In today's digitally-driven world, product designers are the architects of our online experiences, shaping everything from the apps on our phones to the software that powers global businesses. It's a career path celebrated for its blend of creativity and analytical thinking—and it's also known for its significant financial potential. If you're considering a career in this dynamic field, you're likely asking a critical question: "What is a typical product designer salary?"
The answer is encouraging. With high demand and a direct impact on business success, a career as a product designer is not only creatively fulfilling but also financially rewarding, with many professionals earning well into the six-figure range. This guide will break down the salary you can expect, the factors that influence it, and the bright future of the profession.
What Does a Product Designer Do?

Before diving into the numbers, it's essential to understand the role. A product designer is a problem-solver who uses design thinking to create and improve digital products that are useful, usable, and enjoyable for users while also meeting business objectives. Their responsibilities are broad and bridge the gap between user needs and technical feasibility.
Key responsibilities often include:
- User Research: Conducting interviews, surveys, and usability tests to understand user behaviors and pain points.
- Ideation & Wireframing: Brainstorming solutions and creating low-fidelity sketches and wireframes to map out the product's structure.
- Prototyping & UI Design: Building interactive prototypes and designing high-fidelity user interfaces (UI) that are visually appealing and intuitive.
- Collaboration: Working closely with product managers, engineers, and marketers to ensure a cohesive vision and a feasible final product.
- Data Analysis: Using analytics to measure the success of a design and iterate for continuous improvement.
Average Product Designer Salary
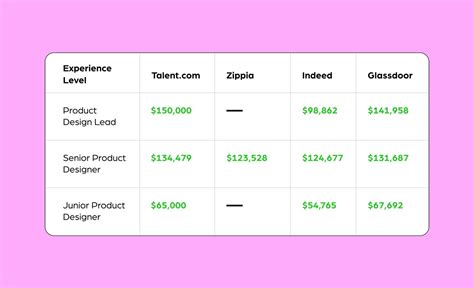
Product designer salaries are competitive and reflect the critical role they play in the tech industry. While figures vary, we can establish a strong baseline by looking at data from several authoritative sources.
According to major salary aggregators, the average base salary for a Product Designer in the United States falls into a strong upper-echelon range.
- Salary.com reports the median salary for a Product Designer III (a mid-to-senior level role) is $118,506 as of early 2024, with a typical range between $107,313 and $130,131.
- Glassdoor states the national average salary is approximately $122,850 per year, with a likely range between $97,000 and $164,000.
- Payscale estimates the average at around $93,500, but notes that senior-level roles with extensive UX skills can easily command upwards of $130,000.
It's also useful to look at the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). While the BLS doesn't have a specific category for "Product Designer," the closest classification is "Web Developers and Digital Designers." For this broader group, the BLS reported a median annual wage of $80,730 in May 2022. This figure is lower because it includes a wider variety of digital design roles, not just the high-paying product design positions concentrated in the tech sector.
Here’s a typical salary progression you can expect based on experience:
| Experience Level | Typical Annual Salary Range |
| :--- | :--- |
| Entry-Level (0-2 years) | $75,000 – $95,000 |
| Mid-Level (3-7 years) | $100,000 – $135,000 |
| Senior/Lead (8+ years) | $140,000 – $185,000+ |
*Note: These figures represent base salary and do not include bonuses, stock options, or other forms of compensation, which can significantly increase total earnings, especially at senior levels.*
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your salary isn't just a single number; it's a reflection of several key factors. Understanding these variables can help you maximize your earning potential throughout your career.
###
Level of Education
While a strong portfolio is the most important hiring asset for a product designer, education provides a crucial foundation. A bachelor's degree in fields like Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), Graphic Design, Computer Science, or even Psychology is common. However, the industry is very open to talent from non-traditional backgrounds, including those who have completed intensive design bootcamps. A master's degree in a specialized field like HCI can provide a salary advantage, particularly for research-heavy or leadership roles, but hands-on experience and a killer portfolio will ultimately have a greater impact on your pay.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the most significant driver of salary growth. As you progress from an entry-level to a senior or principal designer, your responsibilities expand from executing tasks to defining strategy, mentoring junior designers, and leading complex projects. This increase in scope and impact is directly reflected in your compensation. Senior and Principal Product Designers, especially those with over a decade of experience, can command salaries well over $200,000 in top-tier companies.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries for product designers are significantly higher in major tech hubs where the cost of living and demand for talent are greater. The rise of remote work has introduced more flexibility, but many companies still adjust compensation based on location.
Here's a look at how average salaries can vary by city, based on data from aggregators like Glassdoor:
- San Francisco, CA: $145,000+
- New York, NY: $130,000+
- Seattle, WA: $135,000+
- Austin, TX: $115,000+
- Chicago, IL: $110,000+
Cities outside of these primary hubs will typically offer lower base salaries, though the lower cost of living can often offset the difference.
###
Company Type
The type and size of your employer play a massive role in your total compensation.
- Big Tech (FAANG/MAANG): Companies like Meta, Apple, Amazon, Netflix, and Google are known for paying top-of-market salaries. Total compensation packages here often include substantial annual bonuses and lucrative stock grants (RSUs), pushing earnings far beyond the base salary.
- Tech Startups: Early-stage startups may offer a lower base salary but compensate with significant stock options or equity, which can be extremely valuable if the company succeeds.
- Established Corporations (Non-Tech): Banks, retailers, and healthcare companies are increasingly hiring in-house design teams. Salaries are competitive and stable, though they may not reach the peaks seen in Big Tech.
- Design Agencies: Agencies offer the chance to work on diverse projects for various clients. Salaries can be slightly lower than in-house product roles, as the business model is different.
###
Area of Specialization
Generalist product designers are always in demand, but developing a deep expertise in a specific area can significantly boost your value and salary. High-demand specializations include:
- Design Systems: Creating and maintaining a unified library of design components for an entire organization.
- UX Research: Specializing in the qualitative and quantitative research that informs design decisions.
- UI/Motion Design: Focusing on creating beautiful, animated, and highly polished user interfaces.
- Industry-Specific Design: Becoming an expert in complex fields like FinTech, HealthTech, or B2B SaaS, where specialized knowledge is a major asset.
Job Outlook

The future for product designers is exceptionally bright. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that employment for Web Developers and Digital Designers will grow 16% from 2022 to 2032, which is much faster than the average for all occupations.
This robust growth is fueled by the continued digital transformation across all industries. As businesses realize that a superior user experience is a key competitive advantage, the demand for skilled product designers who can create effective and engaging digital products will only continue to rise.
Conclusion

A career as a product designer offers a powerful combination of creative fulfillment, intellectual challenge, and financial security. With average salaries comfortably reaching six figures and multiple pathways for growth, it stands out as one of the most promising professions in the modern economy.
For those aspiring to enter or advance in this field, the key takeaways are clear:
- Build an outstanding portfolio that showcases your problem-solving skills.
- Never stop learning and consider specializing in a high-demand area.
- Understand your market value based on your experience, location, and the type of company you're targeting.
By focusing on these areas, you can build a long and prosperous career shaping the products that define our digital world.
