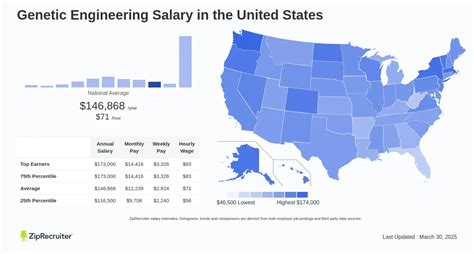
Genetic engineering is no longer science fiction; it's a rapidly expanding scientific field at the forefront of modern medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology. From developing life-saving gene therapies to engineering resilient crops, the work of a genetic engineer is both intellectually stimulating and profoundly impactful. But beyond the breakthroughs, what does a career in this cutting-edge field look like financially?
For those with the passion and expertise, a career in genetic engineering offers significant earning potential, with average salaries comfortably reaching six figures and top earners commanding well over $150,000 annually. This article will provide a comprehensive breakdown of genetic engineering salaries, the key factors that influence your pay, and the promising outlook for this dynamic profession.
What Does a Genetic Engineer Do?

Before we dive into the numbers, it's important to understand the role. A genetic engineer is a specialized scientist who uses biotechnology to manipulate an organism's genetic material (DNA). Their goal is to alter specific traits or produce desired biological products.
Their day-to-day responsibilities often include:
- Designing and conducting experiments to modify genes.
- Utilizing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 for precise gene editing.
- Analyzing genetic data to understand diseases and traits.
- Developing new therapies for genetic disorders.
- Engineering microorganisms for pharmaceutical or industrial production.
- Improving crop yields and nutritional value in agriculture.
They work in diverse settings, from pharmaceutical labs and university research centers to government agencies and biotech startups.
Average Genetic Engineering Salary
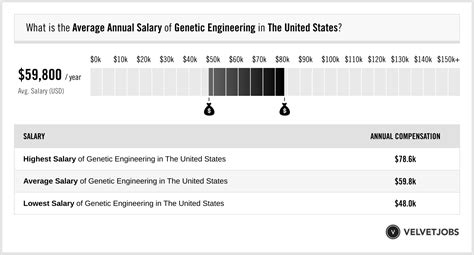
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) does not have a specific category for "Genetic Engineer." However, professionals in this field are most commonly classified as Biochemists and Biophysicists or Biomedical Engineers. These categories provide a highly accurate salary benchmark.
According to the BLS Occupational Outlook Handbook, the median annual salary for Biochemists and Biophysicists was $107,460 as of May 2022. This figure represents the midpoint, meaning half of the professionals in the field earned more, and half earned less. The salary range is quite broad, reflecting the influence of various factors:
- Lowest 10%: Earned less than $62,110
- Highest 10%: Earned more than $179,930
Data from reputable salary aggregators provides a similar picture:
- Salary.com reports the average Geneticist salary in the United States is around $111,740, with a typical range falling between $99,842 and $128,883.
- Payscale.com notes that the average salary for a Research Scientist with gene editing skills is approximately $94,000, with senior roles pushing well into the six-figure range.
These figures confirm that a career in genetic engineering is financially rewarding, with significant room for growth.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary will depend on a combination of critical factors. Understanding these variables is key to maximizing your earning potential.
### Level of Education
Education is arguably the single most important factor in determining both your role and your salary in genetic engineering.
- Bachelor's Degree: A bachelor's in biology, chemistry, or bioengineering can secure you an entry-level position as a lab technician or research assistant. Salaries at this level typically fall in the $50,000 to $70,000 range.
- Master's Degree: A master's degree allows for more advanced roles, such as a Research Associate or a Scientist I position. It demonstrates a higher level of specialization and can lead to a significant salary increase, often in the $75,000 to $100,000 range.
- Doctoral Degree (Ph.D.): A Ph.D. is essential for leading independent research projects, managing teams, and holding senior titles like Principal Scientist or Director of Research. Professionals with a Ph.D. command the highest salaries, frequently starting above $100,000 and often exceeding $150,000+ with experience.
### Years of Experience
As with any profession, experience pays. The field of genetic engineering rewards a proven track record of successful research and development.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): Professionals with a Ph.D. just starting their careers in industry can expect salaries in the $90,000 to $115,000 range.
- Mid-Career (5-9 years): As scientists gain experience and lead more complex projects, their salaries typically climb to $120,000 to $150,000.
- Senior/Experienced (10+ years): Senior Scientists, Principal Investigators, and Directors with over a decade of experience can command salaries of $150,000 to $200,000 or more, especially in high-paying private sector roles.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries for genetic engineers are highest in major biotechnology and pharmaceutical hubs, though this is often offset by a higher cost of living.
According to the BLS, the top-paying states for biochemists and biophysicists are:
- Massachusetts: Home to the Boston/Cambridge biotech cluster.
- California: Driven by hubs in the San Francisco Bay Area and San Diego.
- New Jersey: A longtime center for major pharmaceutical companies.
- Maryland: Benefitting from proximity to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and other federal agencies.
- Connecticut
Working in one of these metropolitan "bio-hubs" can increase your salary by 15-25% compared to the national average.
### Company Type
The type of organization you work for has a major impact on your compensation structure.
- Private Industry (Biotech & Pharma): Large pharmaceutical corporations (e.g., Pfizer, Merck) and established biotech firms (e.g., Genentech, Amgen) are typically the highest payers. They offer competitive base salaries, substantial bonuses, and lucrative stock options.
- Startups: Biotech startups offer a high-risk, high-reward environment. While the initial base salary may be lower than at a large corporation, the potential for significant financial gain through stock equity can be immense if the company is successful.
- Academia & Government: Universities and government agencies (like the NIH or FDA) generally offer lower base salaries than the private sector. However, they often provide excellent benefits, better work-life balance, and unparalleled job security, especially for tenured professors or career government scientists.
### Area of Specialization
Within genetic engineering, certain high-demand specializations can boost your earning potential.
- Gene Therapy: Scientists developing treatments for genetic diseases like cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia are in extremely high demand, commanding premium salaries.
- CRISPR and Gene Editing: Expertise in cutting-edge gene-editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 is a highly valuable and marketable skill.
- Pharmaceutical R&D: Applying genetic engineering to discover and develop new drugs is a core function of the pharmaceutical industry and is compensated accordingly.
- Agricultural Biotechnology: Specialists working to improve crop resistance, yield, and nutrition play a critical role in global food security and are well-compensated, particularly in large agribusiness firms.
Job Outlook

