A career as a Quality Analyst (QA) is more than just finding bugs; it's about being the guardian of user experience and the final gatekeeper of product excellence. This critical role is not only intellectually stimulating but also offers a stable and financially rewarding career path. If you're considering this profession, one of your first questions is likely: "What can I expect to earn?"
The answer is promising. A Quality Analyst salary can range from a solid starting wage of around $60,000 to well over $125,000 for senior specialists in high-demand areas. In this detailed guide, we will break down the salary you can expect and explore the key factors that will directly influence your paycheck.
What Does a Quality Analyst Do?

Before we dive into the numbers, let's briefly define the role. A Quality Analyst is a professional responsible for ensuring that a product—most commonly software, but also in fields like manufacturing and services—meets established standards of quality. They are meticulous, detail-oriented problem-solvers who bridge the gap between development and the end-user.
Key responsibilities include:
- Developing and executing detailed test plans and test cases.
- Performing manual and automated tests to identify, record, and track defects.
- Collaborating with software developers, project managers, and business stakeholders.
- Analyzing test results and providing clear, actionable feedback.
- Verifying that final products are reliable, functional, and meet business requirements.
Average Quality Analyst Salary
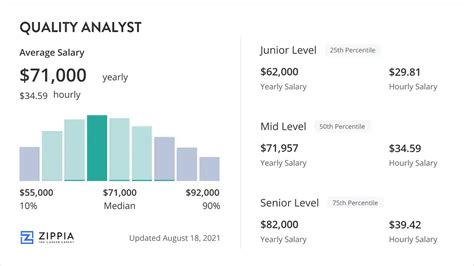
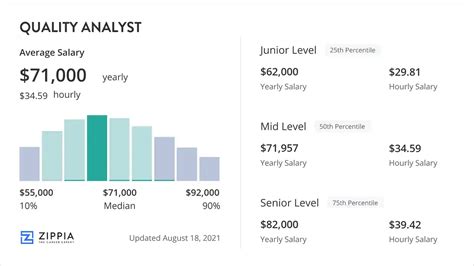
The salary for a Quality Analyst is competitive and shows significant growth with experience. While figures vary between sources due to different methodologies (e.g., employer-reported vs. user-submitted data), a clear picture emerges.
According to Salary.com, as of late 2023, the median salary for a Quality Assurance Analyst I in the United States is approximately $68,300, with a typical range falling between $61,200 and $76,700.
However, this is just the starting point. Data from other leading sources shows how this average grows:
- Payscale reports a slightly lower average base salary of around $64,500 per year but shows a clear progression, with experienced QAs earning closer to $85,000 and beyond.
- Glassdoor lists a national average base pay of $74,800 per year, with "Total Pay" (including bonuses and other compensation) reaching nearly $84,000.
It's also important to look at the broader category from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). The BLS groups "Quality Assurance Analysts" with "Software Developers and Testers." For this group, the median pay was $104,250 per year as of May 2022. While this figure is skewed higher by developer salaries, it reflects the high value placed on technical testing roles within the industry.
Based on this data, we can establish a typical salary progression:
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): $60,000 - $75,000
- Mid-Career (3-6 years): $75,000 - $95,000
- Senior/Lead (7+ years): $95,000 - $125,000+
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your base salary is not a fixed number. It's a dynamic figure influenced by several critical factors. Understanding these levers is the key to maximizing your earning potential throughout your career.
### Level of Education
While you can enter the QA field without a traditional four-year degree, your educational background plays a role. A Bachelor's degree in Computer Science, Information Technology, or a related engineering field is the most common and often preferred qualification. It provides a strong foundation that can lead to higher starting salaries. An advanced degree, such as a Master's, may provide an edge for specialized roles (like AI testing) or leadership positions but is generally not a requirement for most analyst roles.
### Years of Experience
This is arguably the most significant factor in determining your salary. As you accumulate experience, your value to an employer skyrockets.
- Entry-Level: You are primarily executing pre-written test plans and learning the company's processes.
- Mid-Career: You begin designing test strategies, mentoring junior analysts, and taking ownership of the quality for specific features or projects.
- Senior/Lead: You are a strategic leader. You design the entire quality assurance framework, make decisions about testing tools and automation architecture, and have a major impact on product development strategy. This level of responsibility commands a top-tier salary.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries are adjusted based on the cost of living and the concentration of demand for tech talent. Major tech hubs traditionally offer the highest salaries to attract the best professionals.
- Top-Tier Locations: Cities like San Jose (CA), San Francisco (CA), Seattle (WA), and New York City (NY) consistently offer salaries well above the national average to compensate for a high cost of living.
- Mid-Tier Locations: Cities like Austin (TX), Denver (CO), and Chicago (IL) offer strong salaries with a more moderate cost of living, providing excellent value.
- Remote Work: The rise of remote work has changed the landscape. Some companies pay based on their headquarters' location, while others adjust salaries based on the employee's location. This has created more opportunities for talented analysts in lower-cost-of-living areas.
### Company Type
The type of company you work for has a direct impact on your compensation package.
- Big Tech (FAANG, etc.): These companies typically pay the highest base salaries and offer lucrative compensation packages that include stock options and generous bonuses.
- Startups: A startup might offer a lower base salary but compensate with potentially valuable stock options. The risk is higher, but so is the potential reward if the company succeeds.
- Established Corporations (Banking, Healthcare, Retail): These companies offer competitive salaries, excellent job security, and strong benefits packages, though their salary ceilings may be lower than in Big Tech.
### Area of Specialization
Generalist QAs are always in demand, but specialists who cultivate in-demand skills can significantly increase their earning potential.
- QA Automation Engineer: This is the most lucrative specialization. Professionals who can write code to automate tests using frameworks like Selenium, Cypress, or Playwright are highly sought after and command premium salaries.
- Performance and Load Testing: Specialists who ensure applications can handle high traffic and stress are critical for user-facing products. This niche skill set is very valuable.
- Security Testing: Also known as penetration testing, this specialization focuses on finding vulnerabilities in an application. It's a high-stakes, high-reward field.
Job Outlook

The future for Quality Analysts is exceptionally bright. As technology becomes more integrated into every aspect of our lives, the need for robust, reliable, and secure software will only grow.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that employment for "Software Developers, Quality Assurance Analysts, and Testers" will grow by 25 percent from 2022 to 2032. This is described as "much faster than the average for all occupations," signaling fantastic job security and abundant opportunities for years to come.
This growth is driven by the increasing complexity of software, the rise of mobile applications, and the adoption of Agile and DevOps methodologies, where testing is a continuous and integrated part of the development lifecycle.
Conclusion

A career as a Quality Analyst offers a clear and compelling path to professional growth and financial success. While a national average provides a useful benchmark, your personal earning potential is in your hands.
To maximize your salary, focus on these key takeaways:
1. Build Experience: Your salary will grow significantly as you move from executing tests to designing quality strategies.
2. Never Stop Learning: The most valuable QAs are those who specialize. Invest in learning automation, performance, or security testing skills.
3. Be Strategic: Understand the salary landscape in your geographic area and be prepared to negotiate your worth.
4. Consider Your Industry: Choose a company type—be it Big Tech, a startup, or a stable corporation—that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
By staying current with industry trends and continuously honing your skills, you can build a fulfilling and highly compensated career as a guardian of quality in the ever-evolving world of technology.