A career in Teaching English to Speakers of Other Languages (TESOL) offers a unique opportunity to connect cultures, empower individuals, and make a tangible impact on students' lives. But beyond the intrinsic rewards, what is the financial reality? For many considering this path, the crucial question is: "What is a typical TESOL teacher salary?"
The answer is complex, with salaries varying significantly based on a host of factors. While entry-level positions in some settings might start around $35,000, experienced professionals with advanced degrees can earn upwards of $80,000 or more, particularly in specialized roles. This guide will break down the numbers, explore the key factors that influence your earnings, and provide a clear picture of what you can expect in this dynamic field.
What Does a TESOL Teacher Do?

A TESOL teacher, also commonly known as an ESL (English as a Second Language) teacher, is a specialist in language instruction. Their core responsibility is to help non-native English speakers develop proficiency in reading, writing, listening, and speaking. Beyond the classroom lecture, their duties are multifaceted and include:
- Assessing student proficiency levels to tailor instruction.
- Designing and planning engaging lesson plans that cover grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation, and cultural context.
- Creating and sourcing instructional materials suitable for different ages and skill levels.
- Fostering an inclusive and supportive classroom environment where students feel comfortable practicing and making mistakes.
- Evaluating student progress through assignments, presentations, and formal assessments like the TOEFL or IELTS.
- Adapting teaching methods to meet the needs of diverse learners, from young children to business executives.
Average TESOL Teacher Salary
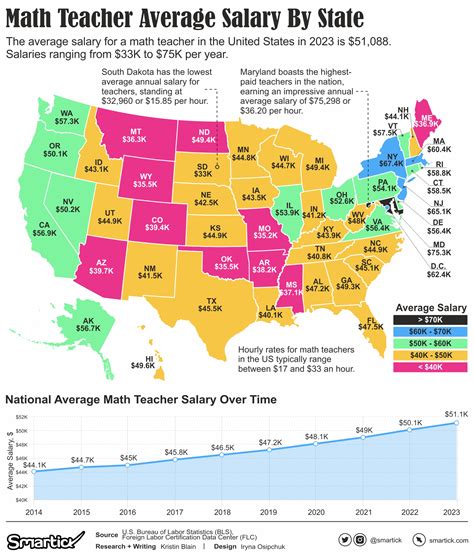
TESOL salaries can vary widely across the United States. To get a clear picture, it's helpful to look at data from several authoritative sources. "TESOL Teacher" as a specific title is often categorized under broader umbrellas in official statistics.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) groups most of these roles under "Adult Basic and Secondary Education and ESL Teachers." As of May 2023, the BLS reports the following:
- Median Annual Salary: $60,560
- Lowest 10%: Earned less than $39,630
- Highest 10%: Earned more than $101,660
Salary aggregator websites, which collect real-time, user-reported data, provide a similar snapshot:
- Salary.com reports that the average ESL Teacher salary in the United States is $61,019 as of May 2024, with a typical range falling between $51,192 and $72,551.
- Glassdoor places the estimated total pay for an ESL Teacher at $61,642 per year in the U.S., with an average base salary of $54,166.
These figures represent a national average. Your personal earning potential will be shaped by the critical factors discussed below.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Understanding what drives salary differences is the first step toward maximizing your income. For TESOL teachers, compensation is directly tied to your qualifications, where you work, and the specific expertise you bring to the role.
### Level of Education
Your educational background is one of the most significant predictors of your salary.
- Bachelor’s Degree + TESOL Certificate: This is the standard entry-level qualification for many positions in private language schools and some community-based programs. It qualifies you for a solid starting salary but may limit access to higher-paying institutional jobs.
- Master’s Degree (MA in TESOL, Applied Linguistics): Holding a master's degree is the key to unlocking the highest-paying and most prestigious positions. It is often a requirement for full-time, tenure-track, or lecturer positions at universities and community colleges. An MA signals a deep level of expertise, qualifying you for roles in curriculum design, teacher training, and program administration, all of which command higher salaries.
### Years of Experience
As with any profession, experience pays. Employers value teachers who have a proven track record of successful student outcomes and classroom management.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): Teachers in this bracket can expect to earn on the lower end of the salary spectrum as they build their practical skills.
- Mid-Career (3-9 years): With several years of experience, teachers can negotiate higher salaries and are eligible for more senior roles, such as Lead Teacher.
