In a world where data is often called "the new oil," professionals who manage, secure, and optimize this critical asset are more valuable than ever. The role of a Database Manager is central to modern business operations, blending deep technical expertise with strategic oversight. If you're considering this rewarding career path, one of your primary questions is likely about compensation.
So, what can you expect to earn? While salaries for Database Managers are consistently strong, often breaking the six-figure mark, the final number depends on a variety of key factors. This guide will break down the typical database manager salary and explore the elements that can significantly boost your earning potential.
What Does a Database Manager Do?

Before diving into the numbers, it's essential to understand the role. A Database Manager is a senior IT professional responsible for the performance, integrity, and security of an organization's databases. Unlike a Database Administrator (DBA), who is often more focused on day-to-day technical tasks, a Manager typically handles higher-level strategic responsibilities.
Key responsibilities include:
- Strategic Oversight: Planning for future database needs, capacity, and upgrades.
- Team Leadership: Managing a team of DBAs and other data professionals.
- Security & Compliance: Implementing and enforcing security protocols to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
- Performance & Availability: Ensuring databases run efficiently and are always available to users and applications.
- Disaster Recovery: Creating and testing backup and recovery plans to prevent data loss.
- Vendor & Budget Management: Liaising with software vendors and managing the budget for database technology.
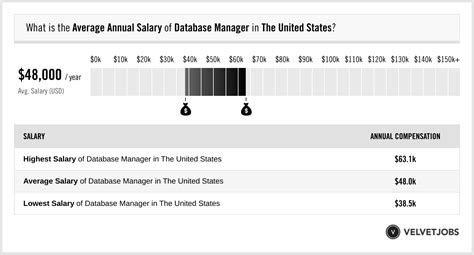
Average Database Manager Salary
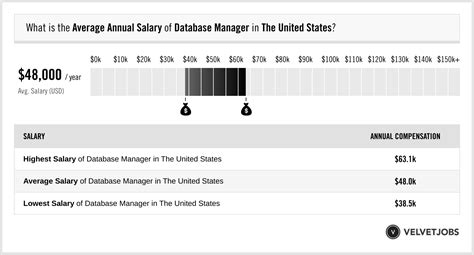
The salary for a database manager is competitive, reflecting the high level of skill and responsibility required. Data from several authoritative sources paint a clear picture of a lucrative career.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for the broader category of "Database Administrators and Architects" was $112,020 in May 2023. The salary range is quite wide, indicating significant room for growth:
- Lowest 10%: Earned less than $64,250 (typically entry-level or junior DBA roles).
- Highest 10%: Earned more than $173,340 (representing senior managers, architects, and top specialists).
Reputable salary aggregators, which can filter specifically for the "Manager" title, often report even higher averages.
- Salary.com places the median salary for a "Database Manager" at approximately $148,609 as of early 2024, with a typical range falling between $131,385 and $164,790.
- Glassdoor reports an average total pay (including bonuses and additional compensation) for a "Database Manager" in the United States at around $146,000 per year.
From this data, it's reasonable to conclude that while a mid-level professional in the database field can expect to earn over $110,000, stepping into a management role pushes that potential closer to the $130,000 to $165,000 range and beyond.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your personal salary will be determined by a combination of factors. Understanding these levers is key to maximizing your earning potential throughout your career.
###
Level of Education
A solid educational foundation is the launching point for a database career. A bachelor's degree in computer science, information technology, or management information systems is considered the standard entry requirement. However, advanced education can provide a significant salary bump. Professionals holding a Master of Science (M.S.) in a related field, or an MBA with a technology focus, are often fast-tracked into management roles and can command higher starting salaries.
Furthermore, professional certifications are highly valued. Earning credentials like the Oracle Certified Professional (OCP), Microsoft Certified: Azure Database Administrator Associate, or AWS Certified Database - Specialty validates your expertise on specific platforms and can directly translate to higher pay.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is perhaps the single most significant factor in salary growth. A typical career and salary progression looks like this:
- Entry-Level (0-4 Years): Often starting as a Junior DBA or Data Analyst. Responsibilities include routine maintenance, backups, and troubleshooting. Salary Range: $70,000 - $95,000.
- Mid-Career (5-9 Years): Progressing to a Senior DBA or a new Database Manager role. This stage involves more complex projects, database design, and potentially mentoring junior staff. Salary Range: $95,000 - $130,000.
- Senior/Lead (10+ Years): As a Senior Database Manager or Database Architect, you are responsible for enterprise-wide data strategy, managing large teams, and overseeing critical systems. This is where salaries reach their peak. Salary Range: $130,000 - $175,000+.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries are often adjusted based on the cost of living and the concentration of tech jobs. Major technology hubs and metropolitan areas with a high demand for IT talent offer the highest salaries.
Top-paying states and metropolitan areas include:
- California (San Francisco Bay Area, Los Angeles)
- Washington (Seattle)
- New York (New York City)
- Virginia & Maryland (D.C. Metro Area)
- Texas (Austin, Dallas)
Salaries in these regions can be 20-35% higher than the national average. Conversely, salaries in rural areas or states with a lower cost of living will likely be closer to the lower end of the national range.
###
Company Type
The industry and size of your employer have a direct impact on your paycheck.
- Big Tech & Software Companies: Companies like Google, Amazon, Microsoft, and Oracle are often the top payers, as their business revolves around data and technology.
- Finance, Banking, and Insurance: These industries rely heavily on secure, high-performance databases to handle financial transactions and manage risk. They pay a premium for top talent to ensure system integrity.
- Healthcare: With the rise of Electronic Health Records (EHR) and medical data analysis, demand in healthcare is strong, offering competitive salaries.
- Government and Education: These sectors typically offer lower base salaries compared to the private sector but often compensate with excellent benefits, job security, and better work-life balance.
###
Area of Specialization
Not all database skills are created equal. Specializing in high-demand areas can make you a more valuable—and higher-paid—candidate.
- Cloud Databases: Expertise in cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS RDS, Aurora), Microsoft Azure (SQL Database), and Google Cloud (Cloud SQL) is in extremely high demand and commands top dollar.
- Database Security: As cyber threats grow, professionals who can secure databases against breaches are critical. This specialization is a major salary booster.
- Big Data Technologies (NoSQL): While traditional SQL databases (like Oracle, SQL Server) are still dominant, skills in NoSQL databases (like MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis) used for large-scale, unstructured data are highly sought after.
- Performance Tuning: Experts who can optimize complex, multi-terabyte databases to run faster and more efficiently are invaluable to large enterprises.
Job Outlook

The future for database professionals is bright. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that employment for database administrators and architects will grow by 7 percent from 2022 to 2032, which is more than double the average growth rate for all occupations.
This growth is fueled by the ever-increasing need for businesses across all sectors to collect, store, analyze, and secure data. The continued migration to cloud services will further drive demand for professionals skilled in managing cloud-native databases.
Conclusion

A career as a Database Manager offers a clear path to a high six-figure salary, strong job security, and a central role in the modern economy. While the national median provides a great benchmark, your ultimate earning potential is in your hands.
To maximize your salary, focus on continuous learning: pursue advanced degrees or certifications, gain deep experience across different systems, and specialize in high-growth areas like cloud computing and data security. By strategically building your skills and expertise, you can position yourself for a financially and professionally rewarding career at the heart of the data revolution.