A career as a U.S. Deputy Marshal is more than just a job; it’s a commitment to justice, integrity, and public service. As a member of America's oldest federal law enforcement agency, you play a critical role in the nation's judicial system. But beyond the profound sense of duty, a career with the U.S. Marshals Service (USMS) offers significant financial stability and a clear path for professional growth. Aspiring deputies can expect a competitive starting salary that can grow to over $100,000 annually with experience and advancement.
This article provides a data-driven analysis of a U.S. Deputy Marshal's salary, the factors that shape it, and the long-term outlook for this prestigious career.
What Does a U.S. Deputy Marshal Do?

Before we analyze the numbers, it's essential to understand the dynamic and demanding nature of the role. U.S. Deputy Marshals are federal law enforcement officers who work for the U.S. Department of Justice. Their responsibilities are vast and vital to the functioning of the federal judiciary. Key duties include:
- Fugitive Apprehension: Locating and arresting wanted federal fugitives.
- Judicial Security: Protecting federal judges, court officials, witnesses, and jurors.
- Witness Security Program: Ensuring the safety of witnesses who risk their lives to testify in major federal cases.
- Prisoner Transportation: Managing the safe and secure transportation of federal prisoners.
- Asset Forfeiture: Seizing and managing assets acquired by criminals through illegal activities.
This is a high-stakes profession that demands tactical skill, sharp intellect, and unwavering composure.
Average U.S. Deputy Marshal Salary
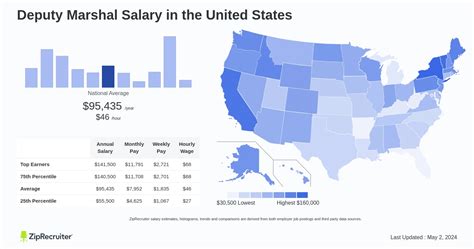
Unlike private-sector jobs, federal law enforcement salaries are highly structured. A U.S. Deputy Marshal's pay is determined by the federal government's General Schedule (GS) pay system, along with specific law enforcement pay scales.
According to data from leading salary aggregators, the average salary for a U.S. Marshal falls in a wide range, reflecting the significant impact of experience and location.
- Salary.com reports the average U.S. Marshal salary in the United States is $92,604 as of 2024, but the range typically falls between $87,903 and $97,357.
- Payscale estimates an average base salary of around $81,000 per year, not including potential overtime or other benefits.
However, the most accurate way to understand salary is to look at the official government pay structure. Entry-level Deputy U.S. Marshals typically start at the GL-07 pay grade. After one year of successful service, they are promoted to GS-09, then progress annually to GS-11 and GS-12. The full performance or "journeyman" level for a non-supervisory Deputy Marshal is GS-13.
- Starting Salary (GL-07): Approximately $52,000 to $65,000, depending heavily on the locality pay adjustment.
- Journeyman Salary (GS-13): Can range from $92,143 to $119,787 or more, based on location and years of service ("steps") within that grade.
Supervisory and management positions can advance to the GS-14, GS-15, and Senior Executive Service (SES) levels, with salaries well exceeding $150,000.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Several key variables determine a U.S. Deputy Marshal's precise earnings. Understanding these factors is crucial for anyone planning a long-term career with the USMS.
### Level of Education
To qualify for a position, candidates typically need a bachelor's degree with a strong academic record or a combination of education and qualifying experience. While an advanced degree (like a Master's or a Juris Doctor) does not automatically grant a higher starting salary, it can make a candidate significantly more competitive in the highly selective application process. Certain specialized roles within the USMS may favor candidates with advanced degrees in fields like finance, law, or information technology.
### Years of Experience
Experience is the single most significant driver of salary growth for a Deputy Marshal. The USMS has a structured career ladder that ensures steady pay progression.
- Entry-Level (GL-07): The starting point for all new hires.
- Promotional Progression: Deputies typically receive non-competitive promotions to GS-9, GS-11, and GS-12 after each successful year of service.
- Journeyman Level (GS-13): Reaching this level signifies full performance and mastery of the role. Further salary increases at this grade are based on "steps," which are periodic increases awarded for longevity and performance.
- Supervisory Roles (GS-14+): Moving into management positions (e.g., Supervisory Deputy, Chief Deputy) opens the door to higher pay grades and substantial income growth.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters immensely. The federal government uses a "Locality Pay" system to adjust salaries based on the cost of living in different metropolitan areas. This ensures that federal employees in expensive cities can afford a comparable standard of living to those in lower-cost areas.
According to the U.S. Office of Personnel Management (OPM) 2024 pay tables, the difference is significant:
- A GS-12, Step 1 Deputy in the "Rest of U.S." locality (the baseline) earns $79,336.
- The same GS-12, Step 1 Deputy in San Jose-San Francisco-Oakland, CA (which has a 45.43% locality adjustment) earns $115,411.
- In New York-Newark, NY-NJ-CT-PA, the same position earns $111,048.
This factor alone can account for a difference of tens of thousands of dollars per year for the same job and level of experience.
### Government Pay Grade and Structure
This factor is intrinsically linked to experience but deserves its own explanation. The General Schedule (GS) is the federal government's primary pay scale. Each grade (e.g., GS-11, GS-12) has 10 "steps." While grade promotions are tied to increased responsibility, step increases are granted for satisfactory performance over time. It takes 18 years to progress from Step 1 to Step 10 within a single GS grade, providing a long-term, predictable path for salary growth even without a promotion.
### Area of Specialization
While most deputies follow the standard career path, joining a specialized unit can lead to higher earning potential through increased overtime opportunities and unique assignments. Elite units within the USMS include:
- Special Operations Group (SOG): A highly trained tactical unit that responds to national crises and high-threat situations.
- Witness Security Program (WITSEC): Deputies in this secretive program are responsible for the protection and relocation of federal witnesses.
- International Investigations: These deputies work on complex cases involving the pursuit of fugitives who have fled the country.
While the base GS pay may be the same, the demanding nature of these roles often results in higher overall compensation.
Job Outlook

According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), employment for Police and Detectives, the category that includes federal law enforcement officers like U.S. Deputy Marshals, is projected to grow 3 percent from 2022 to 2032. While this is about as fast as the average for all occupations, it's important to note that positions within the U.S. Marshals Service are extremely competitive.
However, the need for federal law enforcement remains constant. The stability of a federal career, combined with excellent benefits (including a robust pension, health insurance, and the Thrift Savings Plan), makes it a highly sought-after profession.
Conclusion

A career as a U.S. Deputy Marshal is a challenging but exceptionally rewarding path that offers both profound purpose and financial security. While the average salary provides a good benchmark, your actual earnings will be shaped by a predictable and transparent system based on your experience, career progression, and geographic location.
For those considering this path, the key takeaways are:
- Expect a Competitive Starting Salary: With significant, structured growth in the first few years.
- Experience is Your Greatest Asset: The USMS rewards tenure and performance with a clear promotional ladder.
- Location Matters: Your duty station will have a major impact on your take-home pay due to locality adjustments.
- Long-Term Stability: A federal career offers excellent job security, benefits, and a reliable retirement system.
If you are driven by a mission of service and seek a career with clear financial growth, the role of a U.S. Deputy Marshal presents an outstanding opportunity to achieve both.
