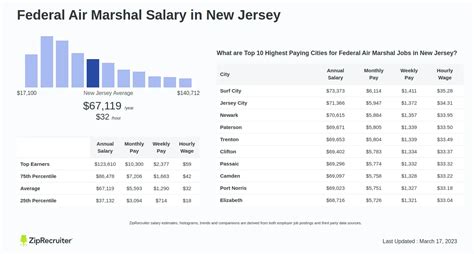
For those drawn to a career in federal law enforcement that combines high-stakes security with global travel, the role of a Federal Air Marshal is a compelling choice. Beyond the critical mission of protecting the nation's aviation system, a significant question for any prospective candidate is: what is the salary for a Federal Air Marshal?
This career offers a robust and structured compensation package, with total earnings for experienced marshals often exceeding six figures. A typical salary range, including mandatory availability pay, can span from approximately $59,000 to over $160,000 per year, depending on a variety of key factors.
This article provides a data-driven breakdown of a Federal Air Marshal's salary, the factors that influence it, and the long-term career outlook.
What Does a Federal Air Marshal Do?

Federal Air Marshals are federal law enforcement officers working for the Transportation Security Administration (TSA), a component of the Department of Homeland Security (DHS). Their primary mission is to detect, deter, and defeat hostile acts targeting U.S. aircraft, airports, passengers, and crews.
Operating covertly, they blend in with passengers on domestic and international flights. Their responsibilities include:
- Providing a visible and anonymous security presence on commercial flights.
- Identifying and assessing potential threats and suspicious behavior.
- Responding to criminal and terrorist activities in the air.
- Coordinating with flight crews, airport security, and other law enforcement agencies.
It's a demanding role that requires extensive training, exceptional judgment, and the ability to remain calm and effective under extreme pressure.
Average Federal Air Marshal Salary
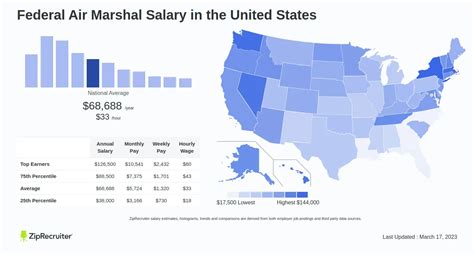
Unlike private-sector jobs, the salary for a Federal Air Marshal is determined by the federal government's structured pay system. Marshals are typically paid on the General Schedule (GS) scale, though the TSA often uses its own pay band system (like "SV" or "FV" pay plans) which corresponds directly to GS levels.
The key components of their salary are:
1. Base Pay: Determined by their pay grade (e.g., G, H, or I band, corresponding to GS grades).
2. Locality Pay: An adjustment based on the cost of living in their assigned duty station.
3. Law Enforcement Availability Pay (LEAP): This is a crucial and significant addition. LEAP provides an extra 25% of adjusted base pay to compensate for the long and irregular hours required of federal law enforcement officers.
According to the official TSA hiring information and the U.S. Office of Personnel Management (OPM) pay tables, the career path looks like this:
- Entry-Level (G Pay Band): New Federal Air Marshals typically start at the "G" pay band, which is equivalent to GS-7/GS-9. Including base pay, locality adjustments, and LEAP, a new marshal's starting salary in 2024 would realistically be in the $59,000 to $82,000 range, depending on their duty location.
- Full Performance Level (H and I Pay Bands): With experience, marshals advance to the "H" and "I" pay bands, equivalent to GS-11, GS-12, and GS-13. At this level, total compensation, including LEAP, typically ranges from $95,000 to over $150,000.
- Supervisory Roles: Senior and supervisory marshals can advance to GS-14 and GS-15 equivalent positions, where total pay can exceed $160,000+, especially in high-cost-of-living areas.
Salary aggregators reflect these government figures. For instance, Salary.com reports the average Federal Air Marshal salary in the U.S. to be around $114,375, with a typical range falling between $103,171 and $127,117.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

