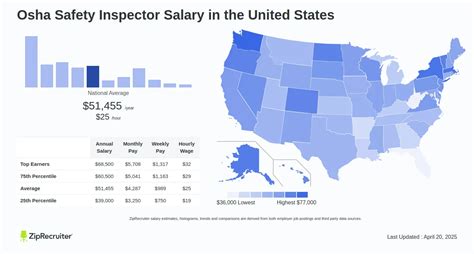
For those drawn to a career that blends technical expertise with a mission to protect others, the role of an occupational safety professional is a compelling choice. At the forefront of this field are OSHA inspectors—and their private-sector counterparts—who ensure safe and healthful working conditions for millions. But beyond the profound job satisfaction, what is the earning potential?
This career path offers not only stability and purpose but also a competitive salary. The median salary for occupational health and safety specialists is well over $80,000 per year, with significant room for growth based on experience, specialization, and location. This guide will break down everything you need to know about an OSHA inspector's salary and the factors that drive it.
What Does an OSHA Inspector Do?

While the term "OSHA inspector" specifically refers to a federal government employee, it's often used more broadly to describe the entire field of Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) Specialists and Technicians. These professionals are the backbone of workplace safety compliance.
A government-employed OSHA Inspector, officially known as a Compliance Safety and Health Officer (CSHO), is responsible for enforcing the standards set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Their private-sector counterparts work within companies to ensure those standards are met proactively.
Key responsibilities for professionals in this field include:
- Inspecting Workplaces: Conducting detailed site walkthroughs to identify physical, chemical, and biological hazards.
- Investigating Incidents: Analyzing accidents, injuries, and illnesses to determine root causes and prevent recurrence.
- Developing Safety Programs: Designing and implementing policies and procedures to reduce workplace risks.
- Providing Training: Educating employees and management on safety protocols, emergency procedures, and regulatory requirements.
- Ensuring Compliance: Verifying that a company adheres to all local, state, and federal safety regulations, including those from OSHA.
Average OSHA Inspector Salary
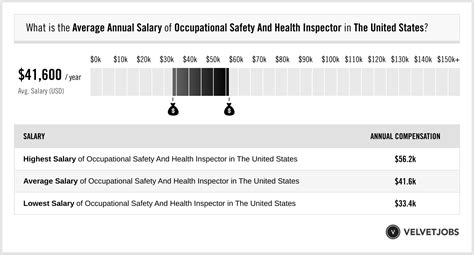
To understand earning potential, we look to data from the most reliable sources. It's important to note that the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) groups OSHA inspectors within the broader category of "Occupational Health and Safety Specialists."
- According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for Occupational Health and Safety Specialists was $81,220 as of May 2023.
- This figure represents the midpoint, with a wide salary range reflecting different experience levels. The lowest 10 percent earned less than $51,130, while the top 10 percent earned more than $124,190.
Salary aggregator sites provide further real-time insight:
- Salary.com reports a median salary for a "Safety Inspector" in the United States at $84,077 as of May 2024, with a typical range falling between $71,154 and $95,788.
- Payscale estimates the average base salary for an Occupational Health and Safety Specialist at around $73,261 per year, noting that this can increase significantly with bonuses and profit-sharing.
This data paints a clear picture: a career in occupational safety is financially sound, with a typical professional earning a strong middle-class income and top earners achieving six-figure salaries.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary as a safety professional isn't set in stone. Several key factors can dramatically impact your earning potential. Understanding these allows you to strategically guide your career toward higher compensation.
### Level of Education
Education forms the foundation of your expertise and pay. A bachelor's degree in a relevant field like occupational health, safety management, engineering, chemistry, or biology is typically the minimum requirement. However, advanced education can unlock higher-level positions and salaries. A Master of Science in Occupational Health (MOH), a Master of Public Health (MPH) with a concentration in environmental and occupational health, or an MBA can qualify you for management, consulting, and senior policy roles with substantially higher pay.
### Years of Experience
Experience is perhaps the most significant driver of salary growth in this field. As you gain hands-on knowledge and a track record of success, your value to an employer increases.
- Entry-Level (0-4 years): Professionals starting out can expect a salary in the range of $55,000 to $70,000. In the federal system, this often corresponds to the GS-7 or GS-9 pay grades.