- Experienced (10+ years): Veteran teachers with a decade or more of experience are top earners. They often move into administrative roles like Program Director or Academic Coordinator, which come with significant pay increases.
### Geographic Location
Where you teach matters immensely. Salaries are often adjusted for the local cost of living and regional demand for ESL instruction.
- High-Paying States: According to BLS data, states like California, New York, Washington, and Massachusetts often offer higher-than-average salaries for ESL teachers, largely due to a higher cost of living and large immigrant populations.
- Metropolitan Areas: Major cities within these states (e.g., New York City, San Francisco, Boston, Seattle) typically offer the highest wages but also come with the highest living expenses.
- International Opportunities: It's also worth noting that some of the most lucrative TESOL jobs are found abroad. Countries in the Middle East (e.g., UAE, Saudi Arabia) and parts of Asia (e.g., South Korea, Japan) often offer highly competitive, tax-free salaries with benefits like free housing and airfare to attract qualified native English-speaking teachers.
### Company Type / Work Environment
The type of institution you work for is a major determinant of your pay scale and benefits.
- K-12 Public Schools: Working as an ESL teacher in a public school district often means being on the same union-negotiated salary schedule as other teachers. Pay is transparently based on your level of education and years of experience ("steps and lanes"). This path offers stability, excellent benefits, and a state pension plan.
- Universities and Community Colleges: These are typically among the highest-paying employers for TESOL professionals, especially for full-time faculty in Intensive English Programs (IEPs). A Master's degree is almost always required.
- Private Language Academies: Salaries here are the most variable. Large, reputable chains may offer competitive pay, while smaller, independent schools might offer lower hourly wages and fewer benefits.
- Corporate Training: A specialized and often lucrative niche, this involves teaching business English to professionals. Companies are often willing to pay a premium for instructors who can help their employees communicate effectively in the global marketplace.
### Area of Specialization
Developing a niche expertise can significantly boost your value and your salary.
- English for Academic Purposes (EAP): Teaching students the language skills needed to succeed in an American university is a highly valued specialty.
- Test Preparation (TOEFL/IELTS): Instructors who can consistently help students achieve high scores on these crucial entrance exams are in high demand.
- Business English: As mentioned, this is a high-paying field that requires an understanding of corporate culture and professional communication.
- Teacher Training: Experienced teachers with advanced degrees can become TESOL trainers, teaching new instructors and commanding a high salary for their expertise.
Job Outlook

The demand for skilled TESOL professionals remains strong. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects overall employment for Adult Basic and Secondary Education and ESL Teachers to grow by 2 percent from 2022 to 2032.
While this number may seem modest, it's important to consider the underlying drivers. Ongoing immigration, the increasing number of international students at U.S. universities, and the globalization of business ensure a persistent need for high-quality English language instruction across all sectors. The skills of a TESOL teacher are transferable and consistently in demand.
Conclusion

A career as a TESOL teacher is a pathway to a professionally and personally fulfilling life. While salaries can start modestly, your earning potential is far from fixed. The data shows a clear trajectory for financial growth for those who invest in their professional development.
For individuals considering this career, the key takeaways are:
- The national median salary hovers around $60,000, with significant upward potential.
- Education is your primary lever for growth. A Master's degree in TESOL or a related field is the single most effective way to access higher-paying positions.
- Strategically choose your location and employer. High-paying opportunities are concentrated in major metropolitan areas and at postsecondary institutions.
- Build experience and specialize. Developing expertise in high-demand areas like academic or business English will set you apart and increase your earning power.
By understanding these factors, you can strategically navigate your career path, turning your passion for teaching into a financially rewarding and impactful profession.