Introduction

Are you a natural connector, a strategic thinker who thrives on bridging divides and creating value? Do you find yourself naturally translating the complex needs of one department into the language of another? If you're looking for a career that places you at the strategic heart of an organization—a role that is both financially rewarding and deeply impactful—then the path of a Business Relationship Manager (BRM) may be your calling.
The role of a Business Relationship Manager is one of the most critical, yet often misunderstood, positions in modern business. It's not sales, it's not account management, and it's not just being a friendly liaison. A true BRM is a strategic partner who ensures that business functions, whether it's IT, HR, or finance, are not just supporting the organization but actively driving its strategy and creating tangible value. This unique position commands a significant salary, with the national average often exceeding $125,000 per year, and top earners in high-demand sectors pushing well past $200,000 with bonuses and incentives.
I once consulted for a global logistics company where their multi-million dollar software deployment was on the verge of collapse. The technology was brilliant, but the operations team saw it as a burden. It was the introduction of a skilled BRM who finally sat both sides down, translated the operational pain points into technical requirements, and articulated the long-term value back to the operations floor, that saved the entire project. That experience crystallized for me the immense power and necessity of this role.
This comprehensive guide is designed to be your ultimate resource for understanding the Business Relationship Manager career. We will dissect salary expectations, explore the factors that can maximize your earnings, and provide a clear roadmap to launching or advancing your career in this dynamic field.
### Table of Contents
- [What Does a Business Relationship Manager Do?](#what-does-a-business-relationship-manager-do)
- [Average Business Relationship Manager Salary: A Deep Dive](#average-business-relationship-manager-salary-a-deep-dive)
- [Key Factors That Influence Salary](#key-factors-that-influence-salary)
- [Job Outlook and Career Growth](#job-outlook-and-career-growth)
- [How to Get Started in This Career](#how-to-get-started-in-this-career)
- [Conclusion](#conclusion)
What Does a Business Relationship Manager Do?

At its core, a Business Relationship Manager (BRM) is a senior-level connector and strategist whose primary function is to cultivate a positive, value-producing relationship between a service provider (like the IT department, HR, or finance) and its business partners (the various other departments or units within the company). The ultimate goal is to move the relationship beyond a transactional, ticket-based system to one of strategic partnership, where the service provider is seen as a co-leader in shaping business strategy, not just fulfilling orders.
Think of a BRM as an internal diplomat, business strategist, and value architect rolled into one. They don't just manage relationships; they orchestrate them to ensure that the capabilities of the service provider are fully leveraged to meet the business's strategic objectives.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks:
A BRM's work is dynamic and multifaceted, blending strategic planning with hands-on communication. Key responsibilities include:
- Strategic Partnering & Demand Shaping: This is the heart of the role. A BRM works with business leaders to understand their long-term goals, challenges, and opportunities. Instead of just waiting for requests, they proactively identify and shape business demand for the service provider's capabilities, ensuring resources are focused on the highest-value initiatives.
- Stakeholder Management: They are the primary point of contact for business partners. This involves regular meetings, establishing governance processes, and managing expectations. They must build trust and credibility at all levels, from front-line managers to C-suite executives.
- Value Realization: A BRM is accountable for ensuring that business initiatives and projects actually deliver their promised value. They work with teams to define, measure, and track value metrics (e.g., increased revenue, cost savings, improved efficiency, enhanced customer satisfaction) and communicate these successes back to the organization.
- Portfolio Management: They oversee the entire portfolio of projects and services for their business partners, helping them prioritize investments and ensuring alignment with both business strategy and the service provider's capacity.
- Business Acumen & Communication: A BRM must speak the language of business (P&L, market share, customer experience) and be able to translate complex technical or functional concepts into clear business terms, and vice versa. They are master communicators, facilitators, and negotiators.
A Day in the Life of an IT Business Relationship Manager:
To make this tangible, let's walk through a hypothetical day for a BRM who partners the IT department with the Marketing division.
- 9:00 AM - 9:30 AM: Sync with the IT Portfolio Lead. Review the status of active projects for Marketing, including the new CRM implementation and the website analytics upgrade. Discuss any resource constraints or roadblocks.