While the pay system is structured, several factors determine where an individual starts and how quickly they advance.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is the primary driver of salary growth for a Federal Air Marshal. The federal pay system is designed to reward longevity and performance. Marshals advance in two ways:
- Step Increases: Within each pay grade (e.g., H-band), there are multiple "steps." Marshals receive periodic step increases based on satisfactory performance, incrementally raising their base pay.
- Grade Promotions: The most significant salary increases come from promotions to higher pay bands (e.g., from G to H, or H to I). This progression from entry-level to the "full performance level" is a standard part of the career path.
###
Level of Education
Education directly impacts a candidate's starting pay grade. The TSA's requirements often allow for a combination of education and experience.
- To qualify for the G-Band (entry-level): A candidate typically needs a bachelor's degree OR at least three years of progressively responsible general experience.
- Higher Starting Point: A candidate with a master's degree or a bachelor's degree with a record of "Superior Academic Achievement" may qualify for a higher starting step or grade, leading to a higher initial salary.
While a specific degree is not required, degrees in criminal justice, homeland security, international relations, or a related field can be advantageous.
###
Geographic Location
Where a marshal is based has a significant impact on their total pay due to Locality Pay adjustments. The federal government adjusts salaries to offset the higher cost of living in certain metropolitan areas.
For example, a marshal at the GS-13, Step 1 level in 2024 would have a different total income based on their location:
- Base Pay (GS-13, Step 1): $89,834
- Location: Houston, TX (30.06% Locality): Base + Locality = $116,839. With LEAP (25%), total pay is $146,048.
- Location: New York City, NY (39.51% Locality): Base + Locality = $125,327. With LEAP (25%), total pay is $156,658.
- Location: Rest of U.S. (16.82% Locality): Base + Locality = $104,946. With LEAP (25%), total pay is $131,182.
*(Source: 2024 OPM General Schedule Pay Tables)*
###
Company Type
As a government role, the "company type" is the U.S. Federal Government, specifically the TSA under the Department of Homeland Security. This is a benefit, as it provides a transparent, predictable, and secure pay structure that is not subject to market volatility in the same way as private-sector jobs. In addition to salary, federal employment includes an excellent benefits package with health insurance, a generous retirement plan (Federal Employees Retirement System - FERS), and paid time off.
###
Area of Specialization
While the core duty is in-flight security, the Federal Air Marshal Service (FAMS) offers various career tracks that lead to higher pay. After gaining experience, marshals can move into specialized, and often higher-graded, positions such as:
- Supervisory Air Marshal: Leading a team of marshals in a field office.
- Instructor/Training Officer: Teaching at the FAMS Training Center.
- Intelligence or Investigations: Working in specialized roles supporting the FAMS mission on the ground.
- Management: Progressing to leadership positions within FAMS or the broader TSA/DHS structure.
These roles often correspond to higher GS grades (GS-14, GS-15), which carry the highest salary potential in the service.
Job Outlook

The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) does not track Federal Air Marshals as a separate category. However, it provides data for the broader category of "Police and Detectives," which it projects will have a job growth of 3% from 2022 to 2032.
While this suggests slower-than-average growth, the demand for Federal Air Marshals is tied directly to national security priorities and the volume of air travel. The need to secure the nation's aviation system is constant, ensuring that this will remain a critical and continuously staffed profession. The role is highly competitive, and the TSA recruits based on operational needs.
Conclusion

A career as a Federal Air Marshal is more than just a job; it's a commitment to public service and national security. For those who can meet the rigorous physical, mental, and professional standards, it offers a financially rewarding path.
Key Takeaways:
- Strong Earning Potential: Total compensation, including the crucial 25% LEAP pay, ranges from around $59,000 at entry-level to over $160,000 for experienced, senior marshals.
- Structured Advancement: Your salary is determined by a predictable federal pay scale, with clear paths for promotion based on experience and performance.
- Location Matters: Your duty station significantly influences your overall salary through locality pay adjustments.
- Beyond Salary: The role comes with comprehensive federal benefits, including health insurance, paid leave, and a robust retirement plan.
If you are a dedicated individual with a strong sense of duty and a desire for a unique career in law enforcement, the Federal Air Marshal Service offers a challenging and well-compensated opportunity to protect and serve.