The future for genetic engineers is incredibly bright. The BLS projects that employment for Biochemists and Biophysicists will grow by 7% from 2022 to 2032, which is faster than the average for all occupations. For Biomedical Engineers, the outlook is 5%, also faster than average.
This growth is fueled by several factors:
- Ongoing advancements in biotechnology and gene-editing technologies.
- An aging population driving demand for new treatments for diseases like cancer and Alzheimer's.
- Increased investment in personalized medicine.
- The need for sustainable agricultural solutions to feed a growing global population.
This sustained demand ensures a stable and growing job market for skilled professionals in the years to come.
Conclusion

A career in genetic engineering offers a rare combination of intellectual challenge, societal impact, and financial security. While entry requires a significant educational investment—often culminating in a Ph.D. for top roles—the return is substantial.
Key takeaways for prospective professionals:
- Expect a Strong Salary: The average salary is well into the six-figure range, with top earners pushing towards $200,000.
- Education is Paramount: A Ph.D. is the gold standard for accessing the highest-paying research and leadership positions.
- Location Matters: Targeting major biotech hubs like Boston, San Francisco, or San Diego can significantly increase your salary.
- Private Industry Pays More: While academia offers its own rewards, the most lucrative opportunities are found in private biotech and pharmaceutical companies.
For those driven by a passion for science and a desire to shape the future, genetic engineering is a career path that delivers on both purpose and prosperity.