- 10:00 AM - 11:30 AM: Monthly Strategic Review with the VP of Marketing. Present the value scorecard from the previous quarter's IT initiatives. Discuss the VP's new goal of personalizing the customer journey and begin shaping the demand for a new marketing automation platform.
- 12:00 PM - 1:00 PM: Lunch & Learn. Host a session for the marketing team to showcase a new collaboration tool that the IT department is rolling out. The goal is to drive adoption and demonstrate immediate value.
- 2:00 PM - 3:30 PM: Project Ideation Workshop. Facilitate a brainstorming session between marketing analysts and IT business analysts to flesh out the requirements for the marketing automation platform discussed earlier. The BRM's role here is to keep the conversation focused on business outcomes, not just technical features.
- 4:00 PM - 5:00 PM: Follow-up and Planning. Document the outcomes of the workshop, send a summary to all stakeholders, and begin drafting the initial business case, outlining the potential ROI and strategic alignment of the proposed project. They then update their relationship management plan for the Marketing department based on the day's conversations.
This day illustrates the BRM's constant toggling between high-level strategy and tactical execution, always with the goal of aligning actions with value.
Average Business Relationship Manager Salary: A Deep Dive
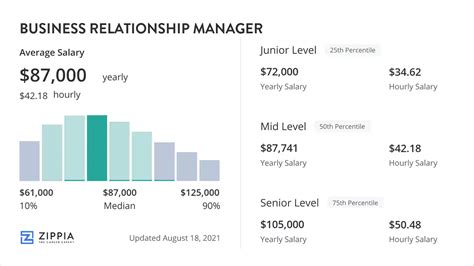
The compensation for a Business Relationship Manager is a direct reflection of the strategic importance and senior-level influence of the role. It is a position that requires a sophisticated blend of soft skills, business acumen, and often technical or functional expertise, and is therefore rewarded handsomely.
Salaries can vary significantly based on the factors we'll explore in the next section, but a clear and lucrative picture emerges when looking at national averages from trusted sources.
National Average Salary and Typical Range
According to data compiled from leading salary aggregators (as of late 2023/early 2024), the financial landscape for a BRM in the United States is strong:
- Salary.com reports that the median salary for a Business Relationship Manager is $129,578 per year, with a typical range falling between $115,108 and $145,558.
- Payscale.com shows an average base salary of around $111,739 per year. However, it also highlights that total pay, including bonuses and profit sharing, can extend up to $158,000.
- Glassdoor.com, which aggregates user-submitted data, indicates a total pay estimate of $144,383 per year, with a likely range between $117,000 and $183,000. This figure incorporates an estimated base salary of $118,295 and additional pay (bonuses, stock, etc.) of around $26,088.
Taking these sources together, it's safe to conclude that a mid-career Business Relationship Manager can confidently expect a base salary in the $115,000 to $135,000 range, with total compensation packages often reaching $150,000 or more.
Salary Brackets by Experience Level
As with any professional career, experience is a primary driver of salary growth. The journey from an entry-level position to a senior, strategic leader comes with substantial financial rewards.
| Experience Level | Years of Experience | Typical Base Salary Range | Key Responsibilities & Expectations |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Entry-Level BRM / Associate BRM | 0-3 years | $80,000 - $105,000 | Focuses on supporting a senior BRM, managing relationships with smaller business units, learning the business, tracking metrics, and coordinating meetings. |
| Mid-Career BRM | 4-9 years | $105,000 - $140,000 | Manages relationships with key business partners independently, shapes demand for new initiatives, develops business cases, and begins to demonstrate measurable value realization. |
| Senior / Principal BRM | 10-15+ years | $140,000 - $180,000+ | Manages relationships with the most critical, complex, or high-revenue business divisions. Acts as a trusted advisor to C-level executives, influences enterprise-level strategy, and mentors junior BRMs. |
| Director / Head of BRM | 15+ years (Leadership) | $180,000 - $250,000+ | Leads a team of BRMs, establishes the enterprise-wide BRM capability, sets governance and standards, and is accountable for the overall strategic alignment between the service provider and the entire business. |
*Sources: Data compiled and synthesized from Payscale, Salary.com, and Glassdoor reports for Business Relationship Manager and Senior Business Relationship Manager roles.*
Beyond the Base Salary: Understanding Total Compensation
A BRM's earnings are often significantly enhanced by variable pay components tied to both personal and company performance. When evaluating a job offer, it's crucial to look at the entire compensation package.
