880 as of May 2022. NASA's salary structure aligns well with this national benchmark and often exceeds it with experience and location adjustments.
Here’s a typical salary progression at NASA, based on the 2024 GS pay scale:
- Entry-Level (Bachelor's Degree): Often start at the GS-7 level, with a salary range of approximately $55,000 to $72,000.
- Entry-Level (Master's Degree): Typically start at the GS-9 level, with a salary range of approximately $68,000 to $88,000.
- Mid-Career (5+ years of experience): Can expect to be at the GS-12 or GS-13 level, earning between $95,000 and $145,000.
- Senior/Expert Level (10+ years): Senior engineers and technical leads often reach the GS-14 or GS-15 level, with salaries ranging from $135,000 to over $191,900 (the maximum for the GS scale in 2024).
Salary aggregators like Glassdoor corroborate this, reporting an average total pay for a NASA Aerospace Engineer of around $127,000 per year, based on user-submitted data.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary at NASA is not arbitrary. It is a direct result of several well-defined factors.
###
Level of Education
Your educational attainment is one of the most significant factors in determining your starting GS grade.
- Bachelor's Degree: Graduates with a B.S. in Aerospace Engineering or a related field typically qualify for a GS-7 position.
- Master's Degree: Holding an M.S. degree generally makes you eligible to start at a GS-9 level, a significant salary bump from the outset.
- Doctorate (Ph.D.): A Ph.D. can qualify you for a GS-11 or GS-12 starting position, placing you firmly in the mid-career salary band from day one.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is rewarded through a transparent system of promotions and step increases.
- Step Increases: Each GS grade has 10 "steps." Employees who demonstrate successful performance receive periodic step increases, raising their salary within their current grade. This provides a steady, predictable path for salary growth.
- Grade Promotions: As you take on more responsibility and demonstrate expertise, you can be promoted to higher GS grades (e.g., from GS-12 to GS-13). These promotions come with a substantial increase in your earning potential.
###
Geographic Location
The GS pay scale includes a crucial component called "locality pay." This is an adjustment made to your base salary to account for the cost of living in the area where your NASA center is located. This factor can have a dramatic impact on your take-home pay.
For example, here is the approximate 2024 salary for a GS-13, Step 1 engineer at different NASA centers:
| NASA Center Location | Locality Pay Area | Approximate Salary (GS-13, Step 1) |
| :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Marshall Space Flight Center, AL | Huntsville, AL | $108,619 |
| Johnson Space Center, TX | Houston, TX | $116,953 |
| Kennedy Space Center, FL | Cape Canaveral, FL | $106,759 |
| Jet Propulsion Laboratory, CA* | Los Angeles, CA | $119,535 |
*Note: The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a Federally Funded Research and Development Center (FFRDC) managed by Caltech. While its pay scale is competitive with NASA's GS system, it operates on a separate structure.*
*(Source: OPM.gov 2024 General Schedule (GS) Salary Tables)*
###
Company Type
While this article focuses on NASA, it's helpful to compare it to the private sector.
- NASA (Government Agency): Offers unparalleled job security, a strong work-life balance, and an excellent federal benefits package, including a pension plan (FERS), which is rare in the private sector. The salary progression is stable and transparent.
- Private Sector (e.g., SpaceX, Blue Origin, Boeing): These companies may offer higher starting base salaries or compensation in the form of stock options to attract top talent. However, the work environment can be more demanding, and job security may be more closely tied to project funding and market performance.
###
Area of Specialization
Within aerospace engineering, certain specializations are in high demand and can lead to faster career progression. Fields like robotics, software and systems engineering, flight controls, artificial intelligence/machine learning applications, and materials science are critical to NASA's future missions. Demonstrating expertise in a high-demand niche can make you a more valuable candidate for promotions to senior technical roles.
Job Outlook

The future for aerospace engineers is bright. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment for aerospace engineers is projected to grow 6 percent from 2022 to 2032, which is faster than the average for all occupations.
This growth is fueled by a renewed national and international focus on space exploration, including NASA's Artemis program to return humans to the Moon, continued robotic exploration of Mars, and the burgeoning commercial space industry. This creates a stable and exciting environment for a long-term career.
Conclusion

Choosing a career as a NASA aerospace engineer is a commitment to a life of learning, innovation, and purpose. While the allure of the mission is the primary driver for most, it's reassuring to know that the career is also financially sound and rewarding.
The salary is not a mystery; it is determined by a transparent, merit-based system that rewards education, experience, and expertise. With a competitive salary range, excellent benefits, and a strong job outlook, a career at NASA offers a unique opportunity to contribute to humanity's next great adventure while building a secure and prosperous life here on Earth.