- Mid-Career (5-9 years): With solid experience, specialists can command salaries from $75,000 to $95,000. They may advance to senior specialist roles or GS-11 and GS-12 levels in government.
- Senior/Managerial (10+ years): Highly experienced professionals, especially those with management responsibilities or sought-after certifications, regularly earn $100,000+. Top-tier directors and consultants can earn well in excess of $150,000.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries are often adjusted to reflect the local cost of living and the concentration of high-risk industries. The BLS identifies the following as the top-paying states for Occupational Health and Safety Specialists:
1. Alaska: $106,780 (Average Annual Mean Wage)
2. District of Columbia: $103,980
3. California: $101,650
4. Washington: $98,690
5. New Jersey: $98,400
For federal OSHA inspectors, salary is determined by the General Schedule (GS) base pay plus a locality pay adjustment, which can significantly increase earnings in high-cost-of-living metropolitan areas like San Francisco, New York City, or Washington, D.C.
### Company Type
The type of organization you work for has a major impact on your salary.
- Federal Government (OSHA): Offers stable careers with excellent benefits. Salaries follow the structured GS pay scale, typically from GS-7 to GS-13. A mid-career CSHO at the GS-12 level in a major city could earn between $90,000 and $115,000+ when factoring in locality pay.
- Private Sector (Industry): This is where the highest salaries are often found. Industries with high inherent risks and strong financial performance pay a premium for top safety talent to mitigate costly accidents and regulatory fines. According to the BLS, the top-paying industries are Oil and Gas Extraction and Manufacturing.
- Consulting: Experienced safety professionals can become independent consultants. While this path involves business development and less stability, it offers the highest earning potential, as expert consultants can charge premium rates for their services.
### Area of Specialization
Specializing in a high-demand area can make you an indispensable asset. Certain certifications are industry gold standards that directly correlate with higher pay.
- Industrial Hygiene: Professionals who specialize in anticipating and controlling chemical, physical, and biological hazards often command higher salaries due to their advanced technical skills.
- Construction Safety: This is a perpetually in-demand specialty due to the high-risk nature of the industry.
- Ergonomics: Specialists who help design workplaces to reduce musculoskeletal injuries are highly valued in both office and industrial settings.
Holding prestigious certifications like the Certified Safety Professional (CSP) or the Certified Industrial Hygienist (CIH) can increase earning potential by 10-20% or more and is often a prerequisite for senior leadership roles.
Job Outlook

The future for occupational health and safety professionals is bright and stable. According to the BLS Occupational Outlook Handbook, employment for Occupational Health and Safety Specialists and Technicians is projected to grow 4 percent from 2022 to 2032.
This steady growth is driven by a continued need to adhere to complex safety regulations and the understanding that robust safety programs are a smart business investment, reducing insurance costs, protecting against litigation, and improving employee morale and productivity. As long as people work, there will be a need for professionals dedicated to keeping them safe.
Conclusion

A career as an OSHA inspector or occupational safety specialist is more than just a job; it's a commitment to protecting the well-being of the workforce. The financial rewards for this commitment are substantial and reliable. With a median salary in the low $80,000s and a clear path to a six-figure income, it offers excellent earning potential.
For those considering this field, the key takeaways are clear:
- Invest in Education: A strong academic foundation is essential.
- Gain Diverse Experience: Build your skills across different environments and challenges.
- Pursue Specializations and Certifications: Differentiate yourself with credentials like the CSP or CIH.
- Be Strategic About Location and Industry: Target areas and sectors that value and reward safety expertise.
By following this path, you can build a career that is not only personally fulfilling but also financially prosperous and professionally respected.