- Annual Bonuses: This is the most common form of additional compensation. Bonuses for BRMs are typically tied to a combination of factors: company profitability, business unit performance, and individual performance against specific goals (MBOs). A target bonus of 10% to 20% of the base salary is standard, with the potential for higher payouts in high-performing years.
- Profit Sharing: Some companies, particularly in the private sector, offer profit-sharing plans where a portion of the company's profits is distributed to employees. This can add an additional 3% to 10% to one's annual earnings.
- Commissions: While not standard for most BRM roles (which are strategic, not sales-focused), some BRMs in client-facing or revenue-generating contexts might have a commission structure tied to business growth or contract value. This is more common in consulting firms or managed service providers.
- Long-Term Incentives (LTIs): In publicly traded companies or mature startups, LTIs are a significant part of senior-level compensation. These can include:
- Stock Options: The right to buy company stock at a predetermined price.
- Restricted Stock Units (RSUs): A grant of company shares that vest over time.
- These incentives are designed to retain top talent and align the BRM's goals with the long-term success of the company. A senior BRM's LTI grant could be worth an additional $20,000 to $50,000+ per year.
- Benefits: Don't underestimate the value of a strong benefits package. This includes quality health insurance, a generous 401(k) match, ample paid time off, and professional development stipends, which can easily add another $20,000+ in annual value.
When you combine a strong base salary with these additional components, it becomes clear why a successful senior BRM can command a total compensation package that comfortably exceeds $200,000.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

While the national averages provide a great benchmark, your specific salary as a Business Relationship Manager will be influenced by a powerful combination of your qualifications, your location, and the context in which you work. Understanding these levers is the key to maximizing your earning potential.
###
Level of Education & Certification
Your educational background provides the foundation for your career and can directly impact your starting salary and long-term growth.
- Bachelor's Degree: A bachelor's degree is considered the minimum entry requirement for a professional BRM role. Relevant fields include Business Administration, Management Information Systems (MIS), Computer Science, Marketing, or Communications. A degree in a business-related field equips you with financial literacy and strategic thinking, while a technical degree provides credibility when partnering with IT.
- Master's Degree (MBA, etc.): An advanced degree, particularly a Master of Business Administration (MBA), can significantly boost your salary potential and accelerate your career trajectory. An MBA deepens your expertise in finance, strategy, and leadership, making you a more credible advisor to senior business leaders. According to Payscale, professionals with an MBA often earn 10-15% more than their counterparts with only a bachelor's degree.
- Professional Certifications: In the BRM field, certifications are not just resume-builders; they are a direct signal of specialized expertise and commitment to the profession. The globally recognized authority is the Business Relationship Management Institute (BRMI).
- Business Relationship Management Professional (BRMP®): This is the foundational certification. It validates your understanding of the BRM role, competencies, and strategic value. Earning your BRMP can open doors to BRM roles and often results in a salary increase, as it demonstrates a baseline level of knowledge that employers value.
- Certified Business Relationship Manager (CBRM®): This is the advanced, practitioner-level certification for experienced BRMs. It requires a deeper understanding of strategic relationship management, portfolio management, and value realization techniques. Holding a CBRM® is a significant differentiator for senior roles and can lead to a substantial salary premium, often placing you in the top quartile of earners.
- Master of Business Relationship Management (MBRM®): This is the highest designation, recognizing thought leaders in the field.
###
Years of Experience
As shown in the salary table, experience is arguably the most significant factor in salary progression. However, it's not just about the number of years, but the *quality* and *type* of experience.
- 0-3 Years (The Foundation): In these early years, you might be in a role like Business Analyst, Project Coordinator, or Junior Account Manager. Your focus is on learning the mechanics of business processes, project lifecycles, and stakeholder communication. You are building the raw materials for a future BRM role.
- 4-9 Years (The Practitioner): This is where you transition into a dedicated BRM role. Your salary jumps as you take on independent responsibility for a business unit. Success is measured by your ability to move from reactive problem-solving to proactive demand shaping. Your salary growth in this phase is tied to the complexity of the business partners you manage and the tangible value you can demonstrate (e.g., "I led the initiative that increased sales team efficiency by 15% through a new CRM strategy").
- 10+ Years (The Strategist): At this senior level, you are no longer just managing relationships; you are shaping enterprise strategy. Your experience with complex political navigation, C-suite influencing, and large-scale portfolio management is what commands top-tier salaries. You might have experience turning around a dysfunctional business-IT partnership or leading the strategic planning for a digital transformation. This proven track record of high-impact leadership is what employers will pay a premium for, pushing your base salary into the $160k-$180k+ range.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work has a massive impact on your paycheck due to variations in cost of living and demand for talent. Major metropolitan areas, particularly tech and finance hubs, offer the highest salaries.
Here's a comparative look at how location affects the average BRM salary, based on data from Salary.com's location-specific calculators (which often factor in cost of living):
| Metropolitan Area | Average Salary (Compared to National Median) | Why It's Higher/Lower |
| :--- | :--- | :--- |
| San Francisco, CA | 25-35% Above National Average | Epicenter of the tech industry, high concentration of large enterprise HQs, and extremely high cost of living. |
| New York, NY | 20-30% Above National Average | Global finance and business hub, high demand in banking, media, and corporate sectors, and high cost of living. |
| Seattle, WA | 15-20% Above National Average | Major tech hub (Amazon, Microsoft), competitive market for tech-savvy business professionals. |
| Boston, MA | 10-15% Above National Average | Strong presence in tech, biotech, finance, and higher education, creating diverse demand. |
| Chicago, IL | 5-10% Above National Average | Major Midwest business hub with a diverse economy in finance, logistics, and professional services. |
| Dallas, TX | On par with National Average | Growing business and tech center with a more moderate cost of living. |
| Des Moines, IA | 5-10% Below National Average | Lower cost of living and less competition from large enterprise HQs compared to coastal hubs. |
If you have mobility, targeting high-demand, high-cost-of-living areas can dramatically increase your nominal salary, though it's always wise to weigh this against the increased living expenses.
###
Company Type & Size
The type of organization you work for will define its culture, its financial resources, and its compensation philosophy.
- Large Corporations (Fortune 500): These companies typically offer the highest base salaries and most structured compensation packages. They have established BRM functions (or "IT Business Partner" roles), clear career ladders, and generous benefits. The work is often more complex, involving global stakeholders and large-scale portfolios.
- Startups & Tech Companies: Compensation here is often a mix. The base salary might be slightly lower or on par with large corporations, but the potential upside from stock options or equity (LTIs) can be enormous if the company is successful. The BRM role in a startup is often more agile and hands-on, with a greater ability to influence the company's direction.
- Consulting Firms: BRMs working for consulting firms (e.g., Accenture, Deloitte, or specialized BRM consultancies) can command very high salaries. Their pay is directly tied to the revenue they generate for the firm. The work is project-based, offering exposure to many different industries, but often comes with demanding travel schedules and high-pressure environments.
- Non-Profits & Government: These sectors typically offer lower base salaries than their for-profit counterparts. However, they often provide excellent work-life balance, strong job security, and generous pension/retirement benefits. The "psychic income" of working for a mission-driven organization can also be a significant factor for many professionals.
###
Area of Specialization
While "Business Relationship Manager" is a role title, the function it partners with creates specializations that have different salary profiles.
- Information Technology (IT BRM): This is the most common and often the highest-paying specialization. IT BRMs are at the center of digital transformation, cloud migration, cybersecurity, and data analytics initiatives—all top priorities for modern businesses. Their ability to bridge the gap between complex technology and business value is highly prized. Synonymous titles include "IT Business Partner" or "Client Services Director."
- Human Resources (HR BRM): These professionals partner with business units to align HR strategy (talent acquisition, performance management, learning & development) with business goals. As companies focus more on talent as a competitive advantage, this role is growing in importance.
- Finance BRM: This BRM works to ensure the finance department's capabilities (e.g., financial planning & analysis, reporting) are meeting the strategic needs of the business divisions.
- External/Client-Facing BRM: Some BRMs manage the relationship between their company and its largest, most strategic clients. This role is a blend of strategic account management and traditional BRM, and compensation is often tied directly to client retention and growth, sometimes including commissions.
Generally, specializations that are closer to an organization's core revenue streams or most critical strategic initiatives (like IT) tend to command higher salaries.
###
In-Demand Skills
Beyond formal qualifications, a specific set of high-value skills will make you a more effective BRM and a more sought-after candidate. Cultivating these skills will directly translate to higher salary offers.
- Strategic Thinking: The ability to see the big picture, understand market trends, and connect daily activities to long-term business goals.
- Financial Acumen: You must be able to read a P&L statement, build a compelling business case, and discuss ROI, NPV, and other financial metrics with business leaders.
- Influence Without Authority: This is a cornerstone of the BRM role. You often don't have direct reports in the business units you partner with, so your ability to persuade, negotiate, and build consensus through influence is paramount.
- Stakeholder & Political Navigation: Excelling at identifying key stakeholders, understanding their motivations, and navigating complex organizational dynamics to achieve strategic objectives.
- Value-Driven Communication: The ability to articulate complex ideas clearly and to frame every conversation around business value and outcomes, not just features or processes.
- Portfolio Management: Skills in prioritizing initiatives based on strategic alignment, resource capacity, and potential value.
- Business Acumen in a Specific Domain: Deep knowledge of the industry (e.g., healthcare, finance, manufacturing) or business function (e.g., marketing, supply chain) you are partnering with makes you an invaluable strategic advisor.
According to Payscale's analysis, skills like IT Strategy, Portfolio Management, and C-level Stakeholder Management show a strong correlation with salaries in the top quartile.
Job Outlook and Career Growth

Investing your time and energy into a career path requires a clear understanding of its future viability. For Business Relationship Managers, the outlook is exceptionally bright. As organizations become more complex, digital, and value-focused, the need for strategic connectors who can break down silos and ensure alignment has never been greater.
Strong Job Growth Projections
While the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) does not have a dedicated category for "Business Relationship Manager," the role is a senior-level hybrid that falls squarely within several fast-growing professional categories. The most relevant proxy is "Management Analysts."
The BLS projects that employment for Management Analysts will grow by 10% from 2022 to 2032, which is "much faster than the average for all occupations." The BLS cites several key reasons for this rapid growth, which directly align with the BRM value proposition:
- Increased Use of Information Technology: As companies adopt new technologies, they need experts who can help them achieve the highest ROI. This is the core function of an IT BRM.
- A Shift to Agile and More Efficient Business Operations: BRMs are central to ensuring that agile technology or business teams are working on the right things that deliver the most value to the business.
- Growth in specific sectors like healthcare: The need for professionals who can help manage costs and improve efficiency is high, creating opportunities for BRMs in these industries.
This projected growth translates to approximately 99,500 new job openings for management analysts each year over the decade, stemming from both new job creation and the need to replace workers who retire or change careers. BRMs are perfectly positioned to fill the most senior and strategic of these roles.
Emerging Trends Shaping the Future of the BRM Profession
The role of the BRM is not static; it is evolving to meet the challenges of the modern enterprise. Staying ahead of these trends is key to long-term career success and growth.
1. The Rise of Enterprise-Wide BRM: Originally rooted in IT, the BRM capability is expanding. Organizations are creating BRM teams for HR, Finance, Legal, and other shared services, leading to the creation of enterprise-level "Business Relationship Management Offices" (BRMOs) led by a Chief Relationship Officer or a Director of Strategic Partnerships.
2. Focus on Digital Transformation and Customer Experience: BRMs are moving to the forefront of digital transformation initiatives. They are essential for ensuring that new digital tools and platforms are not just implemented but are also adopted and used to create a seamless, valuable customer experience.
3. Integration with Agile and Product Management: In agile organizations, the BRM works closely with Product Owners and Product Managers. While the Product Owner focuses on the "what" (the product backlog), the BRM focuses on the "why"—ensuring the product roadmap aligns with the broader strategic goals of the business partner.
4. The Impact of AI and Automation: As AI automates routine tasks, the uniquely human skills of the BRM—empathy, strategic thinking, influence, and creative problem-solving—become even more valuable. BRMs will play a key role in helping business partners understand and leverage AI to achieve their strategic goals.
Advancing Your Career: The BRM Growth